Abstract
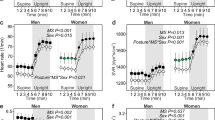
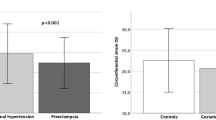
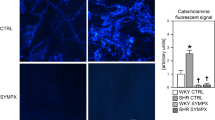
The aim of this study was to determine the normality or otherwise of neurohormone indices, particularly the sympathetic nervous system, in pre-eclamptic patients and document whether changes in body posture magnify any differences between pre-eclamptic and normal women. We studied 11 women with pre-eclampsia and compared them with 17 matched normotensive pregnant women and eight nonpregnant women. Measurements of arterial pressure, heart rate and neurohormones were carried out with subjects in the left lateral position, then supine, left lateral, with upright posture and finally with assumption of the left lateral position again. Main outcome measures were arterial pressure, heart rate and hormones (plasma norepinephrine, renin activity, natriuretic peptides and endothelin-1). We observed that plasma norepinephrine levels were higher in pre-eclamptic than normotensive pregnant women and this was most obvious in the upright position. Plasma renin activity was likewise higher in pre-eclamptic than normotensive pregnant women, again most obvious with upright posture. Plasma natriuretic peptides and endothelin-1 levels were similar in pre-eclamptics and normotensive pregnant women. These data strengthen the premise that pre-eclampsia is associated with sympathetic overactivity as reflected by plasma norepinephrine levels, most obviously observed in the upright position.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gant NF et al. A study of angiotensin II pressor response throughout primigravid pregnancy. J Clin Invest 1973; 52: 2682–2689.
Brown MA, Gallery ED, Ross MR, Esber RP . Sodium excretion in normal and hypertensive pregnancy: a prospective study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1988; 159: 297–307.
Lyall F, Greer IA . Pre-eclampsia: a multifaced vascular disorder of pregnancy. J Hypertens 1994; 12: 1339–1345.
Broughton Pipkin F . The hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. BMJ 1995; 311: 609–613.
Schobel HP et al. Preeclampsia—a state of sympathetic overactivity. N Engl J Med 1996; 335: 1480–1485.
Greenwood JP et al. Sympathetic neural mechanisms in normal and hypertensive pregnancy in humans. Circulation 2001; 104: 2200–2204.
Kaaja RJ et al. Blood pressure and vasoactive hormones in mild Pre-eclampsia and normal pregnancy. Hypertens Pregnancy 1999; 18: 173–187.
National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group Report on High Blood Pressure in Pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990; 163: 1689–1712.
Yandle TG, Espiner EA, Nicholls MG, Duff H . Radioimmunoassay and characterization of atrial natriuretic peptide in human plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1986; 63: 72–79.
Yandle TG et al. Assay for brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) in human plasma: evidence for high molecular weight BNP as a major plasma component in heart failure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1993; 76: 832–838.
Dunn PJ, Espiner EA . Outpatient screening tests for primary aldosteronism. Aust NZ J Med 1976; 6: 131–135.
Lun S, Espiner EA, Nicholls MG, Yandle TG . A direct radioimmunoassay for aldosterone in plasma. Clin Chem 1983; 29: 268–271.
Eisenhofer G et al. Simultaneous liquid chromatography determination of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycol, catecholamines, and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine in plasma, and their responses to inhibition of monoamine oxidase. Clin Chem 1986; 32: 2030–2033.
Esler MD et al. Noradrenaline release and sympathetic nervous system activity. J Hypertens 1985; 3: 117–129.
Viktor RG, Mark AL . The sympathetic nervous system in human hypertension. In: Laragh JH, Brenner BM (eds). Hypertension: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Management. 2nd ed. Raven Press: New York, 1995 pp 863–878.
Polonia J et al. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone, sympathetic and endothelin systems in normal and hypertensive pregnancy: response to postural and volume load stimuli. J Hypertens 1993; 11(Suppl 5): S242–S243.
August P . The renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system in hypertension in human pregnancy. In: Robertson JIS, Nicholls MG (eds). The Renin–Angiotensin System. Gower Medical Publishing: London, 1993, pp 52.1–52.12.
Stella A, Zanchetti A . Neural control of renin secretion. J Hypertens 1984; 2(Suppl 1): 83–87.
Castro LC, Hobel CJ, Gornbein J . Plasma levels of atrial natriuretic peptide in normal and hypertensive pregnancies: a meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994; 171: 1642–1651.
Itoh H et al. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide level in pregnant women with pregnancy-induced hypertension. Obstet Gynecol 1993; 82: 71–77.
Gant NF et al. A clinical test useful for predicting the development of acute hypertension in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1974; 120: 1–7.
Acknowledgements
Financial support for this study was from a Helsinki University Central Hospital Research Grant and a Paarvo Nurmi Foundation Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaaja, R., Leinonen, A., Moore, P. et al. Effect of changes in body posture on vasoactive hormones in pre-eclamptic women. J Hum Hypertens 18, 789–794 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001743
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001743
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hypertensive emergencies: a new clinical approach
Clinical Hypertension (2015)
-
Hemodynamic and neurohumoral profile in patients with different types of hypertension in pregnancy
Internal and Emergency Medicine (2011)