Abstract
Despite mounting evidence linking Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) to Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the shared mechanism of these two conditions’ occurrence remains unclear. This research aims to delve deeper into the molecular process of the occurrence of the two diseases. We retrieved the gene expression profiles of AD (GSE5281) and AMI (GSE66360) from the Gene Expression Omnibus database. Then, a total of 22 common differentially expressed genes (DEGs) including one downregulated gene and 21 upregulated genes were chosen for further analysis. Following the discovery of the common DEGs between AMI and AD, we performed protein–protein interaction analysis and hub gene identification analysis. Next, ten important hub genes were identified. Additionally, the key genes were identified by the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator and support vector machine‐recursive feature elimination and multivariable logistic regression analysis. The BCL6 was identified to be the most connected with AMI and AD. Finally, the BCL6 gene was validated in the GSE40680 (AMI) and GSE122063 (AD) datasets. Our research indicates that AMI and AD share a comparable pathophysiology. The Hub genes, especially BCL6, were essential in developing AMI and AD. In addition, these hub genes and shared pathways can offer fresh perspectives for additional mechanism investigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Chest pain is the second most frequent reason people attend the emergency department (ED) in the United States after injuries, accounting for over 7 million visits of all ED visits1. Therefore, chest pain necessitates a comprehensive clinical evaluation and continues to be a diagnostic difficulty in the ED and outpatient environment2. Although noncardiac causes of chest pain are common, coronary artery disease (CAD) affects more than 18.2 million adults in the United States. With more than 365,000 deaths a year, it continues to be the primary cause of death for both men and women3. Therefore, cardiovascular disease significantly negatively impacts both health and the economy domestically and internationally. In the field of cardiovascular medicine, an acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is a medical disorder that can cause life-threatening symptoms such as abrupt cardiac death, cardiogenic shock, and malignant arrhythmias. Moreover, it is among the main reasons for sudden cardiac death2. The prognosis of individuals with AMI is greatly affected by early diagnosis. While the first ECG is necessary for the evaluation, other aids such as the history, examination, and biomarkers are also important. As a result, we are attempting to uncover novel biomarkers in order to enhance the diagnosis rate of early AMI.
Dementia is a clinical syndrome characterized by a progressive decline in two or more cognitive domains, such as memory, language, executive and visuospatial function, personality, and behavior, resulting in the inability to perform instrumental and/or fundamental everyday activities. Up to 80% of dementia diagnoses are due to Alzheimer’s disease (AD), making it the most frequent cause of dementia4. Alzheimer’s disease was officially classified as the sixth-highest cause of death in the United States in 2019, with 121,499 fatalities from the condition, according to official death certificates. Alzheimer’s dementia is thought to affect 6.7 million Americans 65 years of age and older as of right now. Without medical advancements to prevent, slow down, or treat AD, this population could increase to 13.8 million by 20605. Further, due to their high frequency and modifiability, vascular risk factors are widely acknowledged as the most critical group of risk factors for brain health6. Numerous variables that raise the risk of cardiovascular disease, such as diabetes and hypertension, also raise the risk of dementia7,8,9. Consequently, it seems that AD might be associated with AMI. Furthermore, with blood biomarkers appearing to be within reach, the advances in biomarker detection have completely rethought the approach to diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease prior to clinical symptomatology. Therefore, it makes sense and is required to design a novel biological diagnostic model for preclinical AD diagnosis.
In this study, we first conducted gene co-expression analysis on AMI and AD. We found that compared to normal individuals, 22 genes, including 21 upregulated genes and one downregulated gene, exhibit the same expression trend in patients with AMI and AD. Based on the genes above, we conducted enrichment analysis and obtained ten essential genes to explore disease correlation further. We have successfully constructed bioinformatics models for AMI and AD patients based on the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO), support vector machine recursive feature elimination (SVM-RFE) analysis (SVM-RFE) and multivariable logistic regression analysis. The BCL6 gene is closely associated with AMI and AD patients. This indicates that neither AMI nor AD exists separately, providing new ideas and targets for diagnosing and treating diseases, including AMI and AD, which undoubtedly had specific significance.
