Abstract
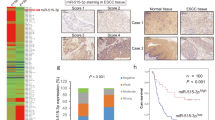
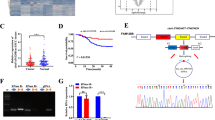
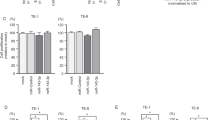
Based on its marked overexpression in multiple malignancies and its roles in promoting cell survival and proliferation, survivin is an attractive candidate for targeted therapy. Toward this end, a detailed understanding of the mechanisms regulating survivin expression in different cancer cells will be critical. We have previously shown that the RNA-binding protein (RBP) CUG-BP1 is overexpressed in esophageal cancer cells and post-transcriptionally regulates survivin in these cells. The objective of this study was to investigate the role of microRNAs (miRs) in regulating survivin expression in esophageal cancer cells. Using miR expression profiling analysis, we found that miR-214-3p is one of the most markedly downregulated miRs in two esophageal squamous cancer cell lines compared with esophageal epithelial cells. Interestingly, using miR target prediction programs, both survivin and CUG-BP1 mRNA were found to contain potential binding sites for miR-214-3p. Forced expression of miR-214-3p in esophageal cancer cells leads to a decrease in the mRNA and protein levels of both survivin and CUG-BP1. This effect is due to decreased mRNA stability of both targets. By contrast, silencing miR-214-3p in esophageal epithelial cells leads to an increase in both survivin and CUG-BP1 mRNA and protein. To determine whether the observed effect of miR-214-3p on survivin expression was direct, mediated through CUG-BP1, or both, binding studies utilizing biotin pull-down assays and heterologous luciferase reporter constructs were performed. These demonstrated that the mRNA of survivin and CUG-BP1 each contain two functional miR-214-3p-binding sites as confirmed by mutational analysis. Finally, forced expression of miR-214-3p enhances the sensitivity of esophageal cancer cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis. This effect is abrogated with rescue expression of survivin or CUG-BP1. These findings suggest that miR-214-3p acts as a tumor suppressor and that its downregulation contributes to chemoresistance in esophageal cancer cells by targeting both survivin and CUG-BP1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Kaufmann SH, Vaux DL . Alterations in the apoptotic machinery and their potential role in anticancer drug resistance. Oncogene 2003; 22: 7414–7430.
Mita AC, Mita MM, Nawrocki ST, Giles FJ . Survivin key regulator of mitosis and apoptosis and novel target for cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 5000–5005.
Kato J, Kuwabara Y, Mitani M, Shinoda N, Sato A, Toyama T et al. Expression of survivin in esophageal cancer: correlation with the prognosis and response to chemotherapy. Int J Cancer 2001; 95: 92–95.
Chang E, Donahue J, Smith A, Hornick J, Rao JN, Wang JY et al. Loss of p53, rather than beta-catenin overexpression, induces survivin-mediated resistance to apoptosis in an esophageal cancer cell line. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2010; 140: 225–232.
Vallböhmer D, Kuhn E, Warnecke-Eberz U, Brabender J, Hoffmann AC, Metzger R et al. Failure in downregulation of intratumoral survivin expression following neoadjuvant chemoradiation in esophageal cancer. Pharmacogenomics 2008; 9: 681–690.
Audic Y, Hartley RS . Post-transcriptional regulation in cancer. Biol Cell 2004; 96: 479–498.
Di Leva G, Garofalo M, Croce CM . MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 2014; 9: 287–314.
Cheetham SW, Gruhl F, Mattick JS, Dinger ME . Long noncoding RNAs and the genetics of cancer. Br J Cancer 2013; 108: 2419–2425.
Keene JD . RNA regulons: coordination of post-transcriptional events. Nat Rev Genet 2007; 8: 533–543.
Chang ET, Donahue JM, Xiao L, Cui Y, Rao JN, Turner DJ et al. The RNA-binding protein CUG-BP1increases survivin expression in oesophageal cancer cells through enhanced mRNA stability. Biochem J 2012; 446: 113–123.
Cao W, Fan R, Wang L, Cheng S, Li H, Jiang J et al. Expression and regulatory function of miRNA-34a in targeting survivin in gastric cancer cells. Tumor Boil 2013; 34: 963–971.
Shen Z, Zhan G, Ye D, Ren Y, Cheng L, Wu Z et al. MicroRNA-34a affects the occurrence of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting the antiapoptotic gene survivin. Med Oncol 2012; 29: 2473–2480.
Saini S, Majid S, Yamamura S, Tabatabai L, Suh SO, Shahryari V et al. Regulatory role of mir-203 in prostate cancer progression and metastasis. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 5287–5298.
Xu D, Wang Q, An Y, Xu L . MiR-203 regulates the proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle progression of pancreatic cancer cells by targeting Survivin. Mol Med Rep 2013; 8: 379–384.
Wei W, Wanjun L, Hui S, Dongyue C, Xinjun Y, Jisheng Z . miR-203 inhibits proliferation of HCC cells by targeting survivin. Cell Biochem Funct 2013; 31: 82–85.
Donahue JM, Chang ET, Xiao L, Wang PY, Rao JN, Turner DJ et al. The RNA-binding protein HuR stabilizes survivin mRNA in human oesophageal epithelial cells. Biochem J 2011; 437: 89–96.
