Abstract
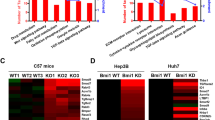
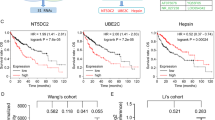
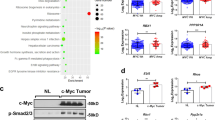
Hyperactivation of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling pathway is a common feature of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression. However, the driver factors leading to enhanced TGF-β activity are not well characterized. Here, we explore the mechanisms that loss of Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) exacerbates oncogenic TGF-β signaling in human HCC. The expression of KLF4 and TGF-β signaling components in primary HCC and their clinicopathologic relevance and significance was evaluated by using tissue microarray and immunohistochemistry. Cellular and molecular impacts of altered KLF4 expression and TGF-β signaling were determined using immunofluorescence, western blot, reverse-transcriptase PCR, chromatin immunoprecipitation and promoter reporter assays. Loss of KLF4 expression in primary HCC closely correlated with decreased Smad7 expression, increased p-Smad2/3 expression and independently predicts reduced overall and relapse-free survival after surgery. TGF-β signaling components were expressed in most HCC cells, and activation of TGF-β signaling promoted cell migration and invasion. Enforced KLF4 expression blocked TGF-β signal transduction and inhibited cell migration and invasion via activation of Smad7 transcription, whereas deletion of its C-terminal zinc-finger domain diminished this effect. KLF4 protein physically interacts with the Smad7 promoter. Promoter deletion and point mutation analyses revealed that a region between nucleotides –15 bp and –9 bp of the Smad7 promoter was required for the induction of Smad7 promoter activity by KLF4. Our data indicate that KLF4 suppresses oncogenic TGF-β signaling by activation of Smad7 transcription, and that loss of KLF4 expression in primary HCC may contribute to activation of oncogenic TGF-β signaling and subsequent tumor progression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ChIP:
-
chromatin immunoprecipitation
- FFPE:
-
formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded
- KLF4:
-
Krüppel-like factor 4
- EMT:
-
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
- ZDF:
-
zinc-finger domain
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- PBS-T:
-
PBS containing 0.1% Triton X-100
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- qPCR:
-
quantitative PCR
- RT:
-
reverse transcription
- siRNA:
-
small interfering RNA
- TGF:
-
transforming growth factor
- TMA:
-
tissue microarray
- UTR:
-
untranslated region.
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D . Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2011; 61: 69–90.
Mazzocca A, Antonaci S, Giannelli G . The TGF-beta signaling pathway as a pharmacological target in a hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Pharm Des 2012; 18: 4148–4154.
Meindl-Beinker NM, Matsuzaki K, Dooley S . TGF-beta signaling in onset and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis 2012; 30: 514–523.
Yan X, Liu Z, Chen Y . Regulation of TGF-beta signaling by Smad7. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 2009; 41: 263–272.
Baek HJ, Pishvaian MJ, Tang Y, Kim TH, Yang S, Zouhairi ME et al. Transforming growth factor-beta adaptor, beta2-spectrin, modulates cyclin dependent kinase 4 to reduce development of hepatocellular cancer. Hepatology 2011; 53: 1676–1684.
Senturk S, Mumcuoglu M, Gursoy-Yuzugullu O, Cingoz B, Akcali KC, Ozturk M . Transforming growth factor-beta induces senescence in hepatocellular carcinoma cells and inhibits tumor growth. Hepatology 2010; 52: 966–974.
Zhu H, Wu K, Yan W, Hu L, Yuan J, Dong Y et al. Epigenetic silencing of DACH1 induces loss of transforming growth factor-beta1 antiproliferative response in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2013; 58: 2012–2022.
Reichl P, Haider C, Grubinger M, Mikulits W . TGF-beta in epithelial to mesenchymal transition and metastasis of liver carcinoma. Curr Pharm Des 2012; 18: 4135–4147.
Fransvea E, Mazzocca A, Antonaci S, Giannelli G . Targeting transforming growth factor (TGF)-betaRI inhibits activation of beta1 integrin and blocks vascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2009; 49: 839–850.
Mazzocca A, Fransvea E, Lavezzari G, Antonaci S, Giannelli G . Inhibition of transforming growth factor beta receptor I kinase blocks hepatocellular carcinoma growth through neo-angiogenesis regulation. Hepatology 2009; 50: 1140–1151.
Mazzocca A, Fransvea E, Dituri F, Lupo L, Antonaci S, Giannelli G . Down-regulation of connective tissue growth factor by inhibition of transforming growth factor beta blocks the tumor-stroma cross-talk and tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2010; 51: 523–534.
Lin TH, Shao YY, Chan SY, Huang CY, Hsu CH, Cheng AL . High serum transforming growth factor-beta1 levels predict outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with sorafenib. Clin Cancer Res 2015; 21: 3678–3684.
Giannelli G, Villa E, Lahn M . Transforming growth factor-beta as a therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 2014; 74: 1890–1894.
Wei D, Wang L, Yan Y, Jia Z, Gagea M, Li Z et al. KLF4 is essential for induction of cellular Identity change and acinar-to-ductal reprogramming during early pancreatic carcinogenesis. Cancer Cell 2016; 29: 324–338.
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Liu Y, Wang N, Qi Y, Du J . Kruppel-like factor 4 transcriptionally regulates TGF-beta1 and contributes to cardiac myofibroblast differentiation. PLoS One 2013; 8: e63424.
