Abstract
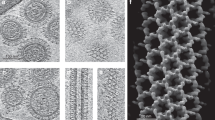
THE nature of intramembranous particles has recently been discussed in relation to the mode of freeze fracturing1,2. It has been argued that particles that do not show complementarity (complementary pits on the opposite fracture face) are a reflection of protein penetrating the membrane. The protein giving rise to an intramembraneous particle is plastically deformed during the fracturing procedure and is probably pulled out to one of the two fracture faces. Moreover we have argued that particles showing complementarity (pits) are possibly of lipidic origin. This latter hypothesis was mainly based on the determination of the nature of the intramembranous particles of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. These complementary particles were shown to be determined by lipo-polysaccharide3,4. We show here that lipid can by itself form intramembranous particles showing complementarity and that these particles may be inverted micelles of phospholipid sandwiched between lipid monolayers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vergergaert, P. H. J. T. & Verkleij, A. J. Experienta 34, 354–355 (1978).
Verkleij, A. J. & Ververgaert, P. H. J. T. Biochim. biophys. Acta 515, 303–327 (1978).
Verkleij, A. J., van Alphen, L., Bijvelt, J. & Lugtenberg, B. Biochim. biophys. Acta 426, 581–586 (1976).
van Alphen, L., Verkleij, A. J., Leunissen-Bijvelt, J. & Lugtenberg, B. J. Bact. 134, 1089–1098 (1978).
Reiss-Husson, F. J. molec. Biol. 25, 363–374 (1967).
Rand, R. P. & Sengupta, S. Biochim. biophys. Acta 255, 484–492 (1972).
Cullis, P. R., Verkleij, A. J. & Ververgaert, P. H. J. T. Biochim. biophys. Acta 513, 11–20 (1978).
Deamer, D. W. & Bangham, A. D. Biochim. biophys. Acta 433, 629–634 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
VERKLEIJ, A., MOMBERS, C., LEUNISSEN-BIJVELT, J. et al. Lipidic intramembranous particles. Nature 279, 162–163 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/279162a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/279162a0
This article is cited by
-
A current assessment of photosystem II structure
Bioscience Reports (1996)
-
Cubic phases in surfactant and surfactant-like lipid systems
Colloid & Polymer Science (1990)
-
Polymorphic regulation of membrane lipid composition
Nature (1987)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.