Abstract
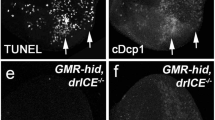
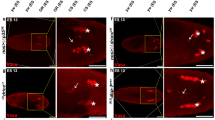
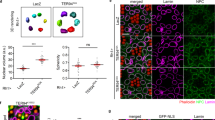
Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) provide a critical barrier to inappropriate apoptotic cell death through direct binding and inhibition of caspases. We demonstrate that degradation of IAPs is an important mechanism for the initiation of apoptosis in vivo. Drosophila Morgue, a ubiquitin conjugase-related protein, promotes DIAP1 down-regulation in the developing retina to permit selective programmed cell death. Morgue complexes with DIAP1 in vitro and mediates DIAP1 degradation in a manner dependent on the Morgue UBC domain. Reaper (Rpr) and Grim, but not Hid, also promote the degradation of DIAP1 in vivo, suggesting that these proteins promote cell death through different mechanisms.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Vaux, D. L. & Korsmeyer, S. J. Cell death in development. Cell 96, 245–254 (1999).
Mori, C. et al. Programmed cell death in the interdigital tissue of the fetal mouse limb is apoptosis with DNA fragmentation. Anat. Rec. 242, 103–110 (1995).
So, K. F., Campbell, G. & Lieberman, A. R. Development of the mammalian retinogeniculate pathway: target finding, transient synapses and binocular segregation. J. Exp. Biol. 153, 85–104 (1990).
Wolff, T. & Ready, D. F. Cell death in normal and rough eye mutants of Drosophila. Development 113, 825–839 (1991).
Cagan, R. L. & Ready, D. F. The emergence of order in the Drosophila pupal retina. Dev. Biol. 136, 346–362 (1989).
Thornberry, N. A. & Lazebnik, Y. Caspases: enemies within. Science 281, 1312–1316 (1998).
Salvesen, G. S. & Dixit, V. M. Caspase activation: the induced-proximity model. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 10964–10967 (1999).
Deveraux, Q. L. & Reed, J. L. IAP family proteins – suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 13, 239–252 (1999).
Hay, B. A. Understanding IAP function and regulation: a view from Drosophila. Cell Death Differ. 7, 1045–1056 (2000).
Yang, Y., Fang, S., Jensen, J. P., Weissman, A. M. & Ashwell, J. D. Ubiquitin protein ligase activity of IAPs and their degradation in proteasomes in response to apoptotic stimuli. Science 288, 874–877 (2000).
Suzuki, Y., Nakabayashi, Y. & Takahashi, R. Ubiquitin-protein ligase activity of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein promotes proteasomal degradation of caspase-3 and enhances its anti-apoptotic effect in Fas-induced cell death. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 8662–8667 (2001).
Huang, H. et al. The inhibitor of apoptosis, cIAP2, functions as a ubiquitin-protein ligase and promotes in vitro monoubiquitination of caspases 3 and 7. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 26661–26664 (2000).
Hawkins, C. J. et al. The Drosophila caspase DRONC cleaves following glutamate or aspartate and is regulated by DIAP1, HID, and GRIM. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 27084–27093 (2000).
Meier, P., Silke, J., Leevers, S. J. & Evan, G. I. The Drosophila caspase DRONC is regulated by DIAP1. EMBO J. 19, 598–611 (2000).
Hawkins, C. J., Wang, S. L. & Hay, B. A. A cloning method to identify caspases and their regulators in yeast: identification of Drosophila IAP1 as an inhibitor of the Drosophila caspase DCP-1. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 2885–2890 (1999).
Kaiser, W. J., Vucic, D. & Miller, L. K. The Drosophila inhibitor of apoptosis D-IAP1 suppresses cell death induced by the caspase drICE. FEBS Lett. 440, 243–248 (1998).
Wang, S. L., Hawkins, C. J., Yoo, S. J., Muller, H. A. & Hay, B. A. The Drosophila caspase inhibitor DIAP1 is essential for cell survival and is negatively regulated by HID. Cell 98, 453–463 (1999).
Hay, B. A., Wassarman, D. A. & Rubin, G. M. Drosophila homologs of baculovirus inhibitor of apoptosis proteins function to block cell death. Cell 83, 1253–1262 (1995).
Goyal, L., McCall, K., Agapite, J., Hartwieg, E. & Steller, H. Induction of apoptosis by Drosophila reaper, hid and grim through inhibition of IAP function. EMBO J. 19, 589–597 (2000).
Lisi, S., Mazzon, I. & White, K. Diverse domains of THREAD/DIAP1 are required to inhibit apoptosis induced by REAPER and HID in Drosophila. Genetics 154, 669–678 (2000).
Vucic, D., Kaiser, W. J., Harvey, A. J. & Miller, L. K. Inhibition of reaper-induced apoptosis by interaction with inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 10183–10188 (1997).
