Abstract
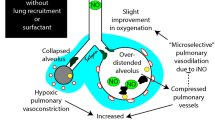
Surfactant treatment has become the standard of care in premature infants with respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). Pulmonary hemorrhage, pulmonary edema, pneumonia, and atelectasis have been shown to liberate inflammatory mediators and plasma proteins, which damage type II pneumocytes and inactivate surfactant. These disease processes may, therefore, lead to a secondary surfactant inactivation or deficiency, which can be an unrecognized cause of respiratory decompensation after initial recovery from RDS in this vulnerable population. This is a descriptive report of three cases, which had acute respiratory decompensation between 1 and 3 weeks of age. All three infants demonstrated a response to secondary doses of surfactant. We submit that the diagnosis and treatment of secondary surfactant deficiency in the critically ill premature neonate warrants further study.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jobe AH . Pathophysiology of respiratory distress syndrome. In: Polin RA, Fox WW, editors. Fetal and Neonatal Physiology. Vol. 2. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Company; 1992 p. 995–1001.
Taeusch HW . Treatment of acute (adult) respiratory distress syndrome. The Holy Grail of surfactant therapy. Biol Neonate 2000;77(Suppl 1):2–8.
Harms K, Herting E . Successful surfactant replacement therapy in two infants with ARDS due to chlamydial pneumonia. Respiration 1994;61:348–352.
Herting E, Gefeller O, Land M, van Sonderen L, Harms K, Robertson B, Members of the Collaborative European Multicenter Study Group. Surfactant treatment of neonates with respiratory failure and group B streptococcal infection. Pediatrics 2000;106(5):957–965.
Lopez-Herce J, de Lucas N, Carrillo A, Bustinza A, Moral R . Surfactant treatment for acute respiratory distress syndrome. Arch Dis Child 1999;80:248–252.
Moreno M, Lopez-Herce J, Alcaraz A, Carrillo A . Exogenous surfactant therapy for acute respiratory distress in infancy. Intens Care Med 1996;22:87–88.
Perez-Benavides F, Riff E, Franks C . Adult respiratory distress syndrome and artificial surfactant replacement in the pediatric patient. Pediatr Emerg Care 1995;11(3):153–155.
Wilson DF, Jiao JH, Bauman LA, et al. Calf's lung surfactant extract in acute hypoxemic respiratory failure in children. Crit Care Med 1996;24(6):1316–1322.
Auten RL, Notter RH, Kendig JW, Davis JM, Shapiro DL . Surfactant treatment of full-term newborns with respiratory failure. Pediatrics 1991;87(1):101–107.
Findlay R, Tauesch W, Walther F . Surfactant replacement therapy for meconium aspiration syndrome. Pediatrics 1996;97(1):48–52.
Thibeault DW, Maabry SM, Ekekezie II, Truog WE . Lung elastic tissue maturation and perturbations during the evolution of chronic lung disease. Pediatrics 2000;106(6):1452–1459.
Nishina K, Mikawa K, Takao Y, Maekawa N, Obara H . Effects of exogenous surfactant on acute lung injury induced by intratracheal instillation of infant formula or human breast milk in rabbits. Anesthesiology 1999;91:240–252.
Kazzi SNJ, Schurch S, McLaughlin KL, Romero R, Janissee J . Surfactant phospholipids and surface activity among preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome who develop bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Acta Paediatr 2000;89:1218–1225.
Davis JM, Richter SE, Kendig JW, Notter RH . High-frequency jet ventilation and surfactant treatment of newborns with severe respiratory failure. Pediatr Pulmonol 1992;13:108–112.
Pandit PB, Dunn MS, Kelly EN, Perlman M . Surfactant replacement in neonates with early chronic lung disease. Pediatrics 1995;95:851–854.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bissinger, R., Carlson, C., Hulsey, T. et al. Secondary Surfactant Deficiency in Neonates. J Perinatol 24, 663–666 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211154
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211154
This article is cited by
-
Surfactant status and respiratory outcome in premature infants receiving late surfactant treatment
Pediatric Research (2019)
-
Surfactant replacement therapy beyond respiratory distress syndrome in neonates
Indian Pediatrics (2016)
-
Exogenous surfactant therapy in 2013: what is next? who, when and how should we treat newborn infants in the future?
BMC Pediatrics (2013)
-
Surfactant Therapy for Maternal Blood Aspiration: An Unusual Cause of Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome
The Indian Journal of Pediatrics (2012)
-
Pilot trial of late booster doses of surfactant for ventilated premature infants
Journal of Perinatology (2011)