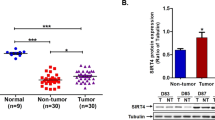
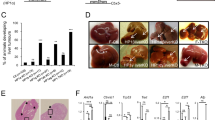
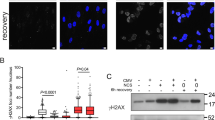
Abstract
Transcription of hepatitis B Virus (HBV), an important risk factor of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is controlled by cellular transcription activators including some of the cellular signaling targets. Consequently, HBV transcription rate changes in response to the cellular physiological conditions. In this report we investigated HBV gene expression and the role of physiological levels of the viral X protein (pX) under cisplatin induced genotoxic stress. We show that under these conditions the RNA level of an HBV mutant which does not express pX is sharply reduced. Studies revealed that transcription repression is responsible for the observed reduction in HBV RNA level. Repression of HBV transcription was obtained only in the p53 proficient cells. Furthermore, HBV transcription rate is recovered by the cotransfected p53 dominant negative plasmid, indicating that p53 is directly responsible for HBV transcription repression. Unexpectedly, p73, the recent p53 homologue, does not repress but rather activates HBV transcription. Interestingly, pX produced either by the HBV genome or by a cotransfected plasmid, relieves the p53 mediated repression. Collectively, these results attribute a physiological role to p53-inactivation by pX, and explain how pX may support HCC development.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agami R and Shaul Y. . 1998 Oncogene 16: 1779–1788.
Benn J, Su F, Doria M and Schneider RJ. . 1996 J. Virol. 70: 4978–4985.
Bressac B, Galvin KM, Liang TJ, Isselbacher KJ, Wands JR and Ozturk M. . 1990 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87: 1973–1977.
Butz K, Geisen C, Ullmann A, Spitkovsky D and Hoppe SF. . 1996 Int. J. Cancer 68: 506–513.
Cheong JH, Yi M, Lin Y and Murakami S. . 1995 EMBO J. 14: 142–150.
Chirillo P, Pagano S, Natoli G, Puri PL, Burgio VL, Balsano C and Levrero M. . 1997 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 8162–8167.
Dikstein R, Heffetz D, Ben-Neriah Y and Shaul Y. . 1992 Cell 69: 751–757.
Doria M, Klein N, Lucito R and Schneider RJ. . 1995 EMBO J. 14: 4747–4757.
Faktor O, Budlovsky S, Ben-Levy R and Shaul Y. . 1990 J. Virol. 64: 1861–1863.
Farmer G, Colgan J, Nakatani Y, Manley JL and Prives C. . 1996a Mol. Cell Biol. 16: 4295–4304.
Farmer G, Friedlander P, Colgan J, Manley JL and Prives C. . 1996b Nucleic Acids Res. 24: 4281–4288.
Feitelson MA, Zhu M, Duan LX and London WT. . 1993 Oncogene 8: 1109–1117.
Fritsche M, Haessler C and Brandner G. . 1993 Oncogene 8: 307–318.
Gottlieb TM and Oren M. . 1996 Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1287: 77–102.
Guidotti LG, Ishikawa T, Hobbs MV, Matzke B, Schreiber R and Chisari FV. . 1996 Immunity 4: 25–36.
Guidotti LG, Matzke B, Schaller H and Chisari FV. . 1995 J. Virol. 69: 6158–6169.
Haffner R and Oren M. . 1995 Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 5: 84–90.
Hagen TM, Huang S, Curnutte J, Fowler P, Martinez V, Wehr CM, Ames BN and Chisari FV. . 1994 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 12808–12812.
Haviv I, Matza Y and Shaul Y. . 1998a Genes Dev. 12: 1217–1226.
Haviv I, Shamay M, Doitsh G and Shaul Y. . 1998b Mol. Cell Biol. 18: 1562–1569.
Haviv I, Vaizel D and Shaul Y. . 1995 Mol. Cell Biol. 15: 1079–1085.
Haviv I, Vaizel D and Shaul Y. . 1996 EMBO J. 15: 3413–3420.
Honigwachs J, Faktor O, Dikstein R, Shaul Y and Laub O. . 1989 J. Virol. 63: 919–924.
Hosono S, Lee CS, Chou MJ, Yang CS and Shih CH. . 1991 Oncogene 6: 237–243.
Jameel S and Siddiqui A. . 1986 Mol. Cell Biol. 6: 710–715.
