Abstract
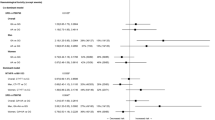
The discovery of pharmacogenomic markers in colorectal cancer (CRC) could be setting-specific. FOLFOX4 is employed in the adjuvant and metastatic setting in CRC. This prospective study is aimed to validate in the adjuvant setting the pharmacogenomic markers of toxicity reported in the metastatic setting (that is, GSTP1-rs947894, and -rs1138272; GSTM1-null genotype; AGXT-rs4426527, -rs34116584 and del-74 bp), and to discover additional markers. CRC patients (n=144) treated with adjuvant FOLFOX4 were genotyped for 57 polymorphisms in 29 genes. Grade ⩾2 neurotoxicity was associated (false discovery rate-adjusted q-value <0.1) with single-nucleotide polymorphisms in ABCC1 (rs2074087: odds ratio=0.43(0.22–0.86)), and ABCC2 (rs3740066: 2.99(1.16–7.70); rs1885301: 3.06(1.35–6.92); rs4148396: 4.69(1.60–13.74); rs717620: 14.39(1.63–127.02)). hMSH6-rs3136228 was associated with grade 3–4 neutropenia (3.23(1.38–7.57), q-value=0.0937). XRCC3-rs1799794 was associated with grade 3–4 non-hematological toxicity (8.90(2.48–31.97), q-value=0.0150). The markers previously identified in metastatic CRC were not validated. We have identified new markers of toxicity in genes of transport and DNA repair. If validated in other studies, they could help to identify patients at risk of toxicity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee SY, McLeod HL . Pharmacogenetic tests in cancer chemotherapy: what physicians should know for clinical application. J Pathol 2011; 223: 15–27.
Sim SC, Ingelman-Sundberg M . Pharmacogenomic biomarkers: new tools in current and future drug therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2011; 32: 72–81.
Cecchin E, Innocenti F, D’Andrea M, Corona G, De Mattia E, Biason P et al. Predictive role of the UGT1A1, UGT1A7, and UGT1A9 genetic variants and their haplotypes on the outcome of metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 2457–2465.
Innocenti F, Undevia SD, Iyer L, Chen PX, Das S, Kocherginsky M et al. Genetic variants in the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 gene predict the risk of severe neutropenia of irinotecan. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 1382–1388.
Ruzzo A, Graziano F, Loupakis F, Santini D, Catalano V, Bisonni R et al. Pharmacogenetic profiling in patients with advanced colorectal cancer treated with first-line FOLFIRI chemotherapy. Pharmacogenomics J 2008; 8: 278–288.
Toffoli G, Cecchin E, Gasparini G, D’Andrea M, Azzarello G, Basso U et al. Genotype-driven phase I study of irinotecan administered in combination with fluorouracil/leucovorin in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 866–871.
Andre T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T et al. Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 2343–2351.
Ibrahim A, Hirschfeld S, Cohen MH, Griebel DJ, Williams GA, Pazdur R . FDA drug approval summaries: oxaliplatin. Oncologist 2004; 9: 8–12.
Kuebler JP, Wieand HS, O’Connell MJ, Smith RE, Colangelo LH, Yothers G et al. Oxaliplatin combined with weekly bolus fluorouracil and leucovorin as surgical adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II and III colon cancer: results from NSABP C-07. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 2198–2204.
Pachman DR, Barton DL, Watson JC, Loprinzi CL . Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: prevention and treatment. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2011; 90: 377–387.
Reilly MM, Murphy SM, Laura M . Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2011; 16: 1–14.
Park SB, Lin CS, Krishnan AV, Goldstein D, Friedlander ML, Kiernan MC . Long-term neuropathy after oxaliplatin treatment: challenging the dictum of reversibility. Oncologist 2011; 16: 708–716.
Cassidy J, Tabernero J, Twelves C, Brunet R, Butts C, Conroy T et al. XELOX (capecitabine plus oxaliplatin): active first-line therapy for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 2084–2091.
Kiernan MC, Krishnan AV . The pathophysiology of oxaliplatin-induced neurotoxicity. Curr Med Chem 2006; 13: 2901–2907.
Adelsberger H, Quasthoff S, Grosskreutz J, Lepier A, Eckel F, Lersch C . The chemotherapeutic oxaliplatin alters voltage-gated Na(+) channel kinetics on rat sensory neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 2000; 406: 25–32.
