Abstract
In the last two decades, it has become clear that γδ T cells recognize a diverse array of antigens including self and foreign, large and small, and peptidic and non-peptidic molecules. In this respect, γδ antigens as a whole resemble more the antigens recognized by antibodies than those recognized by αβ T cells. Because of this antigenic diversity, no single mechanism—such as the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) restriction of αβ T cells—is likely to provide a basis for all observed T-cell antigen receptor (TCR)-dependent γδ T-cell responses. Furthermore, available evidence suggests that many individual γδ T cells are poly-specific, probably using different modes of ligand recognition in their responses to unrelated antigens. While posing a unique challenge in the maintenance of self-tolerance, this broad reactivity pattern might enable multiple overlapping uses of γδ T-cell populations, and thus generate a more efficient immune response.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chien YH, Jores R, Crowley MP . Recognition by γ/δ T cells. Annu Rev Immunol 1996; 14: 511–532.
Haas W, Pereira P, Tonegawa S . γ/δ T cells. Annu Rev Immunol 1993; 11: 637–685.
Davis MM, Bjorkman PJ . T cell antigen receptor genes and T cell recognition. Nature 1988; 334: 395–402.
Asarnow DM, Kuziel WA, Bonyhadi M, Tigelaar RE, Tucker PW, Allison JP . Limited diversity of γδ antigen receptor genes of Thy-1+ dendritic epidermal cells. Cell 1988; 55: 837–847.
Hohlfeld R, Engel AG, Ii K, Harper MC . Polymyositis mediated by T lymphocytes that express that γ/δ receptor. N Engl J Med 1991; 324: 877–881.
Roark CL, French JD, Taylor MA, Bendele AM, Born WK, O'Brien RL . Exacerbation of collagen-induced arthritis by oligoclonal, iL-17-producing γδ T cells. J Immunol 2007; 179: 5576–5583.
Havran W, Allison JP . Developmentally ordered appearance of thymocytes expressing different T cell antigen receptors. Nature 1988; 335: 443–445.
O'Brien RL, Roark CL, Jin N, Aydintug MK, French JD, Chain JL et al. γδ T cell receptors: functional correlations. Immunol Rev 2007; 215: 77–88.
Jin N, Roark CL, Miyahara N, Taube C, Aydintug MK, Wands JM et al. Allergic airway hyperresponsiveness-enhancing γδ T cells develop in normal untreated mice and fail to produce IL-4/13, unlike Th2 and NKT cells. J Immunol 2009; 182: 2002–2010.
Narayan K, Sylvia KE, Malhotra N, Yin CC, Martens G, Vallerskog T et al. Intrathymic programming of effector fates in three molecularly distinct γδ T cell subtypes. Nature Immunol 2012; 13: 511–518
Haas JD, Ravens S, Duber S, Sandrock I, Oberdorfer L, Kashani E et al. Development of interleukin-17-producing γδ T cells is restricted to a functional embryonic wave. Immunity 2012; 37: 48–59.
Bonneville M, O'Brien RL, Born WK . γδ T cell effector functions: a blend of innate programming and acquired plasticity. Nat Rev Immunol 2010; 10: 467–478.
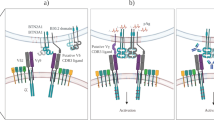
Hayes SM, Love PE . Distinct structure and signalling potential of the γδ TCR complex. Immunity 2002; 16: 1–20.
Hayes SM, Li L, Love PE . TCR signal strength influences αβ/γδ lineage fate. Immunity 2005; 22: 583–593.
Rock EP, Sibbald PR, Davis MM, Chien YH . CDR3 length in antigen-specific immune receptors. J Exp Med 1994; 179: 323–328.
Born W, Cady C, Jones-Carson J, Mukasa A, Lahn M, O'Brien R . Immunoregulatory functions of γδ T cells. Adv Immunol 1999; 71: 77–144.
Morita CT, Beckman EM, Bukowski JF, Tanaka Y, Band H, Bloom BR et al. Direct presentation of nonpeptide prenyl pyrophosphate antigens to human γδ T cells. Immunity 1995; 3: 495–507.
Cady CT, Lahn M, Vollmer M, Tsuji M, Seo SJ, Reardon CL et al. Response of murine γδ T cells to the synthetic polypeptide poly-Glu50Tyr50. J Immunol 2000; 165: 1790–1798.
