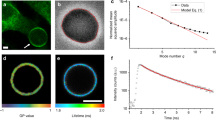
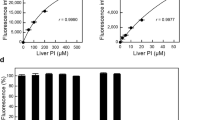
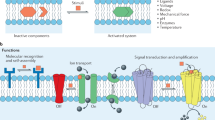
Abstract
To delineate some of the relationships between membrane composition and the functional states of mammalian cells, we are exploring the possibility of producing controlled modifications in the plasma membrane of cultured cells, using artificially generated lipid vesicles1–3. Although other groups have reported the use of lipid dispersions for producing cellular modifications4–10, the underlying molecular mechanisms by which these effects are produced have not been determined. We present here preliminary findings on the mechanism of interaction of chemically and physically well-defined phospholipid vesicles with cultured mammalian cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saunders, L., Perrin, J., and Gammack, D., J. Pharm. Pharmac., 14, 567–572 (1962).
Bangham, A. D., Standish, M. M., and Watkins, J. C., J. molec. Biol., 13, 238–252 (1965).
Huang, C., Biochemistry, 8, 344–352 (1969).
Rahman, Y., Rosenthal, M. W., and Cerny, E. A., Science, 180, 300–302 (1973).
Magee, W. E., and Miller, O. V., Nature, 235, 339–341 (1972).
Gregoriadis, G., FEBS Lett., 36, 292–296 (1973).
Gregoriadis, G., and Buckland, R. A., Nature, 244, 170–172 (1973).
Papahadjopoulos, D., Poste, G., and Schaeffer, B. E., Biochim. biophys. Acta, 323, 23–42 (1973).
Grant, C. W. M., and McConnell, H. M., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci U.S.A., 70, 1238–1240 (1973).
Inbar, M., and Shinitzky, M., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 71, 2128–2130 (1974).
Gey, G. G., Am. J. Cancer., 27, 45–68 (1936).
Danon, D., Goldstein, L., Marikovsky, Y., and Skutelsky, E., J. Ultrastr. Res., 38, 500–510 (1972).
Wirtz, K. W. A., and Zilversmit, D. B., J. biol. Chem., 243, 3596–3602 (1968).
Demel, R. A., Wirtz, K. W. A., Kamp, H. H., Geurts van Kessel, W. S. M., and van Deenen, L. L. M., Nature new biol., 246, 102–105 (1973).
Papahadjopoulos, D., Mayhew, E., Poste, G., Smith, S., and Vail, W. J., Nature, 252, 163–166 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
PAGANO, R., HUANG, L. & WEY, C. Interaction of phospholipid vesicles with cultured mammalian cells. Nature 252, 166–167 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1038/252166a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/252166a0
This article is cited by
-
Fusion of liposome membranes by then-alkyl bromides
The Journal of Membrane Biology (1980)
-
Transport of lipids through water as exchange mechanism between two liposome populations
Biophysics of Structure and Mechanism (1978)
-
Hybridization by cosonication of pigeon erythrocyte membrane with exogenous lipid vesicles
The Journal of Membrane Biology (1978)
-
Preparation of liposomes with immunological specificity
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine (1977)
-
Pharmacological effects of phosphatidylserine liposomes
Nature (1976)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.