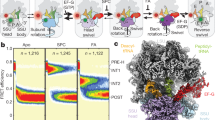
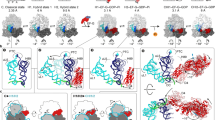
Abstract
During protein synthesis, mRNA and tRNAs must be moved rapidly through the ribosome while maintaining the translational reading frame. This process is coupled to large- and small-scale conformational rearrangements in the ribosome, mainly in its rRNA. The free energy from peptide-bond formation and GTP hydrolysis is probably used to impose directionality on those movements. We propose that the free energy is coupled to two pawls, namely tRNA and EF-G, which enable two ratchet mechanisms to act separately and sequentially on the two ribosomal subunits.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogle, J.M. et al. Recognition of cognate transfer RNA by the 30S ribosomal subunit. Science 292, 897–902 (2001).
Demeshkina, N., Jenner, L., Westhof, E., Yusupov, M. & Yusupova, G. A new understanding of the decoding principle on the ribosome. Nature 484, 256–259 (2012).
Nissen, P., Hansen, J., Ban, N., Moore, P.B. & Steitz, T.A. The structural basis of ribosome activity in peptide bond synthesis. Science 289, 920–930 (2000).
Frank, J. & Agrawal, R.K. A ratchet-like inter-subunit reorganization of the ribosome during translocation. Nature 406, 318–322 (2000).
Horan, L.H. & Noller, H.F. Intersubunit movement is required for ribosomal translocation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 4881–4885 (2007).
Moazed, D. & Noller, H.F. Intermediate states in the movement of transfer RNA in the ribosome. Nature 342, 142–148 (1989).
Cornish, P.V., Ermolenko, D.N., Noller, H.F. & Ha, T. Spontaneous intersubunit rotation in single ribosomes. Mol. Cell 30, 578–588 (2008).
Sharma, H. et al. Kinetics of spontaneous and EF-G-accelerated rotation of ribosomal subunits. Cell Rep. 16, 2187–2196 (2016).
Gavrilova, L.P., Kostiashkina, O.E., Koteliansky, V.E., Rutkevitch, N.M. & Spirin, A.S. Factor-free (“non-enzymic”) and factor-dependent systems of translation of polyuridylic acid by Escherichia coli ribosomes. J. Mol. Biol. 101, 537–552 (1976).
Gavrilova, L.P. & Spirin, A.S. Stimulation of “non-enzymic” translocation in ribosomes by p-chloromercuribenzoate. FEBS Lett. 17, 324–326 (1971).
Fredrick, K. & Noller, H.F. Catalysis of ribosomal translocation by sparsomycin. Science 300, 1159–1162 (2003).
Schuwirth, B.S. et al. Structures of the bacterial ribosome at 3.5 A resolution. Science 310, 827–834 (2005).
Spahn, C.M. et al. Domain movements of elongation factor eEF2 and the eukaryotic 80S ribosome facilitate tRNA translocation. EMBO J. 23, 1008–1019 (2004).
Ratje, A.H. et al. Head swivel on the ribosome facilitates translocation by means of intra-subunit tRNA hybrid sites. Nature 468, 713–716 (2010).
Zhou, J., Lancaster, L., Donohue, J.P. & Noller, H.F. Crystal structures of EF-G-ribosome complexes trapped in intermediate states of translocation. Science 340, 1236086 (2013).
Ramrath, D.J. et al. Visualization of two transfer RNAs trapped in transit during elongation factor G-mediated translocation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 20964–20969 (2013).
Zhou, J., Lancaster, L., Donohue, J.P. & Noller, H.F. How the ribosome hands the A-site tRNA to the P site during EF-G-catalyzed translocation. Science 345, 1188–1191 (2014).
Mohan, S. & Noller, H.F. Recurring RNA structural motifs underlie the mechanics of L1 stalk movement. Nat. Commun. 8, 14285 (2017).
Bock, L.V., Blau, C., Vaiana, A.C. & Grubmüller, H. Dynamic contact network between ribosomal subunits enables rapid large-scale rotation during spontaneous translocation. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, 6747–6760 (2015).
Mohan, S., Donohue, J.P. & Noller, H.F. Molecular mechanics of 30S subunit head rotation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, 13325–13330 (2014).
Lescoute, A. & Westhof, E. Topology of three-way junctions in folded RNAs. RNA 12, 83–93 (2006).
Réblová, K., Sponer, J. & Lankas, F. Structure and mechanical properties of the ribosomal L1 stalk three-way junction. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, 6290–6303 (2012).
Trabuco, L.G. et al. The role of L1 stalk-tRNA interaction in the ribosome elongation cycle. J. Mol. Biol. 402, 741–760 (2010).
Fei, J., Kosuri, P., MacDougall, D.D. & Gonzalez, R.L. Jr. Coupling of ribosomal L1 stalk and tRNA dynamics during translation elongation. Mol. Cell 30, 348–359 (2008).
Cornish, P.V. et al. Following movement of the L1 stalk between three functional states in single ribosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 2571–2576 (2009).
Valle, M. et al. Incorporation of aminoacyl-tRNA into the ribosome as seen by cryo-electron microscopy. Nat. Struct. Biol. 10, 899–906 (2003).
Schmeing, T.M. et al. The crystal structure of the ribosome bound to EF-Tu and aminoacyl-tRNA. Science 326, 688–694 (2009).
Korostelev, A., Trakhanov, S., Laurberg, M. & Noller, H.F. Crystal structure of a 70S ribosome-tRNA complex reveals functional interactions and rearrangements. Cell 126, 1065–1077 (2006).
