Abstract
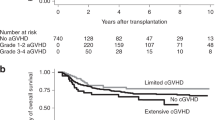
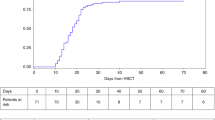
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of a bone marrow transplantation (BMT) on renal function in children. In a 5-year period, 142 children received a BMT at the Department of Pediatrics of the University Hospital Leiden. The study was performed retrospectively using the estimated glomerular filtration rate before and 1 year after BMT, and weekly measurements of serum creatinine during the first 3 months after BMT for assessment of renal function. Patient characteristics (sex, age, diagnosis), conditioning regimen, type of BMT, major complications (sepsis, veno-occlusive disease and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)) and the use of nephrotoxic medication were listed. In the first 3 months after BMT 17 (12%) patients died, 13 from transplant-related complications other than renal failure and four from relapse of the disease. Forty-eight children (34%) had a period with acute renal insufficiency. A high pre-BMT serum creatinine, transplantation with either a non-HLA-identical related or a matched unrelated donor were risk factors for acute renal insufficiency after BMT. Sepsis and the use of intravenous vancomycin were risk factors for acute renal insufficiency only for patients with a high pre-BMT serum creatinine. GVHD seemed to have a beneficial effect on renal function of BMT recipients. One year after BMT a total of 35 (25%) patients had died, 16 from transplant-related complications and 19 from relapse of the disease; another 17 patients could not be evaluated. Twenty-five of 90 evaluable children (28%) had chronic renal insufficiency. Chronic renal insufficiency 1 year after BMT was correlated with a high serum creatinine in the first 3 months after BMT. None of the children of this retrospective study on renal function after BMT needed dialysis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holthe, Jv., van Zwet, J., Brand, R. et al. Bone marrow transplantation in children: consequences for renal function shortly after and 1 year post-BMT. Bone Marrow Transplant 22, 559–564 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1701388
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1701388
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Risk factors for acute kidney injury in pediatric patients after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Pediatric Nephrology (2024)
-
Predictors of kidney complications and analysis of hypertension in children with allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Pediatric Nephrology (2023)
-
Incidence of acute kidney injury after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
European Journal of Pediatrics (2023)
-
Teenagers and young adults with a past of allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation are at significant risk of chronic kidney disease
Pediatric Nephrology (2022)
-
Kidney complications in 107 Fanconi anemia patients submitted to hematopoietic cell transplantation
European Journal of Pediatrics (2022)