Abstract
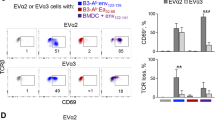
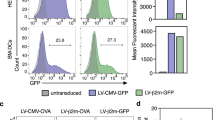
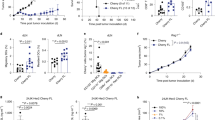
Tumor vaccination with dendritic cells (DC) presenting tumor antigens to T cells is a promising approach in immunotherapy. The aim of this study was to enhance T cell stimulatory ability of human DC by retroviral expression of the interleukin-7 (IL-7) gene. IL-7 has been shown to provide a potent costimulatory signal for the proliferation of T cells and the generation of cytotoxic T cells (CTL). DC were generated from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). DC were analyzed by light- and electron-microscopy, immunophenotype (CD1a+, CD14−, CD80+, CD86+, HLA-DR+) and functional assays. According to these criteria, 75–85% of the cells were DC. The cells did not produce measurable amounts of IL-7 spontaneously nor did they express the IL-7 receptor. A retroviral IL-7 expression vector was constructed. Retroviral infection was performed with either the LXSN-hIL-7 vector or its variant LXSN. Using the LXSN-hIL-7 vector, IL-7 production of 2296 pg/106 cells/24 h could be achieved on average. Transduction of DC was confirmed by RT-PCR in a CD1a-enriched cell fraction. Transduction efficiency by a control virus coding for β-galactosidase was about 30%. In autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR), IL-7 transduced DC augmented T cell proliferation by a factor of two compared with unmodified or mock-transfected DC, and in allogeneic MLR there was a 2.7-fold increase in T cell proliferation. The increase in T cell proliferation could be correlated to IL-7 secretion by DC. Dendritic cells that have been simultaneously peptide-loaded and gene-modified to secrete IL-7 are a potential tool to amplify activation of tumor-specific T cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Westermann, J., Aicher, A., Qin, Z. et al. Retroviral interleukin-7 gene transfer into human dendritic cells enhances T cell activation. Gene Ther 5, 264–271 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3300568
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3300568
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
IL‐7 induces clathrin‐mediated endocytosis of CD127 and subsequent degradation by the proteasome in primary human CD8 T cells
Immunology & Cell Biology (2016)
-
Comparison of AAV/IL-7 autocrine (T cell) versus paracrine (DC) gene delivery for enhancing CTL stimulation and function
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2010)
-
A prostate cancer vaccine comprising whole cells secreting IL-7, effective against subcutaneous challenge, requires local GM-CSF for intra-prostatic efficacy
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2009)
-
Generation of dendritic cell-based vaccines for cancer therapy
British Journal of Cancer (2002)
-
Adenoviral transduction of tumor cells induces apoptosis in co-cultured T lymphocytes
Gene Therapy (2002)