Abstract
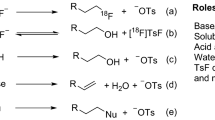
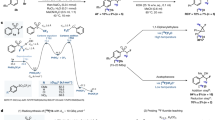
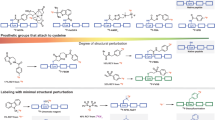
Herein we present a general protocol for the functionalization of biomolecules with an organotrifluoroborate moiety so that they can be radiolabeled with aqueous 18F fluoride (18F−) and used for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging. Among the β+-emitting radionuclides, fluorine-18 (18F) is the isotope of choice for PET, and it is produced, on-demand, in many hospitals worldwide. Organotrifluoroborates can be 18F-labeled in one step in aqueous conditions via 18F–19F isotope exchange. This protocol features a recently designed ammoniomethyltrifluoroborate, and it describes the following: (i) a synthetic strategy that affords modular synthesis of radiolabeling precursors via a copper-catalyzed 'click' reaction; and (ii) a one-step 18F-labeling method that obviates the need for HPLC purification. Within 30 min, 18F-labeled PET imaging probes, such as peptides, can be synthesized in good chemical and radiochemical purity (>98%), satisfactory radiochemical yield of 20–35% (n > 20, non-decay corrected) and high specific activity of 40–111 GBq/μmol (1.1–3.0 Ci/μmol). The entire procedure, including the precursor preparation and 18F radiolabeling, takes 7–10 d.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tarkin, J.M., Joshi, F.R. & Rudd, J.H.F. PET imaging of inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 11, 443–457 (2014).
Cai, L.S., Lu, S.Y. & Pike, V.W. Chemistry with F-18 fluoride ion. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 17, 2853–2873 (2008).
Tsien, R.Y. Imagining imaging's future. Nat. Cell Biol. 4, S16–S21 (2003).
Garrison, J.C. et al. In vivo evaluation and small-animal PET/CT of a prostate cancer mouse model using Cu-64 bombesin analogs: Side-by-side comparison of the CB-TE2A and DOTA chelation systems. J. Nucl. Med. 48, 1327–1337 (2007).
Jacobson, O., Kiesewetter, D.O. & Chen, X. Fluorine-18 radiochemistry, labeling strategies and synthetic routes. Bioconjug. Chem. 26, 1–18 (2014).
Brabez, N. et al. Synthesis and evaluation of cholecystokinin trimers: a multivalent approach to pancreatic cancer detection and treatment. Biorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 23, 2422–2425 (2013).
Liu, Z. et al. Kit-like 18F-labeling of RGD-19F-arytrifluroborate in high yield and at extraordinarily high specific activity with preliminary in vivo tumor imaging. Nucl. Med. Biol. 40, 841–849 (2013).
Wangler, C. et al. One-step F-18 labeling of peptides for positron emission tomography imaging using the SiFA methodology. Nat. Protoc. 7, 1946–1955 (2012).
Lee, E. et al. A fluoride-derived electrophilic late-stage fluorination reagent for PET imaging. Science 334, 639–642 (2011).
Huiban, M. et al. A broadly applicable [18F]trifluoromethylation of aryl and heteroaryl iodides for PET imaging. Nat. Chem. 5, 941–944 (2013).
McBride, W.J., D'Souza, C.A., Karacay, H., Sharkey, R.M. & Goldenberg, D.M. New lyophilized kit for rapid radiofluorination of peptides. Bioconjug. Chem. 23, 538–547 (2012).
Jacobson, O. et al. Rapid and simple one-step F-18 labeling of peptides. Bionconj. Chem. 22, 422–428 (2011).
Pascali, G. et al. Optimization of nucleophilic 18F radiofluorinations using a microfluidic reaction approach. Nat. Protoc. 9, 2017–2029 (2014).
Richarz, R. et al. Neither azeotropic drying, nor base nor other additives: a minimalist approach to 18F labeling. Org. Biomol. Chem. 12, 8094–8099 (2014).
Glaser, M. et al. Three methods for 18F labeling of the HER2-binding affibody molecule ZHER2:2891 including preclinical assessment. J. Nucl. Med. 54, 1981–1988 (2013).
D'Souza, C.A., McBride, W.J., Sharkey, R.M., Todaro, L.J. & Goldenberg, D.M. High-yielding aqueous F-18 labeling of peptides via (AlF)-F-18 chelation. Bioconjug. Chem. 22, 1793–1803 (2011).
Lang, L.X. et al. Comparison study of F-18 FAl-NOTA-PRGD2, F-18 FPPRGD2, and Ga-68 Ga-NOTA-PRGD2 for PET Imaging of U87MG tumors in mice. Bioconjug. Chem. 22, 2415–2422 (2011).
Liu, Z. et al. An organotrifluoroborate for broadly applicable one-step 18F labeling. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 53, 11876–11880 (2014).
Ting, R., Adam, M.J., Ruth, T.J. & Perrin, D.M. Arylfluoroborates and alkylfluorosilicates as potential PET imaging agents: high-yielding aqueous biomolecular 18F labeling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 13094–13095 (2005).
Li, Y. et al. Towards kit-like F-18 labeling of marimastat, a noncovalent inhibitor drug for in vivo PET imaging cancer associated matrix metalloproteases. MedChemComm 2, 942–949 (2011).
Ting, R. et al. Towards [18F]-labeled aryltrifluoroborate radiotracers–in vivo PET imaging of stable aryltrifluoroborate clearance in mice. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 12045–12055 (2008).
Liu, Z. et al. From minutes to years: predicting organotrifluoroborate solvolysis rates. Chem. Eur. J. 21, 3924–3928 (2015).