Ta LE, Espeset L, Podratz J, Windebank AJ . Neurotoxicity of oxaliplatin and cisplatin for dorsal root ganglion neurons correlates with platinum-DNA binding. Neurotoxicology 2006; 27: 992–1002.
Martin LP, Hamilton TC, Schilder RJ . Platinum resistance: the role of DNA repair pathways. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 1291–1295.
Lecomte T, Landi B, Beaune P, Laurent-Puig P, Loriot MA . Glutathione S-transferase P1 polymorphism (Ile105Val) predicts cumulative neuropathy in patients receiving oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 2006; 12: 3050–3056.
Ruzzo A, Graziano F, Loupakis F, Rulli E, Canestrari E, Santini D et al. Pharmacogenetic profiling in patients with advanced colorectal cancer treated with first-line FOLFOX-4 chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 1247–1254.
Knupfer H, Preiss R . Serum interleukin-6 levels in colorectal cancer patients—a summary of published results. Int J Colorectal Dis 2010; 25: 135–140.
Sparmann A, Bar-Sagi D . Ras-induced interleukin-8 expression plays a critical role in tumor growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 2004; 6: 447–458.
Erreni M, Mantovani A, Allavena P . Tumor-associated Macrophages (TAM) and Inflammation in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Microenviron 2011; 4: 141–154.
Caussanel JP, Levi F, Brienza S, Misset JL, Itzhaki M, Adam R et al. Phase I trial of 5-day continuous venous infusion of oxaliplatin at circadian rhythm-modulated rate compared with constant rate. J Natl Cancer Inst 1990; 82: 1046–1050.
Chen YC, Tzeng CH, Chen PM, Lin JK, Lin TC, Chen WS et al. Influence of GSTP1 I105V polymorphism on cumulative neuropathy and outcome of FOLFOX-4 treatment in Asian patients with colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Sci 2010; 101: 530–535.
Gamelin L, Capitain O, Morel A, Dumont A, Traore S, Anne lB et al. Predictive factors of oxaliplatin neurotoxicity: the involvement of the oxalate outcome pathway. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13: 6359–6368.
McLeod HL, Sargent DJ, Marsh S, Green EM, King CR, Fuchs CS et al. Pharmacogenetic predictors of adverse events and response to chemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: results from North American Gastrointestinal Intergroup Trial N9741. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 3227–3233.
Pare L, Marcuello E, Altes A, del Rio E, Sedano L, Salazar J et al. Pharmacogenetic prediction of clinical outcome in advanced colorectal cancer patients receiving oxaliplatin/5-fluorouracil as first-line chemotherapy. Br J Cancer 2008; 99: 1050–1055.
Benjamini YA, Hochberg Y . Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J Royal Stat Soc Ser B 1995; 57: 289–300.
Purcell S, Cherny SS, Sham PC . Genetic Power Calculator: design of linkage and association genetic mapping studies of complex traits. Bioinformatics 2003; 19: 149–150.
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ . Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005; 21: 263–265.
Stephens M, Smith NJ, Donnelly P . A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am J Hum Genet 2001; 68: 978–989.
Stephens M, Donnelly P . A comparison of bayesian methods for haplotype reconstruction from population genotype data. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 73: 1162–1169.
Boige V, Mendiboure J, Pignon JP, Loriot MA, Castaing M, Barrois M et al. Pharmacogenetic assessment of toxicity and outcome in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer treated with LV5FU2, FOLFOX, and FOLFIRI: FFCD 2000-05. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 2556–2564.
Walther A, Johnstone E, Swanton C, Midgley R, Tomlinson I, Kerr D . Genetic prognostic and predictive markers in colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 489–499.
de Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, Homerin M, Hmissi A, Cassidy J et al. Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 2938–2947.
Cavaletti G, Alberti P, Marmiroli P . Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity in the era of pharmacogenomics. Lancet Oncol 2011; 12: 1151–1161.
Denkert C, Budczies J, Weichert W, Wohlgemuth G, Scholz M, Kind T et al. Metabolite profiling of human colon carcinoma—deregulation of TCA cycle and amino acid turnover. Mol Cancer 2008; 7: 72.
Rabik CA, Dolan ME . Molecular mechanisms of resistance and toxicity associated with platinating agents. Cancer Treat Rev 2007; 33: 9–23.
