Abstract
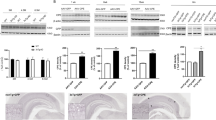
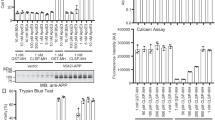
There is growing evidence that leptin is able to ameliorate Alzheimer’s disease (AD)-like pathologies, including brain amyloid-β (Aβ) burden. In order to improve the therapeutic potential for AD, we generated a lentivirus vector expressing leptin protein in a self-inactivating HIV-1 vector (HIV-leptin), and delivered this by intra-cerebroventricular administration to APP/PS1 transgenic model of AD. Three months after intra-cerebroventricular administration of HIV-leptin, brain Aβ accumulation was reduced. By electron microscopy, we found that APP/PS1 mice exhibited deficits in synaptic density, which were partially rescued by HIV-leptin treatment. Synaptic deficits in APP/PS1 mice correlated with an enhancement of caspase-3 expression, and a reduction in synaptophysin levels in synaptosome preparations. Notably, HIV-leptin therapy reverted these dysfunctions. Moreover, leptin modulated neurite outgrowth in primary neuronal cultures, and rescued them from Aβ42-induced toxicity. All the above changes suggest that leptin may affect multiple aspects of the synaptic status, and correlate with behavioral improvements. Our data suggest that leptin gene delivery has a therapeutic potential for Aβ-targeted treatment of mouse model of AD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hardy J, Selkoe DJ . The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 2002; 297: 353–356.
Selkoe DJ . Alzheimer's disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev 2001; 81: 741–766.
Coleman PD, Yao PJ . Synaptic slaughter in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 2003; 24: 1023–1027.
Shankar GM, Li S, Mehta TH, Garcia-Munoz A, Shepardson NE, Smith I et al. Amyloid-beta protein dimers isolated directly from Alzheimer's brains impair synaptic plasticity and memory. Nat Med 2008; 14: 837–842.
Hsieh H, Boehm J, Sato C, Iwatsubo T, Tomita T, Sisodia S et al. AMPAR removal underlies Abeta-induced synaptic depression and dendritic spine loss. Neuron 2006; 52: 831–843.
Snyder EM, Nong Y, Almeida CG, Paul S, Moran T, Choi EY et al. Regulation of NMDA receptor trafficking by amyloid-beta. Nat Neurosci 2005; 8: 1051–1058.
Spires-Jones TL, Meyer-Luehmann M, Osetek JD, Jones PB, Stern EA, Bacskai BJ et al. Impaired spine stability underlies plaque-related spine loss in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model. Am J Pathol 2007; 171: 1304–1311.
Spires TL, Meyer-Luehmann M, Stern EA, McLean PJ, Skoch J, Nguyen PT et al. Dendritic spine abnormalities in amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice demonstrated by gene transfer and intravital multiphoton microscopy. J Neurosci 2005; 25: 7278–7287.
Tsai J, Grutzendler J, Duff K, Gan WB . Fibrillar amyloid deposition leads to local synaptic abnormalities and breakage of neuronal branches. Nat Neurosci 2004; 7: 1181–1183.
Carro EM . Therapeutic approaches of leptin in Alzheimer's disease. Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov 2009; 4: 200–208.
Friedman JM . Leptin, leptin receptors, and the control of body weight. Nutr Rev 1998; 56: s38–s46; discussion s54-75.
Alvira-Botero X, Pérez-Gonzalez R, Spuch C, Vargas T, Antequera D, Garzón M et al. Megalin interacts with APP and the intracellular adapter protein FE65 in neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 2010; 45: 306–315.
Weng Z, Signore AP, Gao Y, Wang S, Zhang F, Hastings T et al. Leptin protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced dopaminergic cell death via mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 34479–34491.
Marwarha G, Dasari B, Prasanthi JR, Schommer J, Ghribi O et al. Leptin reduces the accumulation of Abeta and phosphorylated tau induced by 27-hydroxycholesterol in rabbit organotypic slices. J Alzheimers Dis 2010; 19: 1007–1019.
Fewlass DC, Noboa K, Pi-Sunyer FX, Johnston JM, Yan SD, Tezapsidis N et al. Obesity-related leptin regulates Alzheimer's Abeta. FASEB J 2004; 18: 1870–1878.
Greco SJ, Bryan KJ, Sarkar S, Zhu X, Smith MA, Ashford JW et al. Leptin reduces pathology and improves memory in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2010; 19: 1155–1167.
Sharma AN, Elased KM, Garrett TL, Lucot JB . Neurobehavioral deficits in db/db diabetic mice. Physiol Behav 2010; 101: 381–388.
Li XL, Aou S, Oomura Y, Hori N, Fukunaga K, Hori T et al. Impairment of long-term potentiation and spatial memory in leptin receptor-deficient rodents. Neuroscience 2002; 113: 607–615.
Dietrich MO, Spuch C, Antequera D, Rodal I, de Yébenes JG, Molina JA et al. Megalin mediates the transport of leptin across the blood-CSF barrier. Neurobiol Aging 2008; 29: 902–912.
