Abstract
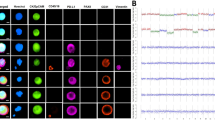
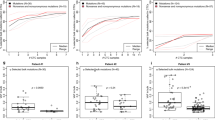
Detection of loss of heterozygosity (LOH) and DNA flow cytometry (FCM) were used to trace the origin of bilateral ovarian cancer from 16 patients. From each tumour the DNA index (DI) and LOH patterns for chromosomes 1, 3, 6, 11, 17, 18, 22 and X were determined with 36 microsatellite markers. Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded as well as frozen specimens were used. Flow cytometric cell sorting was used to enrich tumour cells for polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-driven LOH analysis. Analysis of the LOH data showed that in 12 of the 16 cases concordance was observed for all informative markers, namely retention of heterozygosity (ROH) or loss of identical alleles in both tumour samples. In four cases discordant LOH patterns were observed. In two cases the discordant LOH was found for one of the chromosomes tested while other LOH patterns clearly indicated a unifocal origin. This suggests limited clonal divergence. In the other two cases all LOH patterns were discordant, most likely indicating an independent origin. The number of chromosomes showing LOH ranged from 0 to 6. Comparison of DNA FCM and the LOH data showed that the latter technique has a higher sensitivity for the detection of a unifocal origin. In 14/16 cases evidence was found for a unifocal origin, while in two cases clonal divergence was found at LOH level and in two other cases clonal divergence at DNA ploidy level. In 12 cases the complete observed allelotype had developed before the formation of metastases, including the two cases showing a large DNA ploidy difference.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abeln, E., Kuipers-Dijkshoorn, N., Berns, E. et al. Molecular genetic evidence for unifocal origin of advanced epithelial ovarian cancer and for minor clonal divergence. Br J Cancer 72, 1330–1336 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1995.510
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1995.510
This article is cited by
-
Genomic and proteomic characterization of YDOV-157, a newly established human epithelial ovarian cancer cell line
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2008)