Gottesman MM, Fojo T, Bates SE . Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 48–58.
Theile D, Grebhardt S, Haefeli WE, Weiss J . Involvement of drug transporters in the synergistic action of FOLFOX combination chemotherapy. Biochem Pharmacol 2009; 78: 1366–1373.
Haenisch S, May K, Wegner D, Caliebe A, Cascorbi I, Siegmund W . Influence of genetic polymorphisms on intestinal expression and rifampicin-type induction of ABCC2 and on bioavailability of talinolol. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2008; 18: 357–365.
Han B, Gao G, Wu W, Gao Z, Zhao X, Li L et al. Association of ABCC2 polymorphisms with platinum-based chemotherapy response and severe toxicity in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer 2011; 72: 238–243.
Ballatori N, Hammond CL, Cunningham JB, Krance SM, Marchan R . Molecular mechanisms of reduced glutathione transport: role of the MRP/CFTR/ABCC and OATP/SLC21A families of membrane proteins. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2005; 204: 238–255.
Taniguchi K, Wada M, Kohno K, Nakamura T, Kawabe T, Kawakami M et al. A human canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter (cMOAT) gene is overexpressed in cisplatin-resistant human cancer cell lines with decreased drug accumulation. Cancer Res 1996; 56: 4124–4129.
Matullo G, Palli D, Peluso M, Guarrera S, Carturan S, Celentano E et al. XRCC1, XRCC3, XPD gene polymorphisms, smoking and (32)P-DNA adducts in a sample of healthy subjects. Carcinogenesis 2001; 22: 1437–1445.
Ott K, Rachakonda PS, Panzram B, Keller G, Lordick F, Becker K et al. DNA repair gene and MTHFR gene polymorphisms as prognostic markers in locally advanced adenocarcinoma of the esophagus or stomach treated with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol 2011; 18: 2688–2698.
Damaraju S, Murray D, Dufour J, Carandang D, Myrehaug S, Fallone G et al. Association of DNA repair and steroid metabolism gene polymorphisms with clinical late toxicity in patients treated with conformal radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2006; 12: 2545–2554.
Matheson EC, Hall AG . Expression of DNA mismatch repair proteins in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia and normal bone marrow. Adv Exp Med Biol 1999; 457: 579–583.
Muller CI, Schulmann K, Reinacher-Schick A, Andre N, Arnold D, Tannapfel A et al. Predictive and prognostic value of microsatellite instability in patients with advanced colorectal cancer treated with a fluoropyrimidine and oxaliplatin containing first-line chemotherapy. A report of the AIO Colorectal Study Group. Int J Colorectal Dis 2008; 23: 1033–1039.
Gazzoli I, Kolodner RD . Regulation of the human MSH6 gene by the Sp1 transcription factor and alteration of promoter activity and expression by polymorphisms. Mol Cell Biol 2003; 23: 7992–8007.
Inoue N, Ishida H, Sano M, Kishino T, Okada N, Kumamoto K et al. Discrepancy between the NCI-CTCAE and DEB-NTC scales in the evaluation of oxaliplatin-related neurotoxicity in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 2011.
Postma TJ, Heimans JJ . Grading of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Ann Oncol 2000; 11: 509–513.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the The Pharmacogenomics Journal website
Supplementary information
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cecchin, E., D'Andrea, M., Lonardi, S. et al. A prospective validation pharmacogenomic study in the adjuvant setting of colorectal cancer patients treated with the 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin/oxaliplatin (FOLFOX4) regimen. Pharmacogenomics J 13, 403–409 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2012.31
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2012.31
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pharmacogenomics, biomarker network, and allele frequencies in colorectal cancer
The Pharmacogenomics Journal (2020)
-
Genetic variants in RPA1 associated with the response to oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in colorectal cancer
Journal of Gastroenterology (2019)
-
Sex-Related Differences in Impact on Safety of Pharmacogenetic Profile for Colon Cancer Patients Treated with FOLFOX-4 or XELOX Adjuvant Chemotherapy
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity: management informed by pharmacogenetics
Nature Reviews Neurology (2017)
-
AGXT and ERCC2 polymorphisms are associated with clinical outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with 5-FU/oxaliplatin
The Pharmacogenomics Journal (2016)