Feinberg MW, Cao Z, Wara AK, Lebedeva MA, Senbanerjee S, Jain MK . Kruppel-like factor 4 is a mediator of proinflammatory signaling in macrophages. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 38247–38258.
Ding B, Liu P, Liu W, Sun P, Wang CL . Emerging roles of kruppel-like factor 4 in cancer and cancer stem cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2015; 16: 3629–3633.
Lin ZS, Chu HC, Yen YC, Lewis BC, Chen YW . Kruppel-like factor 4, a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma cells reverts epithelial mesenchymal transition by suppressing slug expression. PLoS One 2012; 7: e43593.
Hu B, Wu Z, Liu T, Ullenbruch MR, Jin H, Phan SH . Gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor interaction with Smad3 inhibits myofibroblast differentiation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2007; 36: 78–84.
Shields JM, Yang VW . Identification of the DNA sequence that interacts with the gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor. Nucleic Acids Res 1998; 26: 796–802.
Fleming NI, Jorissen RN, Mouradov D, Christie M, Sakthianandeswaren A, Palmieri M et al. SMAD2, SMAD3 and SMAD4 mutations in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 725–735.
Chen YW, Hsiao PJ, Weng CC, Kuo KK, Kuo TL, Wu DC et al. SMAD4 loss triggers the phenotypic changes of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. BMC Cancer 2014; 14: 181.
Matsuzaki K, Date M, Furukawa F, Tahashi Y, Matsushita M, Sakitani K et al. Autocrine stimulatory mechanism by transforming growth factor beta in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 1394–1402.
Mima K, Okabe H, Ishimoto T, Nakagawa S, Hayashi H, Kuroki H et al. CD44s regulates the TGF-beta-mediated mesenchymal phenotype and is associated with poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 3414–3423.
Morris SM, Baek JY, Koszarek A, Kanngurn S, Knoblaugh SE, Grady WM . Transforming growth factor-beta signaling promotes hepatocarcinogenesis induced by p53 loss. Hepatology 2012; 55: 121–131.
Li Q, Gao Y, Jia Z, Mishra L, Guo K, Li Z et al. Dysregulated Kruppel-like factor 4 and vitamin D receptor signaling contribute to progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012; 143: e1–e2.
Wei D, Kanai M, Jia Z, Le X, Xie K . Kruppel-like factor 4 induces p27Kip1 expression in and suppresses the growth and metastasis of human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 4631–4639.
Yan X, Chen YG . Smad7: not only a regulator, but also a cross-talk mediator of TGF-beta signalling. Biochem J 2011; 434: 1–10.
Stolfi C, Marafini I, De Simone V, Pallone F, Monteleone G . The dual role of Smad7 in the control of cancer growth and metastasis. Int J Mol Sci 2013; 14: 23774–23790.
Park YN, Chae KJ, Oh BK, Choi J, Choi KS, Park C . Expression of Smad7 in hepatocellular carcinoma and dysplastic nodules: resistance mechanism to transforming growth factor-beta. Hepatogastroenterology 2004; 51: 396–400.
Xia H, Ooi LL, Hui KM . MicroRNA-216a/217-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition targets PTEN and SMAD7 to promote drug resistance and recurrence of liver cancer. Hepatology 2013; 58: 629–641.
Wang J, Zhao J, Chu ES, Mok MT, Go MY, Man K et al. Inhibitory role of Smad7 in hepatocarcinogenesis in mice and in vitro. J Pathol 2013; 230: 441–452.
von Gersdorff G, Susztak K, Rezvani F, Bitzer M, Liang D, Böttinger EP . Smad3 and Smad4 mediate transcriptional activation of the human Smad7 promoter by transforming growth factor beta. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 11320–11326.
Sun HC, Li M, Lu JL, Yan DW, Zhou CZ, Fan JW et al. Overexpression of Forkhead box M1 protein associates with aggressive tumor features and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep 2011; 25: 1533–1539.
Zhou A, Lin K, Zhang S, Chen Y, Zhang N, Xue J et al. Nuclear GSK3β promotes tumorigenesis by phosphorylating KDM1A and inducing its deubiquitylation by USP22. Nat Cell Biol 2016; 18: 954–966.
Zhang N, Wei P, Gong A, Chiu WT, Lee HT, Colman H et al. FoxM1 promotes β-catenin nuclear localization and controls Wnt target-gene expression and glioma tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2011; 20: 427–442.
Acknowledgements
We thank Don Norwood for editorial comments. The work is supported in part by grants R01-CA129956 and R01-CA148954 from the National Institutes of Health (K Xie), grant #81101623 from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and grant #81101623 and #81672846 from Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (H Sun).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, H., Peng, Z., Tang, H. et al. Loss of KLF4 and consequential downregulation of Smad7 exacerbate oncogenic TGF-β signaling in and promote progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 36, 2957–2968 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.447
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.447
This article is cited by
-
KLF4 transcription factor in tumorigenesis
Cell Death Discovery (2023)
-
Prognostic significance of KLF4 in solid tumours: an updated meta-analysis
BMC Cancer (2022)
-
GTSE1 promotes tumor growth and metastasis by attenuating of KLF4 expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Laboratory Investigation (2022)
-
Multi-omics data integration reveals novel drug targets in hepatocellular carcinoma
BMC Genomics (2021)
-
Expression and function of Smad7 in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2021)