Methods
Date preparation
The microarray datasets for AMI, AD, and normal controls were obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. The gene expression profiles of 50 controls and 49 AMI patients were included in the GSE66360 dataset. Additionally, the GSE48060 was chosen as the validation dataset; it comprises 31 AMI patients and 21 normal people. 87 AD patients and 74 healthy controls were included in the analysis of the GSE5281 dataset. Additionally, from GSE122063, which served as the validation dataset, 56 AD patients and 44 controls were chosen. Since these gene expression profiles were taken from a publicly available, free internet database, our research did not need permission from the Ethics Committee.
Identification of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in AMI and AD
After the data downloaded from the GEO database, the primary data was annotated to form an expression matrix, each probe was matched to their homologous gene symbols, and the repeated gene symbols in the matrix were excluded. Next, the matrix was then normalized using the RMA method10. Then, the R software’s “limma” package was used to analyze the differential expression of the AMI and AD samples. DEGs were defined as genes with p < 0.05 and (|log fold change (FC)|≥ 1. As the demographics of age, sex, and weight of the individuals were not available from the primary data, we were unable to adjust the data for subgroup analysis based on these factors. DEG heat maps and volcano plots were produced using the “pheatmap” and “ggplot2” packages. Following our use of these screening parameters, two sets of DEGs were found. With the “venn” package, these DEGs were analyzed to determine the intersecting genes between the AMI and AD11. Further analysis was conducted using these common genes that intersected.
Functional enrichment analysis for common DEGs
The functional enrichment analysis was carried out in three GO domains: biological process (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF)12. Databases of pathways involving illnesses, medications, chemicals, and biological processes can be found in the KEGG database13,14,15,16. In order to ascertain the biological roles of the genes and related pathways, the enrichment analysis was performed using the R package “clusterProfiler.” A p value of less than 0.05 was deemed statistically significant.
Construction of protein–protein interaction (PPI) network and identification of hub genes
We created a PPI network17 using the Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes (STRING) (http://string-db.org/) in order to investigate the interactions between the common genes that were found above in more detail. Cytoscape 3.9.1 was used to display the findings. The proteins were represented by nodes in the network result, while the interactions between proteins were shown by lines. We installed the MCODE and cytoHubba plugin, which can be downloaded for free via Cytoscape software, after finding the hub genes among these common genes in order to analyze the correlation among these genes18,19. Additionally, genes for functional tests were prioritized by GeneMANIA (http://genemania.org/)20.
Establishment and evaluation of the prognosis model
In biomedical research, it is important to select the variables most associated with the studied outcome and to determine the strength of this association. The “glmnet” package was used to obtain the LASSO algorithm to minimize the dimensionality of the data21. Besides, using an “SVM” package, a support vector machine-recursive feature elimination (SVM-RFE) model was created, and the average misjudgment rates of their tenfold cross-validations were compared22. Additionally, the impact of confounding factors was lessened by applying the multivariable logistic regression analysis23. A nomogram is primarily used to summarise the specific and statistically important parameters obtained from multivariable logistic regression analysis as a simple, two-dimensional graphic24. The “rms” package in R was used to estimate AMI and AD risk. A diagnostic nomogram model for AMI and AD was created by summarising logistic regression’s independent components.
Gene set variation analysis (GSVA) analysis
Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) is a popular method for condensing data from gene expression profiles into pathways or signature summaries. More accurately than GSEA, gene set variation analysis (GSVA) may identify minute changes in pathway activity in sample populations. GSVA is the basis for developing biological models that are centered around pathways25. The GO set served as the study’s background set, and each marker gene was subjected to GSVA analysis using the R software’s “GSVA” package. In the event that t > 0 signifies the activation of a function in the high-expression group, t < 0 implies that this activation is present in the low-expression group.
