Abstract
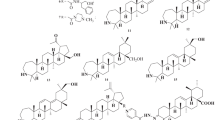
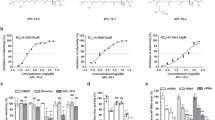
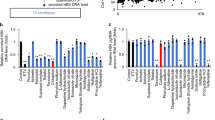
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) causes chronic hepatitis in humans, and current antiviral therapies rarely treat viral infections. To improve the treatment efficacy, novel therapeutic agents, especially those with different mechanisms of action, need to be developed for use in combination with the current antivirals. Here, we isolated new anti-HBV compounds, named catenulopyrizomicins A–C, from the fermentation broth of rare actinomycete Catenuloplanes sp. MM782L-181F7. Structural analysis revealed that these compounds contained a structure that is composed of thiazolyl pyridine moiety. The catenulopyrizomicins reduced the amount of intracellular viral DNA in HepG2.2.15 cells with EC50 values ranging from 1.94 to 2.63 µM with small but notable selectivity. Mechanistic studies indicated that catenulopyrizomicin promotes the release of immature virion particles that fail to be enveloped through alterations in membrane permeability.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang HI, Lu SN, Liaw YF, You SL, Sun CA, Wang LY, Hsiao CK, Chen PJ, Chen DS, Chen CJ, Taiwan Community-Based Cancer Screening Project Group 2002. Hepatitis B e antigen and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. N Eng J Med. 2002;347:168–74.
Durantel D, Zoulim F. New antiviral targets for innovative treatment concepts for hepatitis B virus and hepatitis delta virus. J Hepatol. 2016;64:S117–31.
Pei Y, Wang C, Yan SF, Liu G. Past, current, and future developments of therapeutic agents for treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Med Chem. 2017;60:6461–79.
Beck J, Nassal M. Hepatitis B virus replication. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:48–64.
Seeger C, Mason WS. Molecular biology of hepatitis B virus infection. Virology. 2015;479-480:672–86.
Suzuki M, Kondo S, Yamasaki M, Matsuda N, Nomoto A, Suzuki T, Saito I, Kanegae Y. Efficient genome replication of hepatitis B virus using adenovirus vector: a compact pregenomic RNA-expression unit. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41851.
Takizawa N, Yamasaki M. Current landscape and future prospects of antiviral drugs derived from microbial products. J Antibiot. 2017;71:45–52.
Yamasaki M, Matsuda N, Matoba K, Kondo S, Kanegae Y, Saito I, Nomoto A. Acetophenone 4-nitrophenylhydrazone inhibits Hepatitis B virus replication by modulating capsid assembly. Virus Res. 2021;306:198565.
Nishio M, Tomatsu K, Konishi M, Tomita K, Oki T, Kawaguchi H, Clardy J. Karnamicin, a complex of new antifungal antibiotics. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and physico-chemical and biological properties. J Antibiot. 1989;42:852–68.
Urban M, McMillan DJ, Canning G, Newell A, Brown E, Mills JS, Jupp R. In vitro activity of hepatitis B virus polymerase: requirement for distinct metal ions and the viral epsilon stem-loop. J Gen Virol. 1998;79:1121–31.
Toyoda T, Wang Y, Wen Y, Tanaka Y. Fluorescence-based biochemical analysis of human hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase activity. Anal Biochem. 2020;597:113642.
Chang LJ, Hirsch RC, Ganem D, Varmus HE. Effects of insertional and point mutations on the functions of the duck hepatitis B virus polymerase. J Virol. 1990;64:5553–8.
Wei X, Peterson DL. Expression, purification, and characterization of an active RNase H domain of the hepatitis B viral polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:32617–22.
Lu G, Lomonosova E, Cheng X, Moran EA, Meyers MJ, Le Grice SF, Thomas CJ, Jiang JK, Meck C, Hirsch DR, D’Erasmo MP, Suyabatmaz DM, Murelli RP, Tavis JE. Hydroxylated tropolones inhibit hepatitis B virus replication by blocking viral ribonuclease H activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:1070–9.
Jiang B, Hildt E. Intracellular trafficking of HBV particles. Cells. 2020;9:2023.
Lenhoff RJ, Summers J. Coordinate regulation of replication and virus assembly by the large envelope protein of an avian hepadnavirus. J Virol. 1994;68:4565–71.
Ning X, Nguyen D, Mentzer L, Adams C, Lee H, Ashley R, Hafenstein S, Hu J. Secretion of genome-free hepatitis B virus - single strand blocking model for virion morphogenesis of para-retrovirus. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7:e1002255.
Bai L, Zhang X, Kozlowski M, Li W, Wu M, Liu J, Chen L, Zhang J, Huang Y, Yuan Z. Extracellular hepatitis B Virus RNAs are heterogeneous in length and circulate as capsid-antibody complexes in addition to virions in chronic hepatitis B patients. J Virol. 2018;92:e00798–18.
Yu Z, Huang JP, Yang J, Liu C, Yan Y, Wang L, Zhao J, Chen Y, Xiang W, Huang SX. Discovery and biosynthesis of karnamicins as angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. Nat Commun. 2023;14:209.
Tsurumi Y, Ueda H, Hayashi K, Takase S, Nishikawa M, Kiyoto S, Okuhara M. WS75624 A and B, new endothelin converting enzyme inhibitors isolated from Saccharothrix sp. No. 75624. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation, physico-chemical properties and biological activities. J Antibiot. 1995;48:1066–72.
Yoshimura S, Tsurumi Y, Takase S, Okuhara M. WS75624 A and B, new endothelin converting enzyme inhibitors isolated from Saccharothrix sp. No. 75624. II. Structure elucidation of WS75624 A and B. J Antibiot. 1995;48:1073–5.
Kimura T, Inahashi Y, Matsuo H, Suga T, Iwatsuki M, Shiomi K, Takahashi Y, Ōmura S, Nakashima T. Pyrizomicin A and B: structure and bioactivity of new thiazolyl pyridines from Lechevalieria aerocolonigenes K10-0216. J Antibiot. 2018;71:606–8.
Guo F, Zhao Q, Sheraz M, Cheng J, Qi Y, Su Q, Cuconati A, Wei L, Du Y, Li W, Chang J, Guo JT. HBV core protein allosteric modulators differentially alter cccDNA biosynthesis from de novo infection and intracellular amplification pathways. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13:e1006658.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Yasuhiro Takehana and Ms. Rie Arisaka for their technical assistance with isolating catenulopyrizomicins, and Dr. Kiyoko Iijima for the HRESI-MS and NMR measurements. We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.jp) for English language editing. This study is dedicated to the memory of Dr. Akio Nomoto, passed away in 2014, who inspired us a lot to find microbial compounds with antiviral activities. This study was supported by JSPS KAKENHI (grant number JP15K08507) and the Research Program on Hepatitis of the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) (grant number JP20fk0310102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yamasaki, M., Sawa, R., Muramatsu, H. et al. Catenulopyrizomicins, new anti-Hepatitis B virus compounds, from the rare actinomycete Catenuloplanes sp. MM782L-181F7. J Antibiot 77, 85–92 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-023-00681-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-023-00681-4