Zhang L, Jin N, Nakayama M, O'Brien RL, Eisenbarth GS, Born WK . γδ T cell receptors confer autonomous responsiveness to the insulin-peptide B:9-23. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: 478–484.
Blackman M, Yague J, Kubo R, Gay D, Coleclough C, Palmer E et al. The T cell recpertoire may be biased in favor of MHC recognition. Cell 1986; 47: 349–357.
Garcia KC, Gapin L, Adams JJ, Birnbaum ME, Scott-Browne JP, Kappler JW et al. A closer look at TCR germline recongition. Immunity 2012; 36: 887–888.
Adams EJ, Strop P, Shin S, Chien YH, Garcia KC . An autonomous CDR3δ is sufficient for recognition of the nonclassical MHC class I molecules T10 and T22 by γδ T cells. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 777–784.
Boyden LM, Lewis JM, Barbee SD, Bas A, Girardi M, Hayday AC et al. Skint1, the prototype of a newly identified immunoglobulin superfamily gene cluster, positively selects epidermal γδ T cells. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 656–662.
Born WK, O'Brien RL . Antigen-restricted γδ T-cell receptors? Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 2009; 57: 129–135
Matis LA, Cron R, Bluestone JA . Major histocompatibility complex-linked specificity of γδ receptor-bearing T lymphocytes. Nature 1987; 330: 262–264.
Matis LA, Fry AM, Cron RQ, Cotterman MM, Dick RF, Bluestone JA . Structure and specificity of a class II alloreactive γδ T cell receptor heterodimer. Science 1989; 245: 746–749.
Wingren C, Crowley MP, Degano M, Chien YH, Wilson IA . Crystal structure of a γδ T cell receptor ligand T22: a truncated MHC-like fold. Science 2000; 287: 310–314.
Adams EJ, Chien YH, Garcia KC . Structure of a γδ T cell receptor in complex with the nonclassical MHC T22. Science 2005; 308: 227–231.
Shin S, El-Diwany R, Schaffert S, Adams EJ, Garcia KC, Pereira P et al. Antigen recognition determinants of γδ T cell receptors. Science 2005; 308: 252–255.
Hampl J, Schild H, Litzenberger C, Baron M, Crowley MP, Chien YH . The specificity of a weak γδ TCR interaction can be modulated by the glycosylation of the ligand. J Immunol 1999; 163: 288–294.
Sugita M, Brenner MB . T lymphocyte recognition of human group 1 CD1 molecules: implications for innate and acquired immunity. Semin Immunol 2000; 12: 511–516.
Das H, Sugita M, Brenner MB . Mechanisms of Vδ1 γδ T cell activation by microbial components. J Immunol 2004; 172: 6578–6586.
Cui Y, Kang L, Cui L, He W . Human γδ T cell recognition of lipid A is predominately presented by CD1b or CD1c on dendritic cells. Biol Direct 2009; 4: 47–58.
Agea E, Russano A, Bistoni O, Mannucci R, Nicoletti I, Corazzi L et al. Human CD1-restricted T cell recognition of lipids from pollens. J Exp Med 2005; 202: 295–308.
Russano AM, Agea E, Corazzi L, Postle AD, de Libero G, Porcelli SA et al. Recognition of pollen-derived phosphatidyl-ethanolamine by human CD1d-restricted gamma delta T cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 117: 1178–1184.
Dieude M, Striegl H, Tyznik AJ, Wang J, Behar SM, Piccirillo CA et al. Cardiolipin binds to CD1d and stimulates CD1d-restricted γδ T cells in the normal murine repertoire. J Immunol 2011; 186: 4771–4781.
Huber S, Sartini D, Exley M . Role of CD1d in Coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis. J Immunol 2003; 170: 3147–3153.
Gapin L . iNKT cell autoreactivity: what is ‘self’ and how is it recognized? Nat Rev Immunol 2010; 10: 272–277.
Russano AM, Bassotti G, Agea E, Bistoni O, Mazzocchi A, Morelli A et al. CD1-restricted recognition of exogenous and self-lipid antigens by duodenal γδ+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol 2007; 178: 3620–3626.
Bai L, Picard D, Anderson B, Chaudhary V, Luoma A, Jabri B et al. The majority of CD1d-sulfatide-specific T cells in human blood use a semiinvariant Vδ1 TCR. Eur J Immunol 2012; 42: 2505–2510.