Construction of ceRNA network
For the ceRNA network, based on the BCL6 gene, mRNA-miRNA interaction pairings were predicted using the starBase database (http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn/). In the meantime, the human miRNA sequences were retrieved from 3 miRNA target prediction databases: miRbase (https://www.mirbase.org/cgi-bin/browse.pl), TargetScan (http://www.targetscan.org/vert_72/), miRDB (http://mirdb.org/), and we extract the results with three occurrences in the three databases as our prediction result. Besides, lncRNAs and miRNAs were analyzed based on the lncRNA target prediction database: Spongescan (http://spongescan.rc.ufl.edu). With a critical score threshold of 140, the Miranda online predicts the nucleic acid binding between mRNA and miRNA (http://www.bioinformatics.com.cn/local_miranda_miRNA_target_prediction_120). After that, with the help of the Cytoscape (version 3.9.1), we screened miRNA-lncRNAs in starBase for projected miRNAs and created a ceRNA network of mRNA-miRNA-lncRNAs26.
Results
Differential expression analysis of DEGs in AMI and AD
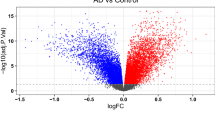
Figure 1 displays the flowchart for this article. In the GSE5281 dataset, we found 414 upregulated genes and 295 downregulated genes for AD patients after excluding the batch effect (Fig. 2A) (Supplementary Table 1). The GSE66360 dataset revealed 350 genes with substantial changes for AMI patients, including 288 upregulated and 62 downregulated genes (Fig. 2B) (Supplementary Table 2). Based on this, we compared the differentially expressed genes in AMI and AD patients, ultimately obtaining a total of 22 differentially expressed genes, consisting of 21 upregulated genes and 1 downregulated gene (Fig. 2C,D).
Functional enrichment analysis
In order to obtain a more comprehensive understanding of the role of DEGs, enrichment studies of KEGG and GO pathways were made. Changes in BP mainly included inflammatory reactions (e.g., regulation of inflammatory response) and signal transduction (e.g., maintenance of protein location and positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis). Besides, the changes in CC were notably focused on cell secretion, such as secretory granule lumen, cytoplasmic vesicle lumen, and vesicle lumen. Moreover, in the MF section, changes were significant in DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific (Fig. 3A–C) (Supplementary Table 3). In particular, changes in the KEGG pathway mainly were enriched in several immune-related pathways (IL-17 signaling pathway, TNF signaling pathway, and Chemokine signaling pathway) (Fig. 3D–F) (Supplementary Table 4).
PPI network analysis and hub gene selection
To identify hub genes and show potential interactions between proteins encoded by common DEGs, STRING screened the DEGs’ PPI network, which had 19 nodes and 64 edges (Fig. 4A). To find important clustering modules, module analysis was carried out using the Cytoscape plug-in MCODE. Two modules were retrieved from the PPI network constructed using common DEGs. Module 1 included ten nodes and 18 edges, and module 2 with three nodes and three edges (Fig. 4B). Besides, through the seven plug-in cytoHubba algorithms, we calculated the top ten hub genes for the following analysis (Supplementary Table 5), and the relationship among ten hub genes was displayed in Fig. 4C.
GeneMANIA conducted PPI analysis of the ten hub genes and their twenty interacting genes to predict correlations between colocalization, pathways, shared protein domains, coexpression, and prediction (Fig. 4D). The inner circle contains the hub genes, and the outside circle contains the predicted genes. As shown in Fig. 4D, the network illustrates that these genes were mainly enriched in positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II, positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to stress, and myeloid leukocyte differentiation.
Hub gene functional enrichment analysis
GO analysis showed that these hub genes are mainly involved in regulation of inflammatory response, chromatin DNA binding, and ossification (Fig. 5A) (Supplementary Table 6). In addition, KEGG Pathway analysis showed that they are mainly involved in the IL-17 signaling pathway, TNF signaling pathway, and Chemokine signaling pathway (Fig. 5B) (Supplementary Table 7). The above hub genes functional analysis shows that the AMI and the AD have a strong relationship with inflammation.
