Abstract
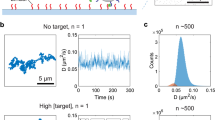
An electrochemical immunosensor for real-time determination of corticosteroids, a group of steroidal hormones, is reported. The sensor measures competitive binding of endogenous corticosteroid and a corticosteroid-peroxidase conjugate with antibodies, immobilized on a platinum electrode, by monitoring of peroxidase activity. The electrode is encased within a dialysate membrane, which separates the electrode environment from the sampled fluid, allowing corticosteroid to equilibrate across the membrane. This permits measurements to be made in vivo. The small size of the probe (350 μm D) allows implantation into tissue or circulatory systems. The electrode was viable for 200 to 400 sequential measurements and at least 48 h in vivo. Detection sensitivity is 0.2 to 0.6 μg/100 ml of cortisol or corticosterone. The results suggest the possibility of monitoring hormones in real-time within the blood or organ systems of conscious animals.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sapolsky, R.M. 1992. Stress, the aging brain, and mechanisms of neuron death. Bradford Books, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA.
Franek, M., Kolar, V., Granatova, M., and Nevorankova, Z. 1994. Monoclonal ELISA for 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid: characterisation of antibodies and assay optimisation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 42: 1369–1374.
Wills, M.R. 1983. Laboratory investigations of endocrine disorders. Butterworth,Woburn, MA.
Dzantiev, B.B. and Zherder, A.V. 1996. Electrochemical immunosensors for determination of the pesticides 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic and 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxy-acetic acids. Biosensors & Bioelectronics 11: 179–185.
Green, M.J. 1987. New approaches in electrochemical immunoassay, pp. 57–65 in Biosensors, fundamentals and applications. Turner, A., Karube I., and Wilson, G. (eds.). Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK.
Benveniste, H. 1989. Brain microdialysis. J. Neurochem. 52: 1667–1679.
Kendrick, K.M. 1990. Microdialysis measurement of in vivo neuropeptide release. J. Neurosci. Methods 34: 35–46.
Kendrick, K.M. 1989. Use of microdialysis in neuroendocrinology, pp. 182–205 in Methods in enzymology. Vol 168. Conn, P.M. (ed.). Academic Press, San Diego, CA.
Albery, W.J., Boutelle, M.G., and Galley, P.T. 1992. The dialysis electrode: a new method of in vivo monitoring. J. Chem. Soc. Comm. 12: 900–901.
Zilkha, E., Obrenovitch, T.P., Koshy, A., Kusakabe, H., and Bennetto, H.P. 1995. Extracellular glutamate: on line monitoring using microdialysis coupled to enzyme-amperometric analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 60: 1–9.
Brooke, S.M., Haas-Johnson, A., Kaplan, J.R., Manuck, S.B., and Sapolsky, R.M. 1994. Dexamethasone resistance among nonhuman primates associated with a selective decrease of glucocorticoid receptors in the hippocampus and a history of social instability. Neuroendocrinol. 60: 134–140.
Cook, C.J. and Jacobson, L.H. 1995. Salivary cortisol as an indicator of stress in sheep. N.Z. Vet. J. 43: 248.
Petrie, N.J., Mellor, D.J., Stafford, K.J., Bruce, R.A., and Ward, R.N. 1996. Cortisol responses of calves to two methods of tail docking used with or without local anaesthetic. New Zealand Veterinary Journal 44: 4–8.
Obrenovitch, T.P., Zilkha, E., and Urenjak, J. 1995. Intracerebral microdialysis: elec-trophysiological evidence of a critical pitfall. J. Neurochem. 64: 1884–1887.
Cook, C.J. 1997. Real-time extracellular measurement of neurotransmitters in conscious sheep. J. Neuroscience Methods. In press.
Goodrow, M., Harrison, R., and Hammock, B. 1990. Hapten synthesis, antibody development and competitive inhibition enzyme immunoassay for s-triazine herbicides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 35: 990–996.
Cook, C.J., Maasland, S.A., and Devine, C.E. 1996. Social behaviour in sheep relates to behaviour and neurotransmitter responses to nociceptive stimuli. Physiology and Behaviour 60: 741–751.
Cook, C.J., Devine, C.E., Gilbert, K.V., Smith, D.D., and Maasland, S.A. 1995. The effect of electrical head-only stun duration on electroencephalographic measured seizure and brain amino acid neurotransmitter release. Meat Sci. 40: 137–147.
Cook, C.J., Maasland, S.A., Devine, C.E., Gilbert, K.V., and Blackmore, O.K. 1996. Changes in the release of amino acid neurotransmitters in the brains of calves and sheep after head-only electrical stunning and throat cutting. Res. Vet. Sci. 60: 255–261.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cook, C. Real-time measurements of corticosteroids in conscious animals using an antibody-based electrode. Nat Biotechnol 15, 467–471 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0597-467
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0597-467