Power DA, Noel J, Collins R, O'Neill D . Circulating leptin levels and weight loss in Alzheimer's disease patients. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2001; 12: 167–170.
Moolman DL, Vitolo OV, Vonsattel JP, Shelanski ML . Dendrite and dendritic spine alterations in Alzheimer models. J Neurocytol 2004; 33: 377–387.
Trinchese F, Liu S, Battaglia F, Walter S, Mathews PM, Arancio O et al. Progressive age-related development of Alzheimer-like pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Ann Neurol 2004; 55: 801–814.
Zhang H, Gong B, Liu S, Fa' M, Ninan I, Staniszewski A et al. Synaptic fatigue is more pronounced in the APP/PS1 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 2005; 2: 137–140.
Perez-Gonzalez R, Antequera D, Vargas T, Spuch C, Bolós M, Carro E et al. Leptin induces proliferation of neuronal progenitors and neuroprotection in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2011; 24 (Suppl 2): 17–25.
Lundberg C, Björklund T, Carlsson T, Jakobsson J, Hantraye P, Déglon N et al. Applications of lentiviral vectors for biology and gene therapy of neurological disorders. Curr Gene Ther 2008; 8: 461–473.
Stewart S, Cacucci F, Lever C . Which memory task for my mouse? A systematic review of spatial memory performance in the Tg2576 Alzheimer's mouse model. J Alzheimers Dis 2011; 26: 105–126.
Deacon RM, Rawlins JN . T-maze alternation in the rodent. Nat Protoc 2006; 1: 7–12.
Spuch C, Antequera D, Portero A, Orive G, Hernández RM, Molina JA et al. The effect of encapsulated VEGF-secreting cells on brain amyloid load and behavioral impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Biomaterials 2010; 31: 5608–5618.
O'Malley D, MacDonald N, Mizielinska S, Connolly CN, Irving AJ, Harvey J et al. Leptin promotes rapid dynamic changes in hippocampal dendritic morphology. Mol Cell Neurosci 2007; 35: 559–572.
Pinto S, Roseberry AG, Liu H, Diano S, Shanabrough M, Cai X et al. Rapid rewiring of arcuate nucleus feeding circuits by leptin. Science 2004; 304: 110–115.
Shanley LJ, Irving AJ, Harvey J . Leptin enhances NMDA receptor function and modulates hippocampal synaptic plasticity. J Neurosci 2001; 21: RC186.
Gylys KH, Fein JA, Yang F, Wiley DJ, Miller CA, Cole GM et al. Synaptic changes in Alzheimer's disease: increased amyloid-beta and gliosis in surviving terminals is accompanied by decreased PSD-95 fluorescence. Am J Pathol 2004; 165: 1809–1817.
D'Amelio M, Cavallucci V, Middei S, Marchetti C, Pacioni S, Ferri A et al. Caspase-3 triggers early synaptic dysfunction in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Nat Neurosci 2011; 14: 69–76.
Ivins KJ, Bui ET, Cotman CW . Beta-amyloid induces local neurite degeneration in cultured hippocampal neurons: evidence for neuritic apoptosis. Neurobiol Dis 1998; 5: 365–378.
Abad MA, Enguita M, DeGregorio-Rocasolano N, Ferrer I, Trullas R . Neuronal pentraxin 1 contributes to the neuronal damage evoked by amyloid-beta and is overexpressed in dystrophic neurites in Alzheimer's brain. J Neurosci 2006; 26: 12735–12747.
Zhang Y, Wang H, Pan H, Bao X, Li M, Jin J et al. Gene delivery into primary cerebral cortical neurons by lentiviral vector. Cell Biol Int 2006; 30: 777–783.
Carro E, Spuch C, Trejo JL, Antequera D, Torres-Aleman I . Choroid plexus megalin is involved in neuroprotection by serum insulin-like growth factor I. J Neurosci 2005; 25: 10884–10893.
Carro E, Trejo JL, Spuch C, Bohl D, Heard JM, Torres-Aleman I . Blockade of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor in the choroid plexus originates Alzheimer's-like neuropathology in rodents: new cues into the human disease? Neurobiol Aging 2006; 27: 1618–1631.
Antequera D, Vargas T, Ugalde C, Spuch C, Molina JA, Ferrer I et al. Cytoplasmic gelsolin increases mitochondrial activity and reduces Abeta burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis 2009; 36: 42–50.
Boghossian S, Ueno N, Dube MG, Kalra P, Kalra S . Leptin gene transfer in the hypothalamus enhances longevity in adult monogenic mutant mice in the absence of circulating leptin. Neurobiol Aging 2007; 28: 1594–1604.
Iwaniec UT, Boghossian S, Lapke PD, Turner RT, Kalra SP . Central leptin gene therapy corrects skeletal abnormalities in leptin-deficient ob/ob mice. Peptides 2007; 28: 1012–1019.
Koffie RM, Meyer-Luehmann M, Hashimoto T, Adams KW, Mielke ML, Garcia-Alloza M et al. Oligomeric amyloid beta associates with postsynaptic densities and correlates with excitatory synapse loss near senile plaques. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 4012–4017.