Establishment and evaluation of the prognosis model
We then applied the SVM‐RFE algorithm to filter the ten hub genes to identify the optimal combination of feature genes. Nine genes (maximal accuracy = 0.919, minimal errors = 0.0811) were identified as the optimal feature genes for the AMI patients (Fig. 6A a,b). Meanwhile, we used the LASSO method to construct a model for the target gene set, and based on the ten-fold cross-validation, we obtained a six gene model graph (Fig. 6A c,d). In addition, we took the intersection genes between the SVM-RFE and LASSO results to obtain six model genes (Fig. 6B). Next, we analyzed these six genes with logistic regression and found that only three hub genes with a p-value less than 0.05 were obtained: GAJ1, BCL6 and RGS1. Further, we constructed the predictive model using the two hub genes. To calculate the risk score of each one, the following formula was applied: Risk score = BCL6 × (2.5463) + RGS1 × (1.6769) + RGS1 × (0.7661). This model’s nomogram was also generated in Fig. 6C for visualization and clinical usage of the diagnostic model. Users can find three genes’ blood expression levels on the nomogram and project them to the top point scale to read each variant’s point. By projecting the total points downward, one might estimate the risk likelihood that this patient has AMI based on the bottom scale. In addition, we created a ROC curve to assess the AMI diagnostic model’s predictive accuracy. The training set’s AUC of the ROC curve was 0.970, indicating the model’s strong predictive capacity (Fig. 6D). The calibration curve of the training set was 0.970 when the nomogram was tested using the calibration curve, suggesting that the model has the ability to identify (Fig. 6E).
Meanwhile, six genes (maximal accuracy = 0.888, minimal errors = 0.112) were identified as the optimal feature genes for AD patients through the SVM-RFE algorithm (Fig. 7A a,b). Meanwhile, we used the LASSO method to construct a model for the target gene set, and based on the ten-fold cross-validation, we obtained an eight gene model graph (Fig. 7A c,d). In addition, we took the intersection genes between the SVM-RFE and LASSO results to obtain five model genes (Fig. 7B). Next, we analyzed these six genes with logistic regression and found that three hub genes with a p-value less than 0.05 were obtained: CEBPB, BCL6, and NFKBIA. Further, we constructed the predictive model using the three hub genes. To calculate the risk score of each one, the following formula was applied: Risk score = CEBPB × (0.8110) + BCL6 × (1.3287) + NFKBIA × (1.3785). This model’s nomogram was also generated in Fig. 7C for visualization and clinical usage of the diagnostic model. Moreover, we created a ROC curve to assess the AMI diagnostic model’s predictive accuracy. The training set’s AUC of the ROC curve was 0.935, indicating the model’s strong predictive capacity (Fig. 7D). The calibration curve of the training set was 0.935 when the nomogram was tested using the calibration curve, suggesting that the model has the ability to identify (Fig. 7E).
GSVA analysis
We intersected the model genes based on the AMI and AD prediction models and discovered that the BCL6 gene differed between the two disorders. Subsequently, we ran GSVA analysis on a BCL6-based training set. Based on GO functional analysis, we found that AMI individuals had a high expression about cell proliferation, such as regulation of endodermal cell-differentiation, while had a lower expression about immune response, such as lipopolysaccharide immune receptor activity (Fig. 8A). Besides, for AD patients, we found that AD individuals had a high expression about cell proliferation and migration, such as sphingosine-I-phosphate phosphatase activity, while had a lower expression about immune response, such as tumor necrosis factor binding (Fig. 8B).
Construction of ceRNA network
Next, we constructed a ceRNA network based on BCL6 through StarBase and Miranda databases. The network included 100 nodes (one marker gene, 56 miRNAs, and 43 lncRNAs) and 100 edges (Fig. 9). In detail, we found that only 17 out of 56 miRNAs were associated with 44 lncRNAs. Among them, hsa-miR-361-3p has the highest number of related lncRNAs, which are correlated with seven lncRNAs, including RP3-470B24.5, RP13-507P19.2, HOXC-AS1, RP11-158I9.8, RP11-44M6.7, RP11-561O23.5, and RP4-751H13.7. In addition, we found a correlation between FAM230B and two miRNAs, including hsa-let-7a-3p and hsa-let-7f-2-3p.
Key gene validation
Moreover, we corroborated that BCL6 was expressed in the validation dataset. The expression trends of BCL6 were found to be in agreement with the test dataset. We created ROC curves and determined the associated area under the curve (AUC) of these gene expression levels to validate the diagnostic value of BCL6 found in the investigation. The BCL6 gene was discovered to be expressed at a higher level in AMI patients than in normal patients, and the single gene prediction ability for AMI patients is strong (AUC = 0.734) (Fig. 10A,B). Additionally, AD patients’ BCL6 expression levels were still rising, and the single gene prediction performance is strong (AUC = 0.817) (Fig. 10C,D).