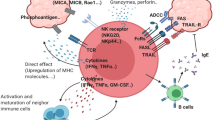
Groh V, Steinle A, Bauer S, Spies T . Recognition of stress-induced MHC molecules by intestinal epithelial γδ T cells. Science 1998; 279: 1737–1740.
Steinle A, Groh V, Spiess T . Diversification, expression, and γδ T cell recognition of evolutionarily distant members of the MIC family of major histocompatibility complex class I-related molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998; 95: 12510–12515.
Groh V, Rhinehart R, Secrist H, Bauer S, Grabstein KH, Spies T . Broad tumor-associated expression and recognition by tumor-derived gamma delta T cells of MICA and MICB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999; 96: 6879–6884.
Bauer S, Groh V, Wu J, Steinle A, Phillips JH, Lanier LL et al. Activation of NK cells and T cells by NKG2D, a receptor for stress-inducible MICA. Science 1999; 285: 727–729.
Das H, Groh V, Kuiji C, Sugita M, Morita CT, Spies T et al. MICA engagement by human Vγ2Vδ2 T cells enhances their antigen-dependent effector function. Immunity 2001; 15: 83–93.
Wu J, Groh V, Spies T . T cell antigen receptor engagement and specificty in the recognition of stress-inducible MHC class I-related chains by human epithelial γδ T cells. J Immunol 2002; 169: 1236–1240.
Xu B, Pizarro JC, Holmes MA, McBeth C, Groh V, Spies T et al. Crystal structure of a γδ T-cell receptor specific for the human MHC class I homolog MICA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011; 108: 2414–2419.
Scotet E, Martinez LO, Grant E, Barbaras R, Jeno P, Saulquin X et al. Tumor recognition following Vγ9Vδ2 T cell receptor interactions with a surface F1-ATPase-related structure and apolipoprotein A-1. Immunity 2005; 22: 71–80.
Born WK, Vollmer M, Reardon C, Matsuura E, Voelker DR, Giclas PC et al. Hybridomas expressing γδ T-cell receptors respond to cardiolipin and β2-glycoprotein 1 (apolipoprotein H). Scand J Immunol 2003; 58: 374–381.
Fisch P, Malkovsky M, Braakman E, Sturm E, Bolhuis RLH, Prieve A et al. γ/δ T-cell clones and natural killer-cell clones mediate distinct patterns of non-major histocompatibility complex-restricted cytolysis. J Exp Med 1990; 171: 1567–1579.
Fisch P, Malkovsky M, Kovats S, Sturm E, Braakman E, Klein BS et al. Recognition by human Vγ9/Vδ2 T cells of a GroEL homolog on Daudi Burkitt's lymphoma cells. Science 1990; 250: 1269–1273.
Fisch P, Oettel K, Fudim N, Surfus JE, Malkovsky M, Sondel PM . MHC-unrestricted cytotoxic and proliferative responses of two distinct human γ/δ T cell subsets to Daudi cells. J Immunol 1992; 148: 2315–2323.
Aydintug MK, Roark CL, Yin X, Wands JM, Born WK, O'Brien RL . Detection of cell surface ligands for the γδ TCR using soluble TCRs. J Immunol 2004; 172: 4167–4175.
Aydintug MK, Roark CL, Chain JL, Born WK, O'Brien RL . Macrophages express multiple ligands for γδ TCRs. Mol Immunol 2008; 45: 3253–3263.
Kozbor D, Trinchieri G, Monos DS, Isobe M, Russo G, Haney JA et al. Human TCR-γ+/δ+, CD8+ T lymphocytes recognize tetanus toxoid in an MHC-restricted fashion. J Exp Med 1989; 169: 1847–1851.
Kozbor D, Cassatella MA, Lessin S, Kagan J, Finver S, Faust J et al. Expression and function of γδ- and αβ-T cell receptor heterodimers on human somatic T cell hybrids. J Immunol 1990; 144: 3677–3683.
Rust CJJ, Verreck F, Vietor H, Koning F . Specific recognition of staphylococcal enterotoxin A by human T cells bearing receptors with the Vγ9 region. Nature 1990; 346: 572–574.
Guo Y, Ziegler HK, Safley SA, Niesel DW, Vaidya S, Klimpel GR . Human T-cell recognition of Listeria monocytogenes: recognition of listeriolysin O by TcRαβ+ and TcRγδ+ T cells. Infect Immunol 1995; 63: 2288–2294.
