Abstract
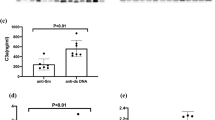
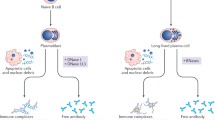
Anti-C1q antibodies were first identified as low-molecular weight C1q precipitins in the sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) over 30 years ago. Anti-C1q antibodies are strongly associated with the development of proliferative lupus nephritis, so much so that active renal inflammation in SLE patients is very unlikely if these antibodies are not present. These antibodies seem to develop through mechanisms that are similar to those of other SLE autoantibodies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sellar, G. C., Blake, D. J. & Reid, K. B. Characterization and organization of the genes encoding the A-, B- and C-chains of human complement subcomponent C1q. The complete derived amino acid sequence of human C1q. Biochem. J. 274 (Pt 2), 481–490 (1991).
Sim, R. B. & Reid, K. B. C1: molecular interactions with activating systems. Immunol. Today 12, 307–311 (1991).
Cooper, N. R. The classical complement pathway: activation and regulation of the first complement component. Adv. Immunol. 37, 151–216 (1985).
Feinstein, A., Richardson, N. & Taussig, M. J. Immunoglobulin flexibility in complement activation. Immunol. Today 7, 169–174 (1986).
Agnello, V., Koffler, D., Eisenberg, J. W., Winchester, R. J. & Kundel, H. G. C1g precipitins in the sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and other hypocomplementemic states: characterization of high and low molecular weight types. J. Exp. Med. 134, 228–241 (1971).
Antes, U., Heinz, H. P. & Loos, M. Evidence for the presence of autoantibodies to the collagen-like portion of C1q in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 31, 457–464 (1988).
Schaller, M., Bigler, C., Danner, D., Ditzel, H. J. & Trendelenburg, M. Autoantibodies against C1q in systemic lupus erythematosus are antigen-driven. J. Immunol. 183, 8225–8231 (2009).
Pickering, M. C., Botto, M., Taylor, P. R., Lachmann, P. J. & Walport, M. J. Systemic lupus erythematosus, complement deficiency, and apoptosis. Adv. Immunol. 76, 227–324 (2000).
Casciola-Rosen, L. A., Anhalt, G. & Rosen, A. Autoantigens targeted in systemic lupus erythematosus are clustered in two populations of surface structures on apoptotic keratinocytes. J. Exp. Med. 179, 1317–1330 (1994).
Korb, L. C. & Ahearn, J. M. C1q binds directly and specifically to surface blebs of apoptotic human keratinocytes: complement deficiency and systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. J. Immunol. 158, 4525–4528 (1997).
Bigler, C., Schaller, M., Perahud, I., Osthoff, M. & Trendelenburg, M. Autoantibodies against complement C1q specifically target C1q bound on early apoptotic cells. J. Immunol. 183, 3512–3521 (2009).
Hunnangkul, S. et al. Familial clustering of non-nuclear autoantibodies and C3 and C4 complement components in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 58, 1116–1124 (2008).
Trendelenburg, M. Antibodies against C1q in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Springer Semin. Immunopathol. 27, 276–285 (2005).
Kallenberg, C. G. Anti-C1q autoantibodies. Autoimmun. Rev. 7, 612–615 (2008).
Siegert, C. E., Daha, M. R., Halma, C., van der Voort, E. A. & Breedveld, F. C. IgG and IgA autoantibodies to C1q in systemic and renal diseases. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 10, 19–23 (1992).
Wisnieski, J. J. & Naff, G. B. Serum IgG antibodies to C1q in hypocomplementemic urticarial vasculitis syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 32, 1119–1127 (1989).
Prada, A. E. & Strife, C. F. IgG subclass restriction of autoantibody to solid-phase C1q in membranoproliferative and lupus glomerulonephritis. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 63, 84–88 (1992).
Trendelenburg, M. et al. High prevalence of anti-C1q antibodies in biopsy-proven active lupus nephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant 21, 3115–3121 (2006).
Trendelenburg, M., Marfurt, J., Gerber, I., Tyndall, A. & Schifferli, J. A. Lack of occurrence of severe lupus nephritis among anti-C1q autoantibody-negative patients. Arthritis Rheum. 42, 187–188 (1999).
Siegert, C., Daha, M., Westedt, M. L., van der Voort, E. & Breedveld, F. IgG autoantibodies against C1q are correlated with nephritis, hypocomplementemia, and dsDNA antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 18, 230–234 (1991).
Coremans, I. E. et al. Changes in antibodies to C1q predict renal relapses in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 26, 595–601 (1995).
Moroni, G. et al. Anti-C1q antibodies may help in diagnosing a renal flare in lupus nephritis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 37, 490–498 (2001).
Siegert, C. E. et al. Predictive value of IgG autoantibodies against C1q for nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 52, 851–856 (1993).
Sinico, R. A. et al. Anti-C1q autoantibodies in lupus nephritis. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1173, 47–51 (2009).
Mannik, M. & Wener, M. H. Deposition of antibodies to the collagen-like region of C1q in renal glomeruli of patients with proliferative lupus glomerulonephritis. Arthritis Rheum. 40, 1504–1511 (1997).
Mannik, M., Merrill, C. E., Stamps, L. D. & Wener, M. H. Multiple autoantibodies form the glomerular immune deposits in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 30, 1495–1504 (2003).
Trouw, L. A. et al. Anti-C1q autoantibodies deposit in glomeruli but are only pathogenic in combination with glomerular C1q-containing immune complexes. J. Clin. Invest. 114, 679–688 (2004).
Holers, V. M. Anti-C1q autoantibodies amplify pathogenic complement activation in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Clin. Invest. 114, 616–619 (2004).
Flierman, R. & Daha, M. R. Pathogenic role of anti-C1q autoantibodies in the development of lupus nephritis—a hypothesis. Mol. Immunol. 44, 133–138 (2007).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge The Wellcome Trust, which funds the research of M. Botto and M. C. Pickering.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pickering, M., Botto, M. Are anti-C1q antibodies different from other SLE autoantibodies?. Nat Rev Rheumatol 6, 490–493 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2010.56
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2010.56
This article is cited by
-
Anti-C1q-Antikörper als Marker für die proliferative Lupusnephritis
Der Nephrologe (2018)
-
Anti-C1q autoantibodies as markers of renal involvement in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus
Pediatric Nephrology (2017)
-
PTX3, Anti-PTX3, and Anti-C1q Autoantibodies in Lupus Glomerulonephritis
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2015)
-
Standardization of autoantibody testing: a paradigm for serology in rheumatic diseases
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2014)
-
Histopathology of Lupus Nephritis
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2011)