Discussion
In modern Western countries, cardiovascular diseases were the leading causes of morbidity and mortality27,28,29. It is presently believed that pathogenetic pathways resulting in atherogenesis and atherosclerosis complications are abnormal lipid metabolism and inflammatory processes. For example, a slight increase in blood C reactive protein (CRP) levels, a measure of inflammation, is linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular events30. Promoter polymorphisms having functional significance in the expression of the cognate inflammatory gene are frequently observed in patients with AMI31.
AD was the most frequent type of dementia in the elderly32. Pathologically, it was distinguished by the loss of neuronal synapses, extracellular amyloid protein deposits known as neuritic plaques, and intracellular production of defective neurofilaments that form neurofibrillary tangles33. Previous studies had revealed that inflammatory processes have been detected in the brains of people with AD34. Besides, gene variations that increase inflammation or change cholesterol transport had been commonly discovered in AD patients35,36.
Despite these similarities, little data explicitly connected AD and AMI. Epidemiological studies that demonstrated the reduction of inflammation by the use of statins or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) decreased the incidence of both AD and AMI might provide the most substantial evidence yet that AMI and AD are related28,37. Nevertheless, no effort had been undertaken to assess the possibility that particular immunological genetic risk factors represent a significant pathogenetic and etiologic connection between AMI and AD. Therefore, it was essential to investigate the molecular mechanisms behind these two diseases and identify targets to stop the early disease’s progression.
We discovered 22 shared DEGs between AD and AMI in this study by exploring the GEO databases for these two disorders. In addition, we carried out analyses of the KEGG pathway and GO enrichment, and we built a PPI network to determine which ten hub genes were among the DEGs. Next, we used the SVM-RFE and multivariable logistic regression analysis technique to build models for patients with AMI and AD. The BCL6 gene exhibited differential expression in both illnesses and demonstrated a strong predictive capacity (p < 0.05, AUC > 0.8). This means we must accept the genetic resemblance between AMI and AD.
While vigorous acute inflammatory responses were necessary for survival, uncontrolled inflammation was at the root of many diseases, including atherosclerosis. Chronic inflammation was a hallmark of atherosclerosis to the extent that acute transcriptional induction is a driver of inflammation. From early fatty streaks to mature lesions, MØ played a critical role in atherogenesis while the BCL6 played a pivotal role in MØ quiescence and the regulation of inflammation38. Previous research had found that BCL6 reduces oxidized LDL and TLR-induced inflammation and atherogenesis, indicating that BCL6 plays an important role in reducing early vascular lesion development39. Surprisingly, nevertheless, our research revealed that BCL6 gene expression was up-regulated, which may be connected to negative feedback regulation in individuals with high levels of atherosclerosis. Interestingly, prior research had also discovered increased BCL6 gene expression in individuals suffering from coronary heart disease40. Hence, additional mechanisms must be proven through additional tests.
Previous data unraveled that bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles carrying miR-302d-3p repressed cardiomyocyte injury and inflammatory response after AMI by disrupting the NF-κB pathway via the BCL6/MD2 axis, which means the BCL6 played an essential role in early inflammation response41. Concurrent with this, a prior work discovered that BCL6 upregulation participated in the promotion of oxygen–glucose deprivation-induced increase of apoptosis and decreased cell proliferation after ischemic stroke42. Also, BCL6 upregulation was able to aggravate the pulmonary inflammation following influenza virus infection43. These data indirectly supported the effect of BCL6 on apoptosis, inflammation, and viability.
Although prior studies individually investigated the hub genes related to AMI and AD, few studies have used bioinformatics approaches to investigate their common molecular mechanism44,45. Due to the significant comorbidity rate between AMI and AD, we found the common DEGs and hub genes for the first time, which helped clarify the process. Nonetheless, this investigation is not without its drawbacks. The current study was based on a thorough bioinformatics analysis; even though we used an external dataset for additional validation, more research is still required to demonstrate the relationship between feature genes and AMI pathophysiology, which will be the focus of our future work.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we carried out enrichment and PPI network analysis, as well as determined the shared DEGs of AMI and AD. Our research revealed that AMI and AD shared numerous pathogenic pathways, maybe mediated by certain hub genes. In the development of AMI and AD, the hub gene, specifically the BCL6, is crucial. This study adds to our understanding of the molecular mechanism of AMI in combination with AD.
