Abstract
Neuropsychiatric events are common in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), but less than one-third of these events can be directly attributed to SLE. Increased generalized SLE disease activity or damage, previous or concurrent major neuropsychiatric SLE (NPSLE) events, and persistently positive moderate-to-high antiphospholipid antibody titers are established risk factors, and their presence could facilitate proper attribution to the disease itself. Diagnostic evaluation is guided by the presenting manifestation; MRI is used to visualize brain or spinal pathologies. For neuropsychiatric events believed to reflect an immune or inflammatory process, or when these events occur in the context of active generalized disease, evidence (primarily from uncontrolled studies) supports the use of glucocorticoids alone or in combination with immunosuppressive therapy. Antiplatelet and/or anticoagulation therapy is recommended for NPSLE manifestations related to antiphospholipid antibodies, especially for thrombotic cerebrovascular disease. For the future, we anticipate that novel biomarkers and advanced neuroimaging tests will better define the underlying pathologic mechanisms of SLE-related neuropsychiatric disease, and help guide therapeutic decisions.
Key Points
-
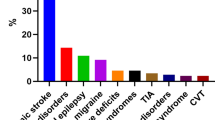
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)-associated neuropsychiatric events occur in 30–40% of patients with this disease, often at disease onset or within the first 2 years after diagnosis
-
Mild neuropsychiatric syndromes, such as headache, anxiety, mild depression, mild cognitive dysfunction, and polyneuropathy without electrophysiologic confirmation, are common, but are not usually related to SLE
-
Risk factors for neuropsychiatric SLE (NPSLE) include persistently positive, moderate-to-high titers of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL), previous or concurrent major NPSLE events, and increased SLE activity or damage
-
Initial diagnostic evaluation should be similar to that in non-SLE patients, aiming to exclude secondary causes of neuropsychiatric events; MRI is the preferred imaging test for visualizing brain and spinal pathologies
-
Management involves symptomatic therapies and treatment of aggravating factors where applicable: immunosuppressive therapy is indicated for inflammatory NPSLE or when generalized SLE activity is present; anticoagulation/antiplatelet therapy is recommended for aPL-associated manifestations
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
[No authors listed] The American College of Rheumatology nomenclature and case definitions for neuropsychiatric lupus syndromes. Arthritis Rheum. 42, 599–608 (1999).
Ainiala, H. et al. Validity of the new American College of Rheumatology criteria for neuropsychiatric lupus syndromes: a population-based evaluation. Arthritis Rheum. 45, 419–423 (2001).
Hanly, J. G. et al. Prospective study of neuropsychiatric events in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 36, 1449–1459 (2009).
Hanly, J. G. et al. Prospective analysis of neuropsychiatric events in an international disease inception cohort of SLE patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 69, 529–535 (2009).
Davey, R., Bamford, J. & Emery, P. The ACR classification criteria for headache disorders in SLE fail to classify certain prevalent headache types. Cephalalgia 28, 296–299 (2008).
Glanz, B. I., Venkatesan, A., Schur, P. H., Lew, R. A. & Khoshbin, S. Prevalence of migraine in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Headache 41, 285–289 (2001).
Omdal, R., Waterloo, K., Koldingsnes, W., Husby, G. & Mellgren, S. I. Somatic and psychological features of headache in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 28, 772–779 (2001).
Mok, C. C., To, C. H. & Mak, A. Neuropsychiatric damage in Southern Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Medicine (Baltimore) 85, 221–228 (2006).
Sanna, G. et al. Neuropsychiatric manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus: prevalence and association with antiphospholipid antibodies. J. Rheumatol. 30, 985–992 (2003).
Zhou, H. Q. et al. Clinical features and outcome of neuropsychiatric lupus in Chinese: analysis of 240 hospitalized patients. Lupus 17, 93–99 (2008).
Hanly, J. G. et al. Short-term outcome of neuropsychiatric events in systemic lupus erythematosus upon enrollment into an international inception cohort study. Arthritis Rheum. 59, 721–729 (2008).
Tam, L. S. et al. The relationship between neuropsychiatric, clinical, and laboratory variables and quality of life of Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 35, 1038–1045 (2008).
