Abstract
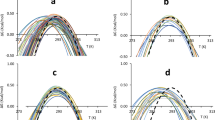
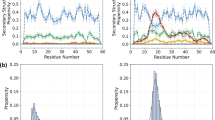
Despite the general observation that single domain proteins denature in a completely cooperative manner, amide hydrogen exchange of ribonuclease H in low levels of denaturant demonstrates the existence of two partially folded species. The structures of these marginally stable species resemble kinetic folding intermediates and the molten globule state of the protein. These data suggest that the first region to fold is the thermodynamically most stable portion of the protein and that the molten globule is a high free energy conformation present at equilibrium in the native state.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim, P.S. & Baldwin, R.L. Intermediates in the folding reactions of small proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 59, 631–660 (1990).
Kuwajima, K. The molten globule state as a clue for understanding the folding and cooperativity of globular-protein structure. Proteins 6, 87–103 (1989).
Ptitsyn, O.B., Pain, R.H., Semisotnov, G.V., Zerovnik, E. & Razgulyaev, O.I. Evidence for a molten globule state as a general intermediate in protein folding. Febs. Lett. 262, 20–24 (1990).
Jennings, P.A. & Wright, P.E. Formation of a molten globule intermediate early in the kinetic folding pathway of apomyoglobin. Science 262, 892–896 (1993).
Dobson, C.M. Protein folding. Solid evidence for molten globules. Curr. Biol. 4, 636–40 (1994).
Mayo, S.L. & Baldwin, R.L. Guanidinium chloride induction of partial unfolding in amide proton exchange in RNase A. Science 262, 873–876 (1993).
Bai, Y., Sosnick, T.R., Mayne, L. & Englander, S.W. Protein folding intermediates: native-state hydrogen exchange. Science 269, 192–197 (1995).
Katayanagi, K. et al. Three-dimensional structure of ribonuclease H from E. coli. Nature 347, 306–309 (1990).
Yamasaki, K., Ogasahara, K., Yutani, K., Oobatake, M. & Kanaya, S. Folding pathway of Escherichia coli ribonuclease HI: a circular dichroism, fluorescence, and NMR study. Biochemistry 34, 16552–16562 (1995).
Dabora, J.M., Pelton, J.G. & Marqusee, S. Structure of the acid state of E. coli ribonuclease HI. Biochemistry, in the press.
Norwood, T.J., Boyd, J., Heritage, J., Soffe, N. & Campbell, I.D. Comparison of techniques for H-1-detected heteronuclear H-1-N-15 spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. 87, 488–501 (1990).
Bax, A., Ikura, M., Kay, L.E., Torchia, D.A. & Tschudin, R. Comparison of different modes of 2-dimensional reverse-correlation NMR for the study of proteins. J. Magn. Reson. 86, 304–318 (1990).
Grzesiek, S. & Bax, A. The Importance of not saturating H2O in protein NMR. Application to sensitivity enhancement and NOE measurements. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115, 12593–12594 (1993).
Hvidt, A. & Nielsen, S.O. Hydrogen exchange in proteins. Adv. Prot Chem. 21, 288–386 (1966).
Englander, S.W. & Kallenbach, N.R. Hydrogen exchange and structural dynamics of proteins and nucleic acids. Q. Rev. Biophys. 16, 521–655 (1983).
Bai, Y., Milne, J.S., Mayne, L. & Englander, S.W. Primary structure effects on peptide group hydrogen exchange. Proteins 17, 75–86 (1993).
Sali, A., Shakhnovich, E. & Karplus, M. How does a protein fold? Nature 369, 248–251 (1994).
O'Shea, E.K., Klemm, J.D., Kim, P.S. & Alber, T. X-ray structure of the GCN4 leucine zipper, a two-stranded, parallel coiled coil. Science 254, 539–544 (1991).
Mandel, A.M., Akke, M. & Palmer, A. A.3. Backbone dynamics of Escherichia coli ribonuclease HI: correlations with structure and function in an active enzyme. J. Mol. Biol. 246, 144–63 (1995).
Yamasaki, K., Saito, M., Oobatake, M. & Kanaya, S. Characterization of the internal motions of Escherichia coli ribonuclease HI by a combination of 15N-NMR relaxation analysis and molecular dynamics simulation: examination of dynamic models. Biochemistry 34, 6587–601 (1995).
Myer, J.K., Pace, C.N. & Scholtz, J.M. Denaturant m values and heat capacity changes: Relation to changes in accessible surface areas of protein folding. Prot. Sci. 4, 2138–2148 (1995).
Dabora, J.M. & Marqusee, S. Equilibrium unfolding of Escherichia coli ribonuclease H: characterization of a partially folded state. Prot. Sci. 3, 1401–1408 (1994).
Matthews, C.R. Pathways of protein folding. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 62, 653–683 (1993).
Loh, S.L., Prehoda, K.E., Wang, J. & Markley, J.L. Hydrogen exchange in unligated and ligated staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry 32, 11022–11028 (1993).
Orban, J., Alexander, P. & Bryan, P. Hydrogen-deuterium exchange in the free and immunoglobulin G-bound protein G B-domain, Biochemistry 33, 5702–5710 (1994).
Perret, S., Clark, J., Hounslow, A.M. & Fersht, A.R. Relationship between equilibrium amide proton exchange behavior and the folding pathway of barnase. Biochemistry 34, 9288–9298 (1995).
Swint-Kruse, L. & Robertson, A.D. Temperature and pH dependences of hydrogen exchange and global stability for ovomucoid third domain. Biochemistry 35, 171–180 (1996).
Sosnick, T.R., Mayne, L., Hiller, R. & Englander, S.W. The barriers in protein folding. Nature Struct. Biol. 1, 149–156 (1994).
Chen, H., Hughes, D.D., Chan, T.-A., Sedat, J.W. & Agard, D.A. IVE(Image Visualization Environment): A software platform for all three-dimensional microscopy applications. J. Struct. Biol. 116, 56–60 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chamberlain, A., Handel, T. & Marqusee, S. Detection of rare partially folded molecules in equilibrium with the native conformation of RNaseH. Nat Struct Mol Biol 3, 782–787 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0996-782
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0996-782
This article is cited by
-
Equilibrium folding dynamics of meACP in water, heavy water, and low concentration of urea
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Opinion: hazards faced by macromolecules when confined to thin aqueous films
Biophysics Reports (2017)
-
Steric trapping reveals a cooperativity network in the intramembrane protease GlpG
Nature Chemical Biology (2016)
-
Design of symmetric TIM barrel proteins from first principles
BMC Biochemistry (2015)
-
Entropic stabilization of myoglobin by subdenaturing concentrations of guanidine hydrochloride
JBIC Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry (2009)