Data availability
The datasets analyzed in this work may be found in the GEO database. All software applications used are included in this article.
References
Writing, C. et al. 2022 Acc Expert Consensus Decision Pathway on the evaluation and disposition of acute chest pain in the emergency department: A report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 80(20), 1925–1960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2022.08.750 (2022).
Gulati, M. et al. 2021 Aha/Acc/Ase/Chest/Saem/Scct/Scmr Guideline for the Evaluation and Diagnosis of Chest Pain: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 144(22), e368–e454. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001029 (2021).
Anderson, J. L. et al. Acc/Aha statement on cost/value methodology in Clinical Practice Guidelines and Performance Measures: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Performance Measures and Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 63(21), 2304–2322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2014.03.016 (2014).
Crous-Bou, M., Minguillon, C., Gramunt, N. & Molinuevo, J. L. Alzheimer’s disease prevention: From risk factors to early intervention. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 9(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-017-0297-z (2017).
Alzheimer’s Association. 2023 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 19(4), 1598–695. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.13016 (2023).
Tsao, C. W. et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2023 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 147(8), e93–e621. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001123 (2023).
Kuzma, E. et al. Stroke and dementia risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Alzheimer’s Dement. 14(11), 1416–1426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2018.06.3061 (2018).
Gottesman, R. F. et al. Associations between midlife vascular risk factors and 25-year incident dementia in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (Aric) Cohort. JAMA Neurol. 74(10), 1246–1254. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.1658 (2017).
Ronnemaa, E., Zethelius, B., Lannfelt, L. & Kilander, L. Vascular risk factors and dementia: 40-Year follow-up of a population-based cohort. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 31(6), 460–466. https://doi.org/10.1159/000330020 (2011).
Chen, J. H. et al. Identification of Myh6 as the potential gene for human Ischaemic cardiomyopathy. J. Cell Mol. Med. 25(22), 10736–10746. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.17015 (2021).
Dai, W. et al. Key genes associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and acute myocardial infarction. Med. Sci. Monit. 26, e922492. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.922492 (2020).
Gene Ontology Consortium. The Gene Ontology (Go) Project in 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 34(Database issue), D322–D326. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkj021 (2006).
Kanehisa, M., Sato, Y., Kawashima, M., Furumichi, M. & Tanabe, M. Kegg as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 44(D1), D457–D462. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1070 (2016).
Kanehisa, M. & Goto, S. Kegg: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28(1), 27–30. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.27 (2000).
Kanehisa, M. Toward understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms. Protein Sci. 28(11), 1947–1951. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3715 (2019).
Kanehisa, M., Furumichi, M., Sato, Y., Kawashima, M. & Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. Kegg for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 51(D1), D587–D592. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac963 (2023).
Vidal, M., Cusick, M. E. & Barabasi, A. L. Interactome networks and human disease. Cell 144(6), 986–998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.016 (2011).
Bader, G. D. & Hogue, C. W. An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinform. 4, 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-4-2 (2003).
Chin, C. H. et al. Cytohubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst. Biol. 8(Suppl 4), S11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-8-S4-S11 (2014).
Warde-Farley, D. et al. The genemania prediction server: Biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids Res. 38(Web Server issue), W214–W2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq537 (2010).
Liu, C., Liu, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, X. & Guan, Y. Immune-related potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets in coronary artery disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 9, 1055422. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2022.1055422 (2022).
Sanz, H., Valim, C., Vegas, E., Oller, J. M. & Reverter, F. Svm-Rfe: Selection and visualization of the most relevant features through non-linear kernels. BMC Bioinform. 19(1), 432. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-018-2451-4 (2018).
Hidalgo, B. & Goodman, M. Multivariate or multivariable regression?. Am. J. Public Health 103(1), 39–40. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2012.300897 (2013).