Matsushima K, Isomoto H, Kohno S, Nakao K . MicroRNAs and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Digestion 2010; 82: 138–144.
Huang SD, Yuan Y, Zhuang CW, Li BL, Gong DJ, Wang SG et al. MicroRNA-98 and microRNA-214 post-transcriptionally regulate enhancer of zeste homolog 2 and inhibit migration and invasion in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer 2012; 11: 51–61.
Ciafrè SA, Galardi S . MicroRNAs and RNA-binding proteins: a complex network of interactions and reciprocal regulations in cancer. RNA Biol 2013; 10: 935–942.
Cui YH, Xiao L, Rao JN, Zou T, Liu L, Chen Y et al. miR-503 represses CUG-binding protein 1 translation by recruiting CUGBP1 mRNA to processing bodies. Mol Biol Cell 2012; 23: 151–162.
Yang H, Kong W, He L, Zhao JJ, O'Donnell JD, Wang J et al. MicroRNA expression profiling in human ovarian cancer: miR-214 induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 425–433.
Zhang ZC, Li YY, Wang HY, Fu S, Wang XP, Zeng MS et al. Knockdown of miR-214 promotes apoptosis and inhibits cell proliferation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One 2014; 9: 1–10.
Duan Q, Wang X, Gong W, Ni L, Chen C, He X et al. ER stress negatively modulates the expression of the miR-199a/214 cluster to regulates tumor survival and progression in human hepatocellular cancer. PLoS One 2012; 7: 1–10.
Wang F, Liu M, Li X, Tang H . MiR-214 reduces cell survival and enhances cisplatin-Induced cytotoxicity via down-regulation of Bcl2l2 in cervical cancer cells. FEBS Lett 2013; 587: 488–495.
Xia H, Ooi LL, Hui KM . MiR-214 targets β-catenin pathway to suppress invasion, stem-like traits and recurrence of human hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One 2012; 7: 1–13.
Talwar S, Balasubramanian S, Sundaramurthy S, House R, Wilusz CJ, Kuppuswamy D et al. Overexpression of RNA-binding protein CELF1 prevents apoptosis and destabilizes pro-apoptotic mRNAs in oral cancer cells. RNA Biol 2013; 10: 277–286.
Gareau C, Fournier MJ, Filion C, Coudert L, Martel D, Labelle Y et al. p21(WAF1/ CIP1) upregulation through the stress granule-associated protein CUGBP1 confers resistance to bortezomib-mediated apoptosis. PLoS One 2011; 6: 1–14.
Richie ME, Silver S, Oshlack A, Holmes M, Diyagama D, Holloway A et al. A comparison of background correction methods for two-colour microarrays. Bioinformatics 2007; 23: 2700–2707.
Smyth GK . Limma linear models for microarray data. In: Gentleman R, Carey V, Huber W, Irizarry R, Dudoit S (eds). Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions using R and Bioconductor. Springer: New York,, 2005, pp 397–420.
Brennan SE, Kuwano Y, Alkharouf N, Blackshear PJ, Gorospe M, Wilson GM . The mRNA-Destabilizing protein tristeraprolin is suppresses in many cancers, altering tumorigenic phenotypes and patient prognosis. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 5168–5176.
Orom UA, Lund AH . Isolation of microRNA targets using biotinylated synthetic microRNAs. Methods 2007; 43: 162–165.
Choi YE, Pan Y, Park E, Konstantinopoulos P, De S, D’Andrea A et al. MicroRNAs down-regulate homologous recombination in the G1 phase of cycling cells to maintain genomic stability. eLIFE 2014; 3: e02445.
Liu L, Rao JN, Zou T, Xiao L, Wang PY, Turner DJ et al. Polyamines regulate c-Myc translation through Chk2-dependent HuR phosphorylation. Mol Biol Cell 2009; 20: 4885–4898.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Department of Veterans Affairs, USA (Merit Review Grants to JNR, DJT and J-YW; VA Career Development Award to JMD); the National Institutes of Health (grant numbers DK-57819, DK-61972 and DK-68491 to J-YW) and departmental funds from the Department of Surgery, University of Maryland School of Medicine (to JMD). The authors also acknowledge Dr Karthika Natarajan, Dr Xi Yang and Ratnakar Potla for their technical assistance as well as Dr Anne W Hamburger for assistance in preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phatak, P., Byrnes, K., Mansour, D. et al. Overexpression of miR-214-3p in esophageal squamous cancer cells enhances sensitivity to cisplatin by targeting survivin directly and indirectly through CUG-BP1. Oncogene 35, 2087–2097 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.271
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.271
This article is cited by
-
NGS-based profiling identifies miRNAs and pathways dysregulated in cisplatin-resistant esophageal cancer cells
Functional & Integrative Genomics (2023)
-
MiR-214-3p targets Ras-related protein 14 (RAB14) to inhibit cellular migration and invasion in esophageal Cancer cells
BMC Cancer (2022)
-
KLF5 inhibition overcomes oxaliplatin resistance in patient-derived colorectal cancer organoids by restoring apoptotic response
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
Molecular mechanisms associated with chemoresistance in esophageal cancer
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
The Effect of miR-98 and miR-214 on Apoptotic and Angiogenic Pathways in Hepatocellular Carcinoma HepG2 Cells
Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry (2020)