Jonsen, A., Bengtsson, A. A., Nived, O., Ryberg, B. & Sturfelt, G. Outcome of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus within a defined Swedish population: increased morbidity but low mortality. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41, 1308–1312 (2002).
Utset, T. O., Fink, J. & Doninger, N. A. Prevalence of neurocognitive dysfunction and other clinical manifestations in disabled patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 33, 531–538 (2006).
Bultink, I. E., Turkstra, F., Dijkmans, B. A. & Voskuyl, A. E. High prevalence of unemployment in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: association with organ damage and health-related quality of life. J. Rheumatol. 35, 1053–1057 (2008).
Panopalis, P. et al. Impact of memory impairment on employment status in persons with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 57, 1453–1460 (2007).
Bernatsky, S. et al. Mortality related to cerebrovascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 15, 835–839 (2006).
Nguyen-Oghalai, T. U., Wu, H., McNearney, T. A., Granger, C. V. & Ottenbacher, K. J. Functional outcome after stroke in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 59, 984–988 (2008).
Lin, Y. C., Wang, A. G. & Yen, M. Y. Systemic lupus erythematosus-associated optic neuritis: clinical experience and literature review. Acta Ophthalmol. 87, 204–210 (2009).
Kovacs, B., Lafferty, T. L., Brent, L. H. & DeHoratius, R. J. Transverse myelopathy in systemic lupus erythematosus: an analysis of 14 cases and review of the literature. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 59, 120–124 (2000).
Lu, X., Gu, Y., Wang, Y., Chen, S. & Ye, S. Prognostic factors of lupus myelopathy. Lupus 17, 323–328 (2008).
Tomietto, P. et al. General and specific factors associated with severity of cognitive impairment in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 57, 1461–1472 (2007).
Appenzeller, S., Cendes, F. & Costallat, L. T. Epileptic seizures in systemic lupus erythematosus. Neurology 63, 1808–1812 (2004).
Bujan, S. et al. Contribution of the initial features of systemic lupus erythematosus to the clinical evolution and survival of a cohort of Mediterranean patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 62, 859–865 (2003).
Mikdashi, J., Krumholz, A. & Handwerger, B. Factors at diagnosis predict subsequent occurrence of seizures in systemic lupus erythematosus. Neurology 64, 2102–2107 (2005).
Mikdashi, J. & Handwerger, B. Predictors of neuropsychiatric damage in systemic lupus erythematosus: data from the Maryland lupus cohort. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43, 1555–1560 (2004).
Locht, H. & Wiik, A. IgG and IgM isotypes of anti-cardiolipin and anti-β2-glycoprotein I antibodies reflect different forms of recent thrombo-embolic events. Clin. Rheumatol. 25, 246–250 (2006).
Roldan, C. A., Gelgand, E. A., Qualls, C. R. & Sibbitt, W. L. Jr. Valvular heart disease as a cause of cerebrovascular disease in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am. J. Cardiol. 95, 1441–1447 (2005).
Andrade, R. M. et al. Seizures in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: data from LUMINA, a multiethnic cohort (LUMINA LIV). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 67, 829–834 (2008).
Mok, M. Y. et al. Antiphospholipid antibody profiles and their clinical associations in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 32, 622–628 (2005).
McLaurin, E. Y., Holliday, S. L., Williams, P. & Brey, R. L. Predictors of cognitive dysfunction in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Neurology 64, 297–303 (2005).
Tarr, T. et al. Analysis of risk factors for the development of thrombotic complications in antiphospholipid antibody positive lupus patients. Lupus 16, 39–45 (2007).
Hereng, T. et al. Influence of aspirin on the clinical outcomes of 103 anti-phospholipid antibodies-positive patients. Lupus 17, 11–15 (2008).
Tektonidou, M. G., Laskari, K., Panagiotakos, D. B. & Moutsopoulos, H. M. Risk factors for thrombosis and primary thrombosis prevention in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with or without antiphospholipid antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 61, 29–36 (2009).
Farzaneh-Far, A. et al. Relationship of antiphospholipid antibodies to cardiovascular manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 54, 3918–3925 (2006).
Gonzalez, L. A. et al. Time to neuropsychiatric damage occurrence in LUMINA (LXVI): a multi-ethnic lupus cohort. Lupus 18, 822–830 (2009).