Vucic, D., Seshagiri, S. & Miller, L. K. Characterization of reaper- and FADD-induced apoptosis in a lepidopteran cell line. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17, 667–676 (1997).
Rusconi, J. C., Hays, R. & Cagan, R. L. Programmed cell death and patterning in Drosophila. Cell Death Differ. 7, 1063–1070 (2000).
Tanenbaum, S., Gorski, S., Rusconi, J. & Cagan, R. L. A screen for dominant modifiers of the irreC-rst cell death phenotype in the developing Drosophila retina. Genetics 156, 205–217 (2000).
Rodriguez, A. et al. Dark is a Drosophila homologue of Apaf-1/CED-4 and functions in an evolutionarily conserved death pathway. Nature Cell Biol. 1, 272–279 (1999).
Song, Z., McCall, K. & Steller, H. DCP-1, a Drosophila cell death protease essential for development. Science 275, 536–540 (1997).
Rorth, P. A modular misexpression screen in Drosophila detecting tissue-specific phenotypes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 12418–12422 (1996).
Jones, D., Crowe, E., Stevens, T. A. & Candido, P. M. Functional and phylogenetic analysis of the ubiquitylation system in Caenorhabditis elegans: ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, ubiquitin-activating enzymes, and ubiquitin-like proteins. Gemone Biol. 3, research002.1–research002.15 (2001).
Thomson, T. et al. Fusion of the human gene for the polyubiquitination coeffector UEV1 with Kua, a newly identified gene. Genome Research 10, 1743–1756 (2000).
Hofmann, R. & Pickart, C. M. Noncanonical MMS2-encoded ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme functions in assembly of novel polyubiquitin chains for DNA repair. Cell 96, 645–653 (1999).
Rebay, I. & Rubin, G. M. Yan functions as a general inhibitor of differentiation and is negatively regulated by activation of the Ras1/MAPK pathway. Cell 81, 857–866 (1995).
Hsu, T., McRackan, D., Vincent, T. S. & Gert de Couet, H. Drosophila Pin1 prolyl isomerase Dodo is a MAP kinase signal responder during oogenesis. Nature Cell Biol. 3, 538–543 (2001).
VanDemark, A. P., Hofman, R. M., Tsui, C., Pickart, C. M. & Wolberger, C. Molecular insights into polyubiquitin chain assembly: crystal structure of the Mms2/Ubc13 heterodimer. Cell 105, 711–720 (2001).
Holley, C.L., Olson, M.R., Colon-Ramos, D.A. & Kornbluth S. Reaper eliminates IAP proteins through stimulated IAP degradation and generalized translational inhibition. Nature Cell Biol. DOI: 10.1038/ncb798.
Ryoo, H.D., Bergmann, A., Gonen, H., Ciechanover, A. & Steller, H. Regulation of Drosophila IAP1 degradation and apoptosis by reaper and ubcD1. Nature Cell Biol. DOI: 10.1038/ncb795.
Wing et al. Drosophila Morgue is a novel F box/ubiquitin conjugase domain protein important for grim-reaper-mediated apoptosis. Nature Cell Biol. DOI: 10.1038/ncb800.
Yoo et al. Hid, Rpr and Grim negatively regulate DIAP1 levels through distinct mechanisms. Nature Cell Biol. DOI: 10.1038/ncb793.
Wilson et al. The DIAP1 RING finger mediates ubiquitination of Dronc and is indispensible for regulating apoptosis. Nature Cell Biol. DOI: 10.1038/ncb799.
Acknowledgements
We would like to especially thank J. Nambu for sharing data on the EP alleles and for naming the locus. The rabbit anti-DIAP1 antibody and HA–DIAP1 construct were a generous gift of K. White. This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health grant R01EY11495; R. Hays received support from NIH postdoctoral fellowship EY13507.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hays, R., Wickline, L. & Cagan, R. Morgue mediates apoptosis in the Drosophila melanogaster retina by promoting degradation of DIAP1. Nat Cell Biol 4, 425–431 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb794
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb794
This article is cited by
-
Thin is required for cell death in the Drosophila abdominal muscles by targeting DIAP1
Cell Death & Disease (2018)
-
The initiator caspase Dronc is subject of enhanced autophagy upon proteasome impairment in Drosophila
Cell Death & Differentiation (2016)
-
Genetic characterization of two gain-of-function alleles of the effector caspase DrICE in Drosophila
Cell Death & Differentiation (2016)
-
Suppression of induced but not developmental apoptosis in Drosophila by Ayurvedic Amalaki Rasayana and Rasa-Sindoor
Journal of Biosciences (2015)
-
The deubiquitinating enzyme DUBAI stabilizes DIAP1 to suppress Drosophila apoptosis
Cell Death & Differentiation (2014)