Abstract
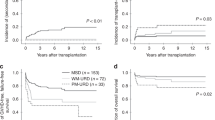
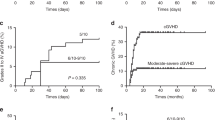
The impact of ABO incompatibility on transplantation outcomes in severe aplastic anemia (SAA) patients receiving haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) remains controversial without published data. A total of 199 SAA patients receiving haploidentical HSCT from ABO-matched (n = 114), minor ABO-incompatible (n = 47), or major ABO-incompatible donors (n = 38) were included in this study. The median time and cumulative incidences of both myeloid and platelet engraftment in the ABO-compatible and ABO-incompatible groups were similar, and pure red cell aplasia was absent. Minor ABO incompatibility increased the rate of grade III–IV acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD) (ABO compatible: 6.14 ± 0.05%, minor incompatible: 19.15 ± 0.34%, and major incompatible: 10.53 ± 0.25%; P = 0.051), but did not influence the rates of grade II–IV aGVHD or chronic GVHD (cGVHD). Minor ABO-incompatibility was identified as an independent risk factor for grade III–IV aGVHD by multivariate analysis (hazard ration (HR) = 4.00 (1.48–10.80), P = 0.006). Chronic GVHD, mortality, and treatment failure were not increased in the minor ABO-incompatible group. For SAA patients receiving haploidentical HSCT, ABO compatible donors are better than ABO minor incompatible donors if several haploidentical donors are available.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Killick SB, Bown N, Cavenagh J, Dokal I, Foukaneli T, Hill A, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of adult aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 2016;172:187–207.
Young NS, Calado RT, Scheinberg P. Current concepts in the pathophysiology and treatment of aplastic anemia. Blood. 2006;108:2509–19.
Scheinberg P, Wu CO, Nunez O, Young NS. Long-term outcome of pediatric patients with severe aplastic anemia treated with antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine. J Pediatr. 2008;153:814–9.
Xu LP, Jin S, Wang SQ, Xia LH, Bai H, Gao SJ, et al. Upfront haploidentical transplant for acquired severe aplastic anemia: registry-based comparison with matched related transplant. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:25.
Damodar S, George B, Mammen J, Mathews V, Srivastava A, Chandy M. Pre-transplant reduction of isohaemagglutinin titres by donor group plasma infusion does not reduce the incidence of pure red cell aplasia in major ABO-mismatched transplants. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2005;36:233–5.
Bolan CD, Leitman SF, Griffith LM, Wesley RA, Procter JL, Stroncek DF, et al. Delayed donor red cell chimerism and pure red cell aplasia following major ABO-incompatible nonmyeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2001;98:1687–94.
Bolan CD, Childs RW, Procter JL, Barrett AJ, Leitman SF. Massive immune haemolysis after allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation with minor ABO incompatibility. Br J Haematol. 2001;112:787–95.
Canaani J, Savani BN, Labopin M, Huang X-J, Ciceri F, Arcese W, et al. Impact of ABO incompatibility on patients’ outcome after haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia—a report from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the EBMT. Haematologica. 2017;102:1066–74.
Ludajic K, Balavarca Y, Bickeboller H, Rosenmayr A, Fischer GF, Fae I, et al. Minor ABO-mismatches are risk factors for acute graft-versus-host disease in hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009;15:1400–6.
Kanda J, Ichinohe T, Matsuo K, Benjamin RJ, Klumpp TR, Rozman P, et al. Impact of ABO mismatching on the outcomes of allogeneic related and unrelated blood and marrow stem cell transplantations for hematologic malignancies: IPD-based meta-analysis of cohort studies. Transfusion. 2009;49:624–35.
Damodar S, Shanley R, MacMillan M, Ustun C, Weisdorf D, Donor-to-Recipient ABO. Mismatch does not impact outcomes of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation regardless of graft source. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017;23:795–804.
McCurdy SR, Zhang M-J, St Martin A, Al Malki MM, Bashey A, Gaballa S, et al. Effect of donor characteristics on haploidentical transplantation with posttransplantation cyclophosphamide. Blood Adv. 2018;2:299–307.
Xu LP, Wang SQ, Wu DP, Wang JM, Gao SJ, Jiang M, et al. Haplo-identical transplantation for acquired severe aplastic anaemia in a multicentre prospective study. Br J Haematol. 2016;175:265–74.
Xiao-Jun H, Lan-Ping X, Kai-Yan L, Dai-Hong L, Huan C, Wei H, et al. HLA-mismatched/haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation without in vitro T cell depletion for chronic myeloid leukemia: improved outcomes in patients in accelerated phase and blast crisis phase. Ann Med. 2008;40:444–55.
Xu LP, Liu KY, Liu DH, Han W, Chen H, Chen YH, et al. A novel protocol for haploidentical hematopoietic SCT without in vitro T-cell depletion in the treatment of severe acquired aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012;47:1507–12.
Huang XJ, Liu DH, Liu KY, Xu LP, Chen H, Han W, et al. Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation without in vitro T-cell depletion for the treatment of hematological malignancies. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2006;38:291–7.
Hirokawa M, Fukuda T, Ohashi K, Hidaka M, Ichinohe T, Iwato K, et al. Efficacy and long-term outcome of treatment for pure red cell aplasia after allogeneic stem cell transplantation from major ABO-incompatible donors. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2013;19:1026–32.