Liu, Z. et al. A new F-18-heteroaryltrifluoroborate radio-prosthetic with greatly enhanced stability that is labelled by F-18–F-19-isotope exchange in good yield at high specific activity. MedChemComm 5, 171–179 (2014).
Liu, Z.B. et al. Stoichiometric leverage: Rapid 18F-aryltrifluoroborate radiosynthesis at high specific activity for click conjugation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 52, 2303–2307 (2013).
Schirrmacher, R., Wangler, C. & Schirrmacher, E. Recent developments and trends in F-18-radiochemistry: syntheses and applications. Mini Rev. Org. Chem. 4, 317–329 (2007).
Richter, S. & Wuest, F. 18F-labeled peptides: the future is bright. Molecules 19, 20536–20556 (2014).
Wagner, S. et al. A new 18F-labelled derivative of the MMP inhibitor CGS 27023A for PET: radiosynthesis and initial small-animal PET studies. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 67, 606–610 (2009).
Schirrmacher, R. et al. F-18-labeling of peptides by means of an organosilicon-based fluoride acceptor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 45, 6047–6050 (2006).
Liu, Z. et al. Preclinical evaluation of a high-affinity 18F-trifluoroborate octreotate derivative for somatostatin receptor imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 55, 1499–1505 (2014).
Liu, Z. et al. Dual mode fluorescent 18F-PET tracers: efficient modular synthesis of rhodamine-[cRGD]2-[18F]-organotrifluoroborate, rapid, and high yielding one-step 18F-labeling at high specific activity, and correlated in vivo pet imaging and ex vivo fluorescence. Bioconjug. Chem. 25, 1951–1962 (2014).
Liu, Z. et al. 18F-Trifluoroborate derivatives of [des-Arg10]kallidin for imaging bradykinin B1 receptor expression with positron emission tomography. Mol. Pharm. 12, 974–982 (2015).
Chin, F.T. et al. First experience with clinical-grade F-18 FPP(RGD)2: an automated multi-step radiosynthesis for clinical PET studies. Mol. Imaging Biol. 14, 88–95 (2012).
Li, Y. et al. Alkyne-18F-ArBF3 for one-pot click 18F-labeling of bombesin for in vivo PET imaging of tumors expressing the GRP-Receptor. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 3, 57–70 (2013).
Liu, Z. et al. Rapid, one-step, high yielding 18F-labeling of an aryltrifluoroborate bioconjugate by isotope exchange at very high specific activity. J. Labelled Comp. Radiopharm. 14, 491–497 (2012).
Monti, S.M., Supuran, C.T. & De Simone, G. Carbonic anhydrase IX as a target for designing novel anticancer drugs. Curr. Med. Chem. 19, 821–830 (2012).
Stillebroer, A.B., Mulders, P.F.A., Boerman, O.C., Oyen, W.J.G. & Oosterwijk, E. Carbonic anhydrase IX in renal cell carcinoma: implications for prognosis, diagnosis, and therapy. Eur. Urol. 58, 75–83 (2010).
Lam, K.S. et al. A new type of synthetic peptide library for identifying ligand-binding activity. Nature 354, 82–84 (1991).
Lee, S., Xie, J. & Chen, X.Y. Peptide-based probes for targeted molecular imaging. Biochemistry 49, 1364–1376 (2009).
Kilbourn, M.R., Hood, J.T. & Welch, M.J. A simple 18O water target for 18F production. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 35, 599–602 (1984).
Wuest, F., Berndt, M., Bergmann, R., van den Hoff, J. & Pietzsch, J. Synthesis and application of 18F FDG-maleimidehexyloxime (18F FDG-MHO): A 18F FDG-based prosthetic group for the chemoselective 18F-labeling of peptides and proteins. Bioconjug. Chem. 19, 1202–1210 (2008).
Lewis, J.S., Srinivasan, A., Schmidt, M.A. & Anderson, C.J. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of Cu-64-TETA-Tyr3-octreotate. A new somatostatin analog with improved target tissue uptake. Nucl. Med. Biol. 26, 267–273 (1999).
Coin, I., Beyermann, M. & Bienert, M. Solid-phase peptide synthesis: from standard procedures to the synthesis of difficult sequences. Nat. Protoc. 2, 3247–3256 (2007).
Bräse, S., Gil, C., Knepper, K. & Zimmermann, V. Organic azides: an exploding diversity of a unique class of compounds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 44, 5188–5240 (2005).
Scriven, E.F.V. & Turnbull, K. Azides: their preparation and synthetic uses. Chem. Rev. 88, 297–368 (1988).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Sciences and Engineering Research Council, and the Canadian Cancer Society Research Institute, with contributions from the intramural research program at National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, US National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.L., D.M.P., K.-S.L., F.B. and X.C. conceived and designed this research; Z.L. and M.P. performed the experiments; Z.L., K.-S.L. and F.B. analyzed the data; and Z.L., D.M.P., D.O.K. and X.C. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Lin, KS., Bénard, F. et al. One-step 18F labeling of biomolecules using organotrifluoroborates. Nat Protoc 10, 1423–1432 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2015.090
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2015.090
This article is cited by
-
Organotrifluoroborate enhances tumor targeting of fibroblast activation protein inhibitors for targeted radionuclide therapy
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (2023)
-
Kit-based synthesis of 2-deoxy-2-[18F]-fluoro-d-sorbitol for bacterial imaging
Nature Protocols (2021)
-
First-in-human study of an 18F-labeled boramino acid: a new class of PET tracers
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (2021)
-
18F-Boramino acid PET/CT in healthy volunteers and glioma patients
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (2021)
-
A near-infrared probe for non-invasively monitoring cerebrospinal fluid flow by 18F-positron emitting tomography and fluorescence
EJNMMI Research (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.