Rust CJJ, Koning F . γδ T cell reactivity towards bacterial superantigens. Semin Immunol 1993; 5: 41–46.
Skeen MJ, Ziegler HK . Intercellular interactions and cytokine responsiveness of peritoneal α/β and γ/δ T cells from Listeria-infected mice: synergistic effects of interleukin 1 and 7 on γ/δ T cells. J Exp Med 1993; 178: 985–996.
Fu YX, Roark CE, Kelly K, Drevets D, Campbell P, O'Brien R et al. Immune protection and control of inflammatory tissue necrosis by γδ T cells. J Immunol 1994; 153: 3101–3115.
O'Brien RL, Xiang Y, Huber S, Ikuta K, Born WK . Depletion of a γδ T cell subset can increase host resistance to a bacterial infection. J Immunol 2000; 165: 6472–6479.
Ryan-Payseur B, Frencher J, Shen L, Chen CY, Huang D, Chen ZW . Multieffector-functional immune responses of HMBPP-specific Vγ2Vδ2 T cells in non-human primates inoculated with Listeria monocytogenes DeltaactA prfA. J Immunol 2012; 189: 1285–1293.
Holoshitz J, Koning F, Coligan JE, de Bruyn J, Strober S . Isolation of CD4−CD8− mycobacteria-reactive T lymphocyte clones from rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid. Nature 1989; 339: 226–229.
Janis EM, Kaufmann SHE, Schwartz RH, Pardoll DM . Activation of γδ T cells in the primary immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science 1989; 244: 713–716.
O'Brien RL, Happ MP, Dallas A, Palmer E, Kubo R, Born WK . Stimulation of a major subset of lymphocytes expressing T cell receptor γδ by an antigen derived from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cell 1989; 57: 667–674.
Happ MP, Kubo RT, Palmer E, Born WK, O'Brien RL . Limited receptor repertoire in a mycobacteria-reactive subset of γδ T lymphocytes. Nature 1989; 342: 696–698.
Bitter W, Houben ENG, Bottai D, Brodin P, Brown EJ, Cox JS et al. Systematic genetic nomenclature for type VII secretion systems. PLOS Pathog 2009; 5: 1–6, e1000507.
Bottai D, Mailessi L, Simeone R, Friqui W, Laurent C, Lenormand P et al. ESAT-6 secretion-independent impact of ESX-1 genes espF and espG1 on virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Infect Dis 2011; 203: 1155–1164.
Rhodes SG, Buddle BM, Hewinson RG, Vordermaier HM . Bovine tuberculosis: immune responses in the peripheral blood and at the site of active disease. Immunology 2000; 99: 195–202.
Welsh MD, Kennedy HE, Smyth AJ, Girvin RM, Andersen P, Pollock JM . Responses of bovine WC1+γδ T cells to protein and nonprotein antigens of Mycobacterium bovis. Infect Immun 2002; 70: 6114–6120.
Maue AC, Waters WR, Davis WC, Palmer MV, Minion FC, Estes DM . Analysis of immune responses directed toward a recombinant early secretory antigenic target six-kilodalton protein-culture filtrate protein 10 fusion protein in Mycobacterium bovis infected cattle. Infect Immun 2005; 73: 6659–6667.
Gioia C, Agrati C, Goletti D, Vincenti D, Carrara S, Amicosante M et al. Different cytokine production and effector/memory dynamics of αβ+ or γδ+ T-cell subsets in the peripheral blood of patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 2003; 16: 247–252.
Li L, Wu CY . CD4+CD25+ Treg cells inhibit human memory γδ T cells to produce IFN-γ in response to M. tuberculosis antigen ESAT-6. Blood 2008; 111: 5629–5636.
Casetti R, Martino A, Sacchi A, Agrati C, Goletti D, Martini F . Do human γδ T cells respond to M. tuberculosis protein antigens? Blood 2008; 112: 4776.
Li L, Wu CY . Human memory but not naive γδ T cells from TST-positive individuals respond to M. tuberculosis antigen. Blood 2008; 112: 4777.
Cendron D, Ingoure S, Martino A, Casetti R, Horand F, Romagne F et al. A tuberculosis vaccine based on phosphoantigens and fusion proteins induces distinct γδ and αβ T cell responses in primates. Eur J Immunol 2007; 37: 549–565.