Rabitsch W, Knöbl P, Prinz E, Keil F, Greinix H, Kalhs P, et al. Prolonged red cell aplasia after major ABO-incompatible allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: removal of persisting isohemagglutinins with Ig-Therasorb immunoadsorption. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2003;32:1015–9.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J, et al. 1994 consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995;15:825–8.
Shulman HM, Sullivan KM, Weiden PL, McDonald GB, Striker GE, Sale GE, et al. Chronic graft-versus-host syndrome in man. A long-term clinicopathologic study of 20 Seattle patients. Am J Med. 1980;69:204–17.
Kimura F, Sato K, Kobayashi S, Ikeda T, Sao H, Okamoto S, et al. Impact of AB0-blood group incompatibility on the outcome of recipients of bone marrow transplants from unrelated donors in the Japan Marrow Donor Program. Haematologica. 2008;93:1686–93.
Stussi G, Muntwyler J, Passweg JR, Seebach L, Schanz U, Gmür J, et al. Consequences of ABO incompatibility in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2002;30:87–93.
Klumpp TR, Herman JH, Ulicny J, Emmons RVB, Martin ME, Mangan KF. Lack of effect of donor-recipient ABO mismatching on outcome following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2006;38:615–20.
Gutierrez-Aguirre CH, Gomez-De-Leon A, Alatorre-Ricardo J, Cantu-Rodriguez OG, Gonzalez-Llano O, Jaime-Perez JC, et al. Allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation using reduced-intensity conditioning in an outpatient setting in ABO-incompatible patients: are survival and graft-versus-host disease different? Transfusion. 2014;54:1269–77.
Eiz-Vesper B, Seltsam A, Blasczyk R. ABO glycosyltransferases as potential source of minor histocompatibility antigens in allogeneic peripheral blood progenitor cell transplantation. Transfusion. 2005;45:960–8.
Nakanuma Y, Sasaki M. Expression of blood group-related antigens in the intrahepatic biliary tree and hepatocytes in normal livers and various hepatobiliary diseases. Hepatology. 1989;10:174–8.
Lapierre V, Mahé C, Aupérin A, Stambouli F, Oubouzar N, Tramalloni D, et al. Platelet transfusion containing ABO-incompatible plasma and hepatic veno-occlusive disease after hematopoietic transplantation in young children. Transplantation. 2005;80:314–9.
Sanchez-Urdazpal L, Batts KP, Gores GJ, Moore SB, Sterioff S, Wiesner RH, et al. Increased bile duct complications in liver transplantation across the ABO barrier. Ann Surg. 1993;218:152–8.
Stussi G, Seebach L, Muntwyler J, Schanz U, Gmür J, Seebach JD. Graft-versus-host disease and survival after ABO-incompatible allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: a single-centre experience. Br J Haematol. 2001;113:251–3.
Quillen K, Sheldon SL, Daniel-Johnson JA, Lee-Stroka AH, Flegel WA. A practical strategy to reduce the risk of passive hemolysis by screening plateletpheresis donors for high-titer ABO antibodies. Transfusion. 2011;51:92–6.
Cooling LLW, Kelly K, Barton J, Hwang D, Koerner TAW, Olson JD. Determinants of ABH expression on human blood platelets. Blood. 2005;105:3356–64.
Booth GS, Gehrie EA, Bolan CD, Savani BN. Clinical guide to ABO-incompatible allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013;19:1152–8.
Blin N, Traineau R, Houssin S, Peffault de Latour R, Petropoulou A, Robin M, et al. Impact of donor-recipient major ABO mismatch on allogeneic transplantation outcome according to stem cell source. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010;16:1315–23.
Kudek MR, Shanley R, Zantek ND, McKenna DH, Smith AR, Miller WP. Impact of graft-recipient ABO compatibility on outcomes after umbilical cord blood transplant for nonmalignant disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2016;22:2019–24.
Chang Y-J, Xu L-P, Liu D-H, Liu K-Y, Han W, Chen Y-H, et al. The impact of CD34+ cell dose on platelet engraftment in pediatric patients following unmanipulated haploidentical blood and marrow transplantation. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2009;53:1100–6.
Michallet M, Le Q-H, Mohty M, Prébet T, Nicolini F, Boiron JM, et al. Predictive factors for outcomes after reduced intensity conditioning hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for hematological malignancies: a 10-year retrospective analysis from the Société Française de Greffe de Moelle et de Thérapie Cellulaire. Exp Hematol. 2008;36:535–44.
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by grants from Innovative Research Groups of the Natural Science Foundation of China (81670167, 81621001), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFA0104500), National Science and Technology Major Project (2017ZX09304021), and CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (CIFMS) (grant number: 2019-I2M-5-034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Y-RM, W-JW, Y-FC, Y-YZ, X-DM, T-TH, F-RW, C-HY, Y-QS, Y-HC, J-ZW, F-FT, WH, YW, X-HZ, X-JH, and L-PX declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, YR., Wang, WJ., Cheng, YF. et al. Impact of ABO incompatibility on outcomes after haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for severe aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 55, 1068–1075 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-020-0779-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-020-0779-7