Hanly, J. G. et al. Autoantibodies and neuropsychiatric events at the time of systemic lupus erythematosus diagnosis: results from an international inception cohort study. Arthritis Rheum. 58, 843–853 (2008).
Brooks, W. M., Jung, R. E., Ford, C. C., Greinel, E. J. & Sibbitt, W. L. Jr. Relationship between neurometabolite derangement and neurocognitive dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 26, 81–85 (1999).
Kozora, E. et al. Cognition, MRS neurometabolites, and MRI volumetrics in non-neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus: preliminary data. Cogn. Behav. Neurol. 18, 159–162 (2005).
Emmer, B. J. et al. Correlation of magnetization transfer ratio histogram parameters with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus criteria and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy: association of magnetization transfer ratio peak height with neuronal and cognitive dysfunction. Arthritis Rheum. 58, 1451–1457 (2008).
Driver, C. B. et al. Clinical validation of the watershed sign as a marker for neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 59, 332–337 (2008).
Sabbadini, M. G. et al. Central nervous system involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus patients without overt neuropsychiatric manifestations. Lupus 8, 11–19 (1999).
Waterloo, K. et al. Neuropsychological dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus is not associated with changes in cerebral blood flow. J. Neurol. 248, 595–602 (2001).
Kovacs, J. A., Urowitz, M. B., Gladman, D. D. & Zeman, R. The use of single photon emission computerized tomography in neuropsychiatric SLE: a pilot study. J. Rheumatol. 22, 1247–1253 (1995).
Zhang, X. et al. Diagnostic value of single-photon-emission computed tomography in severe central nervous system involvement of systemic lupus erythematosus: a case–control study. Arthritis Rheum. 53, 845–849 (2005).
Tokunaga, M. et al. Efficacy of rituximab (anti-CD20) for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus involving the central nervous system. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 66, 470–475 (2007).
DeGiorgio, L. A. et al. A subset of lupus anti-DNA antibodies cross-reacts with the NR2 glutamate receptor in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Med. 7, 1189–1193 (2001).
Kowal, C. et al. Cognition and immunity; antibody impairs memory. Immunity 21, 179–188 (2004).
Kowal, C. et al. Human lupus autoantibodies against NMDA receptors mediate cognitive impairment. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 19854–19859 (2006).
Isshi, K. & Hirohata, S. Differential roles of the anti-ribosomal P antibody and antineuronal antibody in the pathogenesis of central nervous system involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 41, 1819–1827 (1998).
Kang, E. H. et al. Flow cytometric assessment of anti-neuronal antibodies in central nervous system involvement of systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases. Lupus 17, 21–25 (2008).
Lapteva, L. et al. Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antibodies, cognitive dysfunction, and depression in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 54, 2505–2514 (2006).
Omdal, R. et al. Neuropsychiatric disturbances in SLE are associated with antibodies against NMDA receptors. Eur. J. Neurol. 12, 392–398 (2005).
Yoshio, T., Onda, K., Nara, H. & Minota, S. Association of IgG anti-NR2 glutamate receptor antibodies in cerebrospinal fluid with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 54, 675–678 (2006).
Zhang, X., Shu, H., Zhang, F., Tian, X. & Dong, Y. Cell-ELISA detection of antineuronal antibodies in central nervous system involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 66, 530–532 (2007).
Appenzeller, S., Carnevalle, A. D., Li, L. M., Costallat, L. T. & Cendes, F. Hippocampal atrophy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 65, 1585–1589 (2006).
Emmer, B. J., van der Grond, J., Steup-Beekman, G. M., Huizinga, T. W. & van Buchem, M. A. Selective involvement of the amygdala in systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS Med. 3, e499 (2006).
Karassa, F. B. et al. Accuracy of anti-ribosomal P protein antibody testing for the diagnosis of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus: an international meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 54, 312–324 (2006).
Matus, S. et al. Antiribosomal-P autoantibodies from psychiatric lupus target a novel neuronal surface protein causing calcium influx and apoptosis. J. Exp. Med. 204, 3221–3234 (2007).
Fragoso-Loyo, H. et al. Interleukin-6 and chemokines in the neuropsychiatric manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 56, 1242–1250 (2007).
Trysberg, E., Carlsten, H. & Tarkowski, A. Intrathecal cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus with central nervous system involvement. Lupus 9, 498–503 (2000).
