Abstract
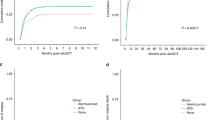
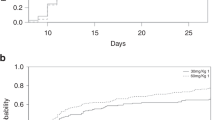
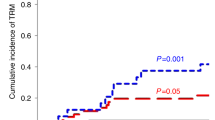
Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (BMT) is an effective therapy for a variety of malignancies and blood disorders, but rarely serves as a frontline treatment because of numerous, potential complications. Important and frequent complications relate to the profound immunosuppression that inevitably occurs during the first several months following treatment. To better elucidate and subsequently improve immune reconstitution, we examined T and B cell subsets among 43 pediatric BMT recipients in a retrospective study. We found that the relative numbers of T cells and B cells (T:B ratios) were discordant and highly variable among patients at day ∼100 after BMT. Further investigation of BMT parameters identified a strong correlation between T:B ratios and immunosuppressive drug treatments, providing an explanation for variable lymphocyte reconstitution profiles. Results suggest that: (1) immunosuppressive therapy inhibits B cell expansion more strongly than T cell expansion following BMT; (2) WBC and absolute lymphocyte counts fail to reveal profound B cell immunodeficiencies in some BMT patients; and (3) routine analyses of T:B ratios serve to identify patients warranting close follow-up and extended supportive immunotherapy. Bone Marrow Transplantation (2001) 28, 573–580.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meyers JD, Flournoy N, Thomas ED . Risk factors for cytomegalovirus infection after human marrow transplantation J Infect Dis 1986 153: 478–488
Zutter MM, Martin PJ, Sale GE et al. Epstein–Barr virus lymphoproliferation after bone marrow transplantation Blood 1988 72: 520–529
Wingard JR . Advances in the management of infectious complications after bone marrow transplantation Bone Marrow Transplant 1990 6: 371–383
Wilson A, Sharp M, Koropchak CM et al. Subclinical varicella-zoster virus viremia, herpes zoster, and T lymphocyte immunity to varicella-zoster viral antigens after bone marrow transplantation J Infect Dis 1992 165: 119–126
Hongeng S, Krance RA, Bowman LC et al. Outcomes of transplantation with matched-sibling and unrelated-donor bone marrow in children with leukaemia Lancet 1997 350: 767–771
Lum LG . Immune recovery after bone marrow transplantation Hematol/Oncol Clin N Am 1990 4: 659–675
Atkinson K . Reconstruction of the haemopoietic and immune systems after marrow transplantation Bone Marrow Transplant 1990 5: 209–226
Buckley RH, Schiff SE, Sampson HA et al. Development of immunity in human severe primary T cell deficiency following haploidentical bone marrow stem cell transplantation J Immunol 1986 136: 2398–2407
Lamb LS, Gee AP, Henslee-Downey PJ et al. Phenotypic and functional reconstitution of peripheral blood lymphocytes following T cell-depleted bone marrow transplantation from partially mismatched related donors Bone Marrow Transplant 1998 21: 461–471
Foot ABM, Potter MN, Donaldson C et al. Immune reconstitution after BMT in children Bone Marrow Transplant 1993 11: 7–13
Heslop HE, Benaim E, Brenner MK et al. Response of steroid-resistant graft-versus-host disease to lymphoblast antibody CBL1 Lancet 1995 346: 805–806
Rousseeuw P, Leroy AM . Robust regression and outlier detection John Wiley and Sons: New York 1987
Ku G, Witte ON . Corticosteroid-resistant bone marrow-derived B lymphocyte progenitor for long term in vitro cultures J Immunol 1986 137: 2802–2807
Denis KA, Witte ON . In vitro development of B lymphocytes from long-term cultured precursor cells Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1986 83: 441–445
Cupps TR, Edgar LC, Thomas CA, Fauci AS . Multiple mechanisms of B cell immunoregulation in man after administration of in vivo corticosteroids J Immunol 1984 132: 170–175
Storek J, Witherspoon RP, Webb D, Storb R . Lack of B cell precursors in marrow transplant recipients with chronic graft-versus-host disease Am J Hematol 1996 52: 82–89
Rencher SD, Houston JA, Lockey TD, Hurwitz JL . Eliminating graft-versus-host potential from T cell immunotherapeutic populations Bone Marrow Transplant 1996 18: 415–420
Slobod KS, Benaim E, Woodruff L et al. T cell immunotherapeutic populations control viral infections in bone marrow transplant recipients Immunol Res 2001 (in press)
Slobod KS, Hurwitz JL . Adoptive Immunotherapy Pediatr Infect Dis J 1999 18: 467–468
Acknowledgements
This work was funded in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute: P30-CA21765 and RO1-CA57419, The Assisi Foundation, and the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities. We thank our clinical colleagues Drs Malcolm K Brenner, Robert Krance and Helen E Heslop for helping care for patients and initiating lymphocyte analyses. We thank Xin Tong of the Biostatistics and Epidemiology Department of St Jude Children's Research Hospital for assistance with statistical calculations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
D'Costa, S., Slobod, K., Benaim, E. et al. Effect of extended immunosuppressive drug treatment on B cell vs T cell reconstitution in pediatric bone marrow transplant recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant 28, 573–580 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1703185
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1703185