Sciammas R, Kodukula P, Tang Q, Hendricks RL, Bluestone JA . T cell receptor-γ/δ cells protect mice from herpes simplex virus type 1-induced lethal encephalitis. J Exp Med 1997; 185: 1969–1975.
Johnson RM, Lancki DW, Sperling AI, Dick RF, Spear PG, Fitch FW et al. A murine CD4−, CD8− T cell receptor-γδ T lymphocyte clone specific for Herpes simplex virus glycoprotein I. J Immunol 1992; 148: 983–988.
Sciammas R, Johnson RM, Sperling AI, Brady W, Linsley PS, Spear PG et al. Unique antigen recognition by a herpsevirus-specific TCR-γδ cell. J Immunol 1994; 152: 5392–5397.
Born W, Hall L, Dallas A, Boymel J, Shinnick T, Young D et al. Recognition of a peptide antigen by heat shock reactive γδ T lymphocytes. Science 1990; 249: 67–69.
Sciammas R, Bluestone JA . HSV-1 glycoprotein I-reactive TCRγδ cells directly recognize the peptide backbone in a conformationally dependent manner. J Immunol 1998; 161: 5187–5192.
Sciammas R, Bluestone JA . TCRγδ cells and viruses. Microbes Infect 1999; 1: 203–212.
Wright A, Lee JE, Link MP, Smith SD, Carroll W, Levy R et al. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for self tumor immunoglobulin express T cell receptor δ chain. J Exp Med 1989; 169: 1557–1564.
Kim HT, Nelson EL, Clayberger C, Sanjanwala M, Sklar J, Krensky AM . γδ T cell recognition of tumor Ig peptide. J Immunol 1995; 154: 1614–1623.
Pluschke G, Rüegg D, Hohlfeld R, Engel AG . Autoaggressive myocytotoxic T lymphocytes expressing an unusual γ/δ T cell receptor. J Exp Med 1992; 176: 1785–1789.
Wiendl H, Malotka J, Holzwarth B, Weltzien HU, Wekerle H, Hohlfeld R et al. An autoreactive γδ TCR derived from a polymyositis lesion. J Immunol 2002; 169: 515–521.
Dornmair K, Schneider CK, Malotka J, Dechant G, Wiendl H, Hohlfeld R . Antigen recongition properties of a Vγ1.3Vδ2-T-cell receptor from a rare variant of polymyositis. J Neuroimmunol 2004; 152: 168–175.
Bruder J, Siewert K, Obermeier B, Malotka J, Scheinert P, Kellermann J et al. Target specificity of an autoreactive pathogenic human γδ-T cell receptor in myositis. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 20986–20995.
Born WK, Zhang L, Nakayama M, Jin N, Chain JL, Huan Y et al. Peptide antigens for γδ T cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 2011; 68: 2335–23343.
Fu YX, Kersh G, Vollmer M, Kalataradi H, Heyborne K, Reardon C et al. Structural requirements for peptides that stimulate a subset of γδ T cells. J Immunol 1994; 152: 1578–1588.
O'Brien RL, Fu YX, Cranfill R, Dallas A, Reardon C, Lang J et al. Heat shock protein Hsp-60 reactive γδ cells: a large, diversified T lymphocyte subset with highly focused specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1992; 89: 4348–4352.
Blond-Elguindi S, Cwirla SE, Dower WJ, Lipshutz RJ, Sprang SR, Sambrook JF et al. Affinity panning of a library of peptides displayed on bacteriophages reveals the binding specificity of BiP. Cell 1993; 75: 717–728.
Mohan JF, Levisetti MG, Calderon B, Herzog JW, Petzold SJ, Unanue ER . Unique autoreactive T cells recognize insulin peptides generated within the islets of Langerhans in autoimmune diabetes. Nat Immunol 2010; 4: 350–354.
Zhang L, Nakayama M, Eisenbarth GS . Insulin as an autoantigen in NOD/human diabetes. Curr Opin Immunol 2008; 20: 111–118.
Holoshitz J, Vila LM, Keroack BJ, McKinley DR, Bayne NK . Dual antigenic recognition by cloned human γδ T cells. J Clin Invest 1992; 89: 308–314.
Vidovic D, Roglic M, McKune K, Guerder S, MacKay C, Dembic Z . Qa-1 restricted recognition of foreign antigen by a γδ T-cell hybridoma. Nature 1989; 340: 646–650.