Jost CA, Marin MC and Kaelin WJ. . 1997 Nature 389: 191–194.
Kaghad M, Bonnet H, Yang A, Creancier L, Biscan JC, Valent A, Minty A, Chalon P, Lelias JM, Dumont X, Ferrara P, McKeon F and Caput D. . 1997 Cell 90: 809–819.
Klein NP and Schneider RJ. . 1997 Mol. Cell Biol. 17: 6427–6436.
Ko LJ and Prives C. . 1996 Genes Dev. 10: 1054–1072.
Lin Y, Nomura T, Cheong J, Dorjsuren D, Iida K and Murakami S. . 1997a J. Biol. Chem. 272: 7132–7139.
Lin Y, Nomura T, Yamashita T, Dorjsuren D, Tang H and Murakami S. . 1997b Cancer Res. 57: 5137–5142.
Liu X and Berk AJ. . 1995 Mol. Cell Biol. 15: 6474–6478.
Luber B, Lauer U, Weiss L, Hohne M, Hofschneider PH and Kekule AS. . 1993 Res. Virol. 144: 311–321.
Natoli G, Avantaggiati ML, Chirillo P, Puri PL, Ianni A, Balsano C and Levrero M. . 1994 Oncogene 9: 2837–4283.
Ohno H, Kaneko S, Kobayashi K and Murakami S. . 1997 J. Med. Virol. 52: 413–418.
Ori A, Zauberman A, Doitsh G, Paran N, Oren M and Shaul Y. . 1998 EMBO J. 17: 544–553.
Raney AK, Johnson JL, Palmer CN and McLachlan A. . 1997 J. Virol. 71: 1058–1071.
Roberts JJ and Friedlos F. . 1981 Biochim. Biophys. Acta 655: 146–151.
Sambrook J, Fitsch EF and Maniatis T. . 1989 Molecular Cloning, a Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, New York.
Schaefer S, Seifer M, Grimmsmann T, Fink L, Wenderhold S, Hohne MW and Gerlich WH. . 1998 J. Gen. Virol. 79: 767–777.
Scheffner M, Werness BA, Huibregtse JM, Levine AJ and Howley PM. . 1990 Cell 63: 1129–1136.
Sells MA, Chen ML and Acs G. . 1987 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84: 1005–1009.
Shaul Y, Kaminchik J and Aviv H. . 1981 Eur. J. Biochem. 116: 461–466.
Shaul Y, Rutter WJ and Laub O. . 1985 EMBO J. 4: 427–340.
Shaulian E, Haviv I, Shaul Y and Oren M. . 1995 Oncogene 10: 671–680.
Siegrist CA, Durand B, Emery P, David E, Hearing P, Mach B and Reith W. . 1993 Mol. Cell Biol. 13: 6375–6384.
Su F and Schneider RJ. . 1996 J. Virol. 70: 4558–4566.
Sureau C, Romet LJ, Mullins JI and Essex M. . 1986 Cell 47: 37–47.
Takada S, Kaneniwa N, Tsuchida N and Koike K. . 1996 Virology 216: 80–89.
Takada S, Kaneniwa N, Tsuchida N and Koike K. . 1997 Oncogene 15: 1895–1901.
Thut CJ, Chen JL, Klemm R and Tjian R. . 1995 Science 267: 100–104.
Truant R, Antunovic J, Greenblatt J, Prives C and Cromlish JA. . 1995 J. Virol. 69: 1851–1859.
Ueda H, Ullrich SJ, Gangemi JD, Kappel CA, Ngo L, Feitelson MA and Jay G. . 1995 Nat. Genet. 9: 41–47.
Wang XW, Forrester K, Yeh H, Feitelson MA, Gu JR and Harris CC. . 1994 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 2230–2234.
Yee JK. . 1989 Science 246: 658–661.
Yuan ZM, Huang Y, Fan MM, Sawyers C, Kharbanda S and Kufe D. . 1996 J. Biol. Chem. 271: 26457–26460.
Zhu J, Jiang J, Zhou W and Chen X. . 1998 Cancer Res. 58: 5061–5065.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr M Oren for p53 and DD plasmids and for anti p53 antibodies. This work was supported by a grant from the national council for research and development. Israel and the Deutsches Krebsforschunszentrum (DKFZ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doitsh, G., Shaul, Y. HBV transcription repression in response to genotoxic stress is p53-dependent and abrogated by pX. Oncogene 18, 7506–7513 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203209
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203209