Lill, R., Robertson, J.M. & Wintermeyer, W. Affinities of tRNA binding sites of ribosomes from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 25, 3245–3255 (1986).
Yusupov, M.M. et al. Crystal structure of the ribosome at 5.5 A resolution. Science 292, 883–896 (2001).
Selmer, M. et al. Structure of the 70S ribosome complexed with mRNA and tRNA. Science 313, 1935–1942 (2006).
Liu, Q. & Fredrick, K. Contribution of intersubunit bridges to the energy barrier of ribosomal translocation. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, 565–574 (2013).
Komoda, T. et al. The A-site finger in 23 S rRNA acts as a functional attenuator for translocation. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 32303–32309 (2006).
Wasserman, M.R., Alejo, J.L., Altman, R.B. & Blanchard, S.C. Multiperspective smFRET reveals rate-determining late intermediates of ribosomal translocation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 23, 333–341 (2016).
Spirin, A.S. [On the mechanism of ribosome function. The hypothesis of locking-unlocking of subparticles]. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 179, 1467–1470 (1968).
Savelsbergh, A. et al. An elongation factor G-induced ribosome rearrangement precedes tRNA-mRNA translocation. Mol. Cell 11, 1517–1523 (2003).
Gao, Y.G. et al. The structure of the ribosome with elongation factor G trapped in the posttranslocational state. Science 326, 694–699 (2009).
Khade, P.K. & Joseph, S. Messenger RNA interactions in the decoding center control the rate of translocation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 18, 1300–1302 (2011).
Liu, G. et al. EF-G catalyzes tRNA translocation by disrupting interactions between decoding center and codon-anticodon duplex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 21, 817–824 (2014).
Samaha, R.R., Green, R. & Noller, H.F. A base pair between tRNA and 23S rRNA in the peptidyl transferase centre of the ribosome. Nature 377, 309–314 (1995).
Kim, D.F. & Green, R. Base-pairing between 23S rRNA and tRNA in the ribosomal A site. Mol. Cell 4, 859–864 (1999).
Julián, P. et al. Structure of ratcheted ribosomes with tRNAs in hybrid states. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 16924–16927 (2008).
Agirrezabala, X. et al. Visualization of the hybrid state of tRNA binding promoted by spontaneous ratcheting of the ribosome. Mol. Cell 32, 190–197 (2008).
Wang, L., Altman, R.B. & Blanchard, S.C. Insights into the molecular determinants of EF-G catalyzed translocation. RNA 17, 2189–2200 (2011).
Woese, C. Molecular mechanics of translation: a reciprocating ratchet mechanism. Nature 226, 817–820 (1970).
Spirin, A.S. The ribosome as a conveying thermal ratchet machine. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 21103–21119 (2009).
Frank, J. & Gonzalez, R.L. Jr. Structure and dynamics of a processive Brownian motor: the translating ribosome. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 79, 381–412 (2010).
Spirin, A.S. Ribosomal translocation: facts and models. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 32, 75–114 (1985).
Dorner, S., Brunelle, J.L., Sharma, D. & Green, R. The hybrid state of tRNA binding is an authentic translation elongation intermediate. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13, 234–241 (2006).
Dunkle, J.A. et al. Structures of the bacterial ribosome in classical and hybrid states of tRNA binding. Science 332, 981–984 (2011).
Brilot, A.F., Korostelev, A.A., Ermolenko, D.N. & Grigorieff, N. Structure of the ribosome with elongation factor G trapped in the pretranslocation state. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 20994–20999 (2013).
Lin, J., Gagnon, M.G., Bulkley, D. & Steitz, T.A. Conformational changes of elongation factor G on the ribosome during tRNA translocation. Cell 160, 219–227 (2015).
Salsi, E., Farah, E., Netter, Z., Dann, J. & Ermolenko, D.N. Movement of elongation factor G between compact and extended conformations. J. Mol. Biol. 427, 454–467 (2015).
Belardinelli, R. et al. Choreography of molecular movements during ribosome progression along mRNA. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 23, 342–348 (2016).
Tourigny, D.S., Fernández, I.S., Kelley, A.C. & Ramakrishnan, V. Elongation factor G bound to the ribosome in an intermediate state of translocation. Science 340, 1235490 (2013).
Jenner, L.B., Demeshkina, N., Yusupova, G. & Yusupov, M. Structural aspects of messenger RNA reading frame maintenance by the ribosome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 17, 555–560 (2010).
Guo, Z. & Noller, H.F. Rotation of the head of the 30S ribosomal subunit during mRNA translocation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 20391–20394 (2012).
Ermolenko, D.N. & Noller, H.F. mRNA translocation occurs during the second step of ribosomal intersubunit rotation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 18, 457–462 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noller, H., Lancaster, L., Zhou, J. et al. The ribosome moves: RNA mechanics and translocation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 24, 1021–1027 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3505
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3505
This article is cited by
-
Fine-tuning fungal effector secretion
Nature Microbiology (2023)
-
A model for ribosome translocation based on the alternated displacement of its subunits
European Biophysics Journal (2023)
-
Specific length and structure rather than high thermodynamic stability enable regulatory mRNA stem-loops to pause translation
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Electron microscopy holdings of the Protein Data Bank: the impact of the resolution revolution, new validation tools, and implications for the future
Biophysical Reviews (2022)
-
Structural basis for +1 ribosomal frameshifting during EF-G-catalyzed translocation
Nature Communications (2021)