Abstract
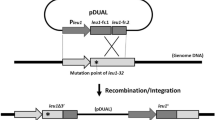
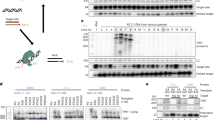
RECOMBINATION between a diffusible reverse transcript and its homologous chromosomal allele has been proposed as a mechanism for the precise removal of introns from DNA and gene conversion of dispersed repeated sequences1,2. We have reported that RNA-mediated recombination occurs in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae3. This recombination requires expression of the retrotransposon Ty, and results in intron loss from a plasmid-borne marker gene and the formation of pseudogenes. Because the pseudogenes are embedded in Ty sequences, chromosomal insertion could have been mediated by Ty integrase or by homologous recombination with endogenous Ty sequences. The structure of the chromosomal recombinants and the fact that plasmid and chromosomal recombination can have different requirements demanded a direct demonstration of RNA-mediated gene conversion of a chromosomal allele. Here we report the first demonstration, to our knowledge, of recombination between a reverse transcript and its chromosomal homologue and describe an assay that specifically detects this novel recombination pathway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baltimore, D. Cell 40, 481–482 (1985).
Fink, G. R. Cell 49, 5–6 (1987).
Derr, L. K., Strathern, J. N. & Garfinkel, D. J. Cell 67, 355–364 (1991).
Malone, R. E. et al. Curr. Genet 14, 211–223 (1988).
McGill, C. M. et al. Curr. Genet. 18, 29–39 (1990).
Linial, M. Cell 49, 93–102 (1987).
Dornburg, R. & Temin, H. M. Molec. cell. Biol. 8, 2328–2334 (1988).
Melamed, C., Nevo, Y. & Kupiec, M. Molec. cell. Biol. 4, 1613–1620 (1992).
Lea, D. E. & Coulson, C. A. J. Genet. 49, 264–285 (1949).
Boeke, J. D., Lacroute, F. & Fink, G. R. Molec. gen. Genet. 197, 345–346 (1984).
Alani, E., Cao, L. & Kleckner, N. Genetics 116, 541–545 (1987).
Struhl, K. Nucleic Acids Res. 13, 8587–8601 (1985).
Oliver, S. G. et al. Nature 357, 38–46 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Derr, L., Strathern, J. A role for reverse transcripts in gene conversion. Nature 361, 170–173 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/361170a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/361170a0
This article is cited by
-
The non-LTR retrotransposons of Entamoeba histolytica: genomic organization and biology
Molecular Genetics and Genomics (2022)
-
The complete mitochondrial genome of Taxus cuspidata (Taxaceae): eight protein-coding genes have transferred to the nuclear genome
BMC Evolutionary Biology (2020)
-
Patterns and Rates of Plastid rps12 Gene Evolution Inferred in a Phylogenetic Context using Plastomic Data of Ferns
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Damage-induced lncRNAs control the DNA damage response through interaction with DDRNAs at individual double-strand breaks
Nature Cell Biology (2017)
-
Evaluation of the mechanisms of intron loss and gain in the social amoebae Dictyostelium
BMC Evolutionary Biology (2015)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.