Modlin RL, Pirmez C, Hofman FM, Torigian V, Uyemura K, Rea TH et al. Lymphocytes bearing antigen-specific γδ T-cell receptors in human infectious disease lesions. Nature 1989; 339: 544–548.
Kabelitz D, Bender A, Schondelmaier S, Schoel B, Kaufmann SHE . A large fraction of human peripheral blood γδ+ T cells is activated by Mycobacterium tuberculosis but not by its 65 kD heat shock protein. J Exp Med 1990; 171: 667–679.
Pfeffer K, Schoel B, Gulle H, Kaufmann SHE, Wagner H . Primary responses to human T cells to mycobacteria: a frequent set of γ/δ T cells are stimulated by protease-resistant ligands. Eur J Immunol 1990; 20: 1175–1179.
Constant P, Davodeau F, Peyrat MA, Poquet Y, Puzo G, Bonneville M et al. Stimulation of human γδ T cells by nonpeptidic mycobacterial ligands. Science 1994; 264: 267–270.
Tanaka Y, Sano S, Nieves E, de Libero G, Rosa D, Modlin RL et al. Nonpeptide ligands for human γδ T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994; 91: 8175–8179.
Tanaka Y, Morita CT, Tanaka Y, Nieves E, Brenner MB, Bloom BR . Natural and synthetic non-peptide antigens recognized by human γδ T cells. Nature 1995; 375: 155–158.
Hintz M, Reichenberg A, Altincicek B, Bahr U, Gschwind RM, Kollas AK et al. Identification of (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate as a major activator for human γδ T cells in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett 2001; 509: 317–322.
Wang H, Fang Z, Morita C . Vγ2Vδ2 T cell receptor recognition of prenyl pyrophosphates is dependent on all CDRs. J Immunol 2010; 184: 6209–6222.
Sarikonda G, Wang H, Puan KJ, Liu XH, Lee HK, Song Y et al. Photoaffinity antigens for human γδ T cells. J Immunol 2008; 181: 7738–7750.
Wei H, Huang D, Lai X, Chen M, Zhong W, Wang R et al. Definition of APC presentation of phosphoantigen (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate to Vγ2Vδ2 TCR. J Immunol 2008; 181: 4798–4806.
Gober HJ, Kistowska M, Angman L, Jeno P, Mori L, de Libero G . Human T cell receptor γδ cells recognize endogenous mevalonate metabolites in tumor cells. J Exp Med 2003; 197: 163–168.
Thompson K, Rojas-Navea J, Rogers MJ . Alkylamines cause Vγ9Vδ2 T cell activation and proliferation by inhibiting the mevalonate pathway. Blood 2006; 107: 651–654.
Kunzmann V, Bauer E, Wilhelm M . γ/δ T-cell stimulation by pamidronate. New Engl J Med 1999; 340: 737–738.
Bukowski JF, Morita CT, Brenner MB . Human γδ T cells recognize alkylamines derived from microbes, edible plants, tea: implications for innate immunity. Immunity 1999; 11: 57–65.
Matsuura E, Lopez LR, Shoenfeld Y, Ames PRJ . β2 glycoprotein I and oxidative inflammation in early atherogenesis: a progression from innate to adaptive immunity? Autoimmun Rev; e-pub ahead of print 2012 Apr 27; doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2012.04.003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Born, W., Kemal Aydintug, M. & O'Brien, R. Diversity of γδ T-cell antigens. Cell Mol Immunol 10, 13–20 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2012.45
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2012.45
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
“Off-the-Shelf” Allogeneic CAR Cell Therapy—Neglected HvG Effect
Current Treatment Options in Oncology (2023)
-
Leishmania mexicana Lipophosphoglycan Activates Dermal γδ T Cells with Participation of TLR2
Acta Parasitologica (2023)
-
Inhibition of γδ T Cells Alleviates Blood–Brain Barrier in Cardiac Arrest and Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Mice
Molecular Biotechnology (2023)
-
BW5147 and Derivatives for the Study of T Cells and their Antigen Receptors
Archivum Immunologiae et Therapiae Experimentalis (2020)
-
Kidney injury in response to crystallization of calcium oxalate leads to rearrangement of the intrarenal T cell receptor delta immune repertoire
Journal of Translational Medicine (2019)