Lesne S, Koh MT, Kotilinek L, Kayed R, Glabe CG, Yang A et al. A specific amyloid-beta protein assembly in the brain impairs memory. Nature 2006; 440: 352–357.
Lesne S, Kotilinek L, Ashe KH . Plaque-bearing mice with reduced levels of oligomeric amyloid-beta assemblies have intact memory function. Neuroscience 2008; 151: 745–749.
Doherty GH, Beccano-Kelly D, Yan SD, Gunn-Moore FJ, Harvey J . Leptin prevents hippocampal synaptic disruption and neuronal cell death induced by amyloid beta. Neurobiol Aging 2013; 34: 226–237.
Walsh DM, Selkoe DJ . Oligomers on the brain: the emerging role of soluble protein aggregates in neurodegeneration. Protein Pept Lett 2004; 11: 213–228.
Klein WL . Abeta toxicity in Alzheimer's disease: globular oligomers (ADDLs) as new vaccine and drug targets. Neurochem Int 2002; 41: 345–352.
Ding Y, Qiao A, Wang Z, Goodwin JS, Lee ES, Block ML et al. Retinoic acid attenuates beta-amyloid deposition and rescues memory deficits in an Alzheimer's disease transgenic mouse model. J Neurosci 2008; 28: 11622–11634.
Torres M, Jimenez S, Sanchez-Varo R, Navarro V, Trujillo-Estrada L, Sanchez-Mejias E et al. Defective lysosomal proteolysis and axonal transport are early pathogenic events that worsen with age leading to increased APP metabolism and synaptic Abeta in transgenic APP/PS1 hippocampus. Mol Neurodegener 2012; 7: 59–59.
Calhoun ME, Wiederhold KH, Abramowski D, Phinney AL, Probst A, Sturchler-Pierrat C et al. Neuron loss in APP transgenic mice. Nature 1998; 395: 755–756.
Wan J, Fu AK, Ip FC, Ng HK, Hugon J, Page G et al. Tyk2/STAT3 signaling mediates beta-amyloid-induced neuronal cell death: implications in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci 2010; 30: 6873–6881.
Guo Z, Jiang H, Xu X, Duan W, Mattson MP . Leptin-mediated cell survival signaling in hippocampal neurons mediated by JAK STAT3 and mitochondrial stabilization. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 1754–1763.
Bouret SG, Draper SJ, Simerly RB . Trophic action of leptin on hypothalamic neurons that regulate feeding. Science 2004; 304: 108–110.
Farr SA, Banks WA, Morley JE . Effects of leptin on memory processing. Peptides 2006; 27: 1420–1425.
Gispen WH, Biessels GJ . Cognition and synaptic plasticity in diabetes mellitus. Trends Neurosci 2000; 23: 542–549.
Santarelli L, Saxe M, Gross C, Surget A, Battaglia F, Dulawa S et al. Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects of antidepressants. Science 2003; 301: 805–809.
Shors TJ, Miesegaes G, Beylin A, Zhao M, Rydel T, Gould E . Neurogenesis in the adult is involved in the formation of trace memories. Nature 2001; 410: 372–376.
Dewachter I, Reversé D, Caluwaerts N, Ris L, Kuipéri C, Van den Haute C et al. Neuronal deficiency of presenilin 1 inhibits amyloid plaque formation and corrects hippocampal long-term potentiation but not a cognitive defect of amyloid precursor protein [V717I] transgenic mice. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 3445–3453.
Arendt T, Zvegintseva HG, Leontovich TA . Dendritic changes in the basal nucleus of Meynert and in the diagonal band nucleus in Alzheimer's disease – a quantitative Golgi investigation. Neuroscience 1986; 19: 1265–1278.
Carro E, Trejo JL, Gomez-Isla T, LeRoith D, Torres-Aleman I . Serum insulin-like growth factor I regulates brain amyloid-beta levels. Nat Med 2002; 8: 1390–1397.
Peters A, Palay SL, de Webster H . The Fine Structure of the Nervous System Neurons and their supporting cells. Oxford University Press: New York, 1991.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Instituto de Salud Carlos III (PI06/0155, FIS2009/01636), Fundación Investigación Médica Mutua Madrileña (2008/93, 2010/0004) and CIBERNED (BESAD-P.2010). We thank Agnieszka Krzyzanowska, PhD, for the careful revision of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Gene Therapy website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pérez-González, R., Alvira-Botero, M., Robayo, O. et al. Leptin gene therapy attenuates neuronal damages evoked by amyloid-β and rescues memory deficits in APP/PS1 mice. Gene Ther 21, 298–308 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2013.85
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2013.85
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cellular and Molecular Regulation of Exercise—A Neuronal Perspective
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Role of sex and high-fat diet in metabolic and hypothalamic disturbances in the 3xTg-AD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2020)
-
MA-[D-Leu-4]-OB3, a Small Molecule Synthetic Peptide Leptin Mimetic, Normalizes Glucose Tolerance and Episodic Memory in a Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Cognitive Impairment
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics (2020)
-
Leptin: role over central nervous system in epilepsy
BMC Neuroscience (2018)
-
Disruption of leptin signalling in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Metabolic Brain Disease (2018)