Iasonos, A., Schrag, D., Raj, G. V. & Panageas, K. S. How to build and interpret a nomogram for cancer prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 26(8), 1364–1370. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2007.12.9791 (2008).
Medina, I. et al. Gene set-based analysis of polymorphisms: Finding pathways or biological processes associated to traits in genome-wide association studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 37(Web Server issue), W340–W344. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp481 (2009).
Qi, X. et al. Cerna in cancer: Possible functions and clinical implications. J. Med. Genet. 52(10), 710–718. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmedgenet-2015-103334 (2015).
Gulati, R. et al. Acute myocardial infarction in young individuals. Mayo Clin. Proc. 95(1), 136–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2019.05.001 (2020).
Mangione, C. M. et al. Statin use for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA 328(8), 746–753. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2022.13044 (2022).
Davidson, K. W. et al. Aspirin use to prevent cardiovascular disease: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA 327(16), 1577–1584. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2022.4983 (2022).
Rifai, N. & Ridker, P. M. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein: A novel and promising marker of coronary heart disease. Clin. Chem. 47(3), 403–411 (2001).
Jenny, N. S. et al. In the elderly, interleukin-6 plasma levels and the − 174g > C polymorphism are associated with the development of cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 22(12), 2066–2071. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.atv.0000040224.49362.60 (2002).
Erkkinen, M. G., Kim, M. O. & Geschwind, M. D. Clinical neurology and epidemiology of the major neurodegenerative diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a033118 (2018).
Khan, S., Barve, K. H. & Kumar, M. S. Recent advancements in pathogenesis, diagnostics and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 18(11), 1106–1125. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X18666200528142429 (2020).
Tarkowski, E., Andreasen, N., Tarkowski, A. & Blennow, K. Intrathecal inflammation precedes development of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 74(9), 1200–1205. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.74.9.1200 (2003).
Vural, P. et al. The combinations of Tnfalpha-308 and Il-6-174 or Il-10-1082 genes polymorphisms suggest an association with susceptibility to sporadic late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neurol. Scand. 120(6), 396–401. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0404.2009.01230.x (2009).
Corder, E. H. et al. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science 261(5123), 921–923. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.8346443 (1993).
Bosch, J. et al. Antihypertensives and statin therapy for primary stroke prevention: A secondary analysis of the Hope-3 trial. Stroke 52(8), 2494–2501. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.030790 (2021).
Barish, G. D. et al. The Bcl6-Smrt/Ncor cistrome represses inflammation to attenuate atherosclerosis. Cell Metab. 15(4), 554–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2012.02.012 (2012).
Barish, G. D. et al. Bcl-6 and Nf-kappab cistromes mediate opposing regulation of the innate immune response. Genes Dev. 24(24), 2760–2765. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1998010 (2010).
Peng, W., Sun, Y. & Zhang, L. Construction of genetic classification model for coronary atherosclerosis heart disease using three machine learning methods. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 22(1), 42. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-022-02481-4 (2022).
Liu, Y. et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicle-shuttled microrna-302d-3p represses inflammation and cardiac remodeling following acute myocardial infarction. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 15(4), 754–771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-021-10200-1 (2022).
Wei, P. et al. Inhibition of the Bcl6/Mir-31/Pkd1 axis attenuates oxidative stress-induced neuronal damage. Exp. Neurol. 335, 113528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113528 (2021).
Zhu, B. et al. Bcl6 modulates tissue neutrophil survival and exacerbates pulmonary inflammation following influenza virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 116(24), 11888–11893. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1902310116 (2019).
Song, Z. et al. Identification of five hub genes based on single-cell Rna sequencing data and network pharmacology in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Front. Public Health 10, 894129. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.894129 (2022).
Wang, Y., Chen, G. & Shao, W. Identification of ferroptosis-related genes in Alzheimer’s disease based on bioinformatic analysis. Front. Neurosci. 16, 823741. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2022.823741 (2022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors are solely responsible for the content and writing of the manuscript. All authors made significant contributions to the design, data collection and interpretation, and manuscript preparation and revision of this study.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Pan, F., Sun, Z. et al. Exploring the pathogenesis and key genes associated of acute myocardial infarction complicated with Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep 14, 1449 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-52094-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-52094-4
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.