Trysberg, E., Blennow, K., Zachrisson, O. & Tarkowski, A. Intrathecal levels of matrix metalloproteinases in systemic lupus erythematosus with central nervous system engagement. Arthritis Res. Ther. 6, R551–R556 (2004).
Bertsias, G. et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Report of a Task Force of the EULAR Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 67, 195–205 (2008).
West, S. G., Emlen, W., Wener, M. H. & Kotzin, B. L. Neuropsychiatric lupus erythematosus: a 10-year prospective study on the value of diagnostic tests. Am. J. Med. 99, 153–163 (1995).
Sibbitt, W. L. Jr, Schmidt, P. J., Hart, B. L. & Brooks, W. M. Fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) imaging in neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 30, 1983–1989 (2003).
Bosma, G. P., Huizinga, T. W., Mooijaart, S. P. & Van Buchem, M. A. Abnormal brain diffusivity in patients with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 24, 850–854 (2003).
Welsh, R. C., Rahbar, H., Foerster, B., Thurnher, M. & Sundgren, P. C. Brain diffusivity in patients with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus with new acute neurological symptoms. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 26, 541–551 (2007).
Hughes, M. et al. Diffusion tensor imaging in patients with acute onset of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective study of apparent diffusion coefficient, fractional anisotropy values, and eigenvalues in different regions of the brain. Acta Radiol. 48, 213–222 (2007).
Petri, M. et al. Brain magnetic resonance imaging in newly diagnosed systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 35, 2348–2354 (2008).
Sundgren, P. C. et al. MRI and 2D-CSI MR spectroscopy of the brain in the evaluation of patients with acute onset of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Neuroradiology 47, 576–585 (2005).
Roldan, C. A., Gelgand, E. A., Qualls, C. R. & Sibbitt, W. L. Jr. Valvular heart disease by transthoracic echocardiography is associated with focal brain injury and central neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Cardiology 108, 331–337 (2007).
Csépány, T. et al. MRI findings in central nervous system systemic lupus erythematosus are associated with immunoserological parameters and hypertension. J. Neurol. 250, 1348–1354 (2003).
Toubi, E., Khamashta, M. A., Panarra, A. & Hughes, G. R. Association of antiphospholipid antibodies with central nervous system disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am. J. Med. 99, 397–401 (1995).
Barile-Fabris, L. et al. Controlled clinical trial of IV cyclophosphamide versus IV methylprednisolone in severe neurological manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 64, 620–625 (2005).
Neuwelt, C. M. The role of plasmapheresis in the treatment of severe central nervous system neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Ther. Apher. Dial. 7, 173–182 (2003).
Bartolucci, P., Brechignac, S., Cohen, P., Le Guern, V. & Guillevin, L. Adjunctive plasma exchanges to treat neuropsychiatric lupus: a retrospective study on 10 patients. Lupus 16, 817–822 (2007).
Levy, Y. et al. A study of 20 SLE patients with intravenous immunoglobulin—clinical and serologic response. Lupus 8, 705–712 (1999).
Milstone, A. M., Meyers, K. & Elia, J. Treatment of acute neuropsychiatric lupus with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG): a case report and review of the literature. Clin. Rheumatol. 24, 394–397 (2005).
Vina, E. R., Fang, A. J., Wallace, D. J. & Weisman, M. H. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: prognosis and outcome. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 35, 175–184 (2005).
Khamashta, M. A. et al. The management of thrombosis in the antiphospholipid-antibody syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 332, 993–997 (1995).
Munoz-Rodriguez, F. J. et al. Clinical study and follow-up of 100 patients with the antiphospholipid syndrome. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 29, 182–190 (1999).
Tektonidou, M. G., Ioannidis, J. P., Boki, K. A., Vlachoyiannopoulos, P. G. & Moutsopoulos, H. M. Prognostic factors and clustering of serious clinical outcomes in antiphospholipid syndrome. QJM 93, 523–530 (2000).
Ruiz-Irastorza, G., Hunt, B. J. & Khamashta, M. A. A systematic review of secondary thromboprophylaxis in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 57, 1487–1495 (2007).
Cervera, R. et al. Chorea in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Clinical, radiologic, and immunologic characteristics of 50 patients from our clinics and the recent literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 76, 203–212 (1997).
