Abstract
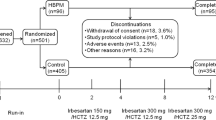
To report blood pressure control in the Hypertension in the Very Elderly Trial, a placebo-controlled trial of hypertensive (systolic blood pressure (SBP) 160–199 mm Hg, diastolic blood pressure (DBP) <110 mm Hg) participants over the age of 80 years, given treatment in three steps: indapamide slow release 1.5 mg alone, indapamide plus 2 mg perindopril and indapamide plus 4 mg perindopril. The difference in control between participants with combined systolic and diastolic hypertension (SDH, DBP⩾90 mm Hg) and those with isolated systolic hypertension (ISH, DBP<90 mm Hg) is determined together with the effects of increments in the treatment regimen. At 2 years, the active treatment lowered blood pressure by 16.5/6.9 mm Hg more than that on placebo in participants with SDH and by 19.3/4.8 mm Hg more in those with ISH. The 2-year falls in pressure on placebo alone were 13.2/8.5 mm Hg in SDH and 8.2/1.5 mm Hg in ISH participants. With full titration of active treatment, 62% of SDH participants achieved goal SBP (<150 mm Hg) by 2 years and 71% of those with ISH. The corresponding results for DBP control (<80 mm Hg) were 40 and 78%. The addition of active perindopril 2 mg roughly doubled the percentage controlled, as did increasing to 4 from 2 mg. Blood pressure control was good with ISH and better than with SDH. The fall in SBP accounted for the observed 30% reduction in strokes, but the 21% reduction in total mortality and 64% reduction in heart failure were greater than predicted.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Staessen JA, Wang J, Thijs L . Cardiovascular protection and blood pressure reduction: a meta-analysis. Lancet 2001; 358: 1305–1315.
Beckett NS, Peters R, Fletcher AE, Staessen JA, Liu LS, Dumitrascu D et al. Treatment of hypertension in patients 80 years of age or older. New Engl J Med 2008; 358: 1887–1898.
Bulpitt CJ, Fletcher A, Beckett NS, Coope J, Gil-Extremera B, Forette F et al. Hypertension in the Very Elderly Trial (HYVET) Protocol for the Main Trial. Drugs Aging 2001; 18 (3): 151–164.
Peters R, Beckett N, Forette F, Tuomilehto J, Clarke R, Ritchie C et al. Incident dementia and blood pressure lowering in the Hypertension in the Very Elderly Trial cognitive function assessment (HYVET-COG): a double-blind, placebo controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 2008; 8 (8): 683–689.
SHEP cooperative research group. Prevention of stroke by antihypertensive drug treatment in older persons with isolated systolic hypertension. Final results of the systolic hypertension in the elderly program (SHEP). JAMA 1991; 265: 3255–3264.
Staessen JA, Fagard R, Thijs L, Celis H, Arabidze GG, Birkenhager WH et al. Randomised double blind comparison of placebo and active treatment for older patients with isolated systolic hypertension. Lancet 1997; 350: 757–764.
Emeriau JP, Knauf H, Pujadas JO, Calvo-Gomez C, Abate G, leonetti G et al. A Comparison of Indapamide SR 1.5 mg with both amlodipine 5 mg and hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg in elderly hypertensive patients: a randomized double-blind controlled study. J Hypertens 2001; 19: 343–350.
Amery A, Birkenhager W, Brixko P, Bulpitt CJ, Clement D, Deruyttere M et al. Mortality and morbidity results from the European Working Party on High Blood Pressure in the Elderly Trial (EWPHE). Lancet 1985; 325: 1349–1354.
Dahlöf B, Lindholm LH, Hansson L, Scherstén T, Wester P-O . morbidity and mortality in the Swedish Trial in Old Patients with Hypertension (STOP-Hypertension). Lancet 1991; 338: 1281–1285.
Coope J, Warrender TS . Randomised trial of treatment of hypertension in elderly patients in primary care. BMJ 1986; 239: 1145.
MRC Working Party. Medical Research Council trial of treatment of hypertension in older adults: principal results. BMJ 1992; 304: 405–412.
Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration. Effects of different regimens to lower blood pressure on major cardiovascular events in older and younger adults: meta-analysis of randomised trials. Brit Med J 2008; 336: 1121–1123.
Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration. Additional information given on http://www.thegeorgeinstitute.org.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the British Heart Foundation and the Institut de Recherches Internationales Servier. The committee members and investigators for HYVET are fully described in NEJM 2008; 358: 1887–98.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
We have received honoraria, research grants, or both, from Servier. We have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organisation or entity in conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bulpitt, C., Beckett, N., Peters, R. et al. Blood pressure control in the Hypertension in the Very Elderly Trial (HYVET). J Hum Hypertens 26, 157–163 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2011.10
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2011.10
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Isoliert systolische Hypertonie beim älteren Menschen
CardioVasc (2018)
-
Insights into the clinical management of the syndrome of supine hypertension – orthostatic hypotension (SH-OH): The Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing (TILDA)
BMC Geriatrics (2013)
-
Olmesartan in the Treatment of Hypertension in Elderly Patients: a Review of the Primary Evidence
Drugs & Aging (2013)