Abstract
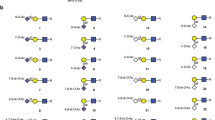
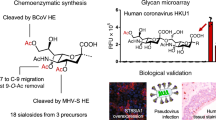
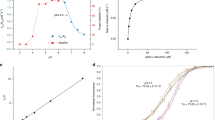
AN interesting field of biochemical research was opened when Blix1 isolated from bovine submaxillary gland mucin a crystalline reducing acid, named sialic acid2. Its most probable composition is given as C13H23NO11 or C13H21NO10.H2O. Bovine sialic acid contains an N-acetyl and an O-acetyl group, one primary alcohol group and a total of five hydroxyl groups3. Consumption of free iodine, when sialic acid is titrated with hypoiodite, and of one molecule of hydrogen, when the acid is submitted to treatment with sodium borohydride, is interpreted by Blix et al. 3 as indicating the presence of a free aldehyde group. The liberation of less than one mole carbon monoxide per mole sialic acid upon treatment with sulphuric acid would suggest the presence of an α-hydroxy group3.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blix, G., Z. physiol. Chem., 240, 43 (1936).
Blix, G., Svennerholm, L., and Werner, I., Acta Chem. Scand., 6, 358 (1952).
Blix, G., Lindberg, E., Odin, L., and Werner, I., Nature, 175, 340 (1955).
Klenk, E., Z. physiol. Chem., 268, 50 (1941).
Klenk, E., and Lauenstein, K., Z. physiol. Chem., 291, 147 (1952).
Gottschalk, A., and Lind, P. E., Nature, 164, 232 (1949).
Gottschalk, A., Nature, 167, 845 (1951).
Odin, L., Nature, 170, 663 (1952).
Gottschalk, A., Nature, 174, 652 (1954).
Gottschalk, A., Biochem. J. [61, 298 (1955)].
Hiyama, N., Tôhoku J. Exp. Med., 51, 317 (1949).
Klenk, E., and Faillard, H., Z. physiol. Chem., 298, 230 (1954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
GOTTSCHALK, A. Structural Relationship between Sialic Acid, Neuraminic Acid and 2-Carboxy-Pyrrole. Nature 176, 881–882 (1955). https://doi.org/10.1038/176881a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/176881a0
This article is cited by
-
Alkali-labile gangliosides
Glycoconjugate Journal (2023)
-
GM1 Ganglioside: Past Studies and Future Potential
Molecular Neurobiology (2016)
-
A reflection on the early history of glycosphingolipids
Glycoconjugate Journal (1996)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.