D'Cruz, D. P. et al. Transverse myelitis as the first manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus or lupus-like disease: good functional outcome and relevance of antiphospholipid antibodies. J. Rheumatol. 31, 280–285 (2004).
Heinlein, A. C. & Gertner, E. Marked inflammation in catastrophic longitudinal myelitis associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 16, 823–826 (2007).
Mitsikostas, D. D., Sfikakis, P. P. & Goadsby, P. J. A meta-analysis for headache in systemic lupus erythematosus: the evidence and the myth. Brain 127, 1200–1209 (2004).
Whitelaw, D. A. & Spangenberg, J. J. An investigation in the possible effect of chronic headache on neuropsychological function in aCL-negative patients with SLE. Lupus 18, 613–617 (2009).
Ainiala, H. et al. Cerebral MRI abnormalities and their association with neuropsychiatric manifestations in SLE: a population-based study. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 34, 376–382 (2005).
Appenzeller, S., Rondina, J. M., Li, L. M., Costallat, L. T. & Cendes, F. Cerebral and corpus callosum atrophy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 52, 2783–2789 (2005).
Appenzeller, S. et al. Longitudinal analysis of gray and white matter loss in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Neuroimage 34, 694–701 (2007).
Denburg, S. D., Carbotte, R. M. & Denburg, J. A. Corticosteroids and neuropsychological functioning in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 37, 1311–1320 (1994).
Gonzalez-Duarte, A., Cantu-Brito, C. G., Ruano-Calderon, L. & Garcia-Ramos, G. Clinical description of seizures in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur. Neurol. 59, 320–323 (2008).
Kasitanon, N., Louthrenoo, W., Piyasirisilp, S., Sukitawu, W. & Wichainun, R. Neuropsychiatric manifestations in Thai patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 20, 179–185 (2002).
Esdaile, J. M. et al. Traditional Framingham risk factors fail to fully account for accelerated atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 44, 2331–2337 (2001).
Ward, M. M. Premature morbidity from cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 42, 338–346 (1999).
Krishnan, E. Stroke subtypes among young patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am. J. Med. 118, 1415 (2005).
Bessant, R. et al. Risk of coronary heart disease and stroke in a large British cohort of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43, 924–929 (2004).
Finazzi, G. et al. Natural history and risk factors for thrombosis in 360 patients with antiphospholipid antibodies: a four-year prospective study from the Italian Registry. Am. J. Med. 100, 530–536 (1996).
Cervera, R., Boffa, M.-C., Khamashta, M. & Hughes, G. The Euro-Phospholipid project: epidemiology of the antiphospholipid syndrome in Europe. Lupus 18, 889–893 (2009).
Birnbaum, J., Petri, M., Thompson, R., Izbudak, I. & Kerr, D. Distinct subtypes of myelitis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 60, 3378–3387 (2009).
Tseng, M. T. et al. Skin denervation and cutaneous vasculitis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Brain 129, 977–985 (2006).
Huynh, C. et al. Peripheral neuropathy in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 16, 164–168 (1999).
Omdal, R. et al. Peripheral neuropathy in systemic lupus erythematosus—a longitudinal study. Acta Neurol. Scand. 103, 386–391 (2001).
Bertsias, G. K. et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus with neuropsychiatric manifestations. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 68 (Suppl. 3), 163 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertsias, G., Boumpas, D. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of neuropsychiatric SLE manifestations. Nat Rev Rheumatol 6, 358–367 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2010.62
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2010.62
This article is cited by
-
Blood–brain barrier: emerging trends on transport models and new-age strategies for therapeutics intervention against neurological disorders
Molecular Brain (2022)
-
Converging evidence of impaired brain function in systemic lupus erythematosus: changes in perfusion dynamics and intrinsic functional connectivity
Neuroradiology (2022)
-
Comparison of systemic lupus erythematosus patients and healthy individuals in terms of autobiographical memory, mood, and cognitive emotion regulation
Cognitive Processing (2021)
-
Cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway and connective tissue diseases
Inflammopharmacology (2021)
-
Lupus autoantibodies act as positive allosteric modulators at GluN2A-containing NMDA receptors and impair spatial memory
Nature Communications (2020)