Abstract
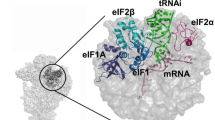
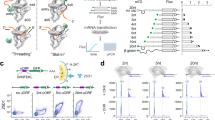
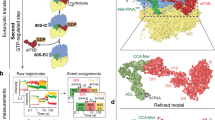
Initiation factors guide the ribosome in the selection of mRNA and translational reading frame. We determined the kinetically favored assembly pathway of the 30S preinitiation complex (30S PIC), an early intermediate in 30S initiation complex formation in Escherichia coli. IF3 and IF2 are the first factors to arrive, forming an unstable 30S–IF2–IF3 complex. Subsequently, IF1 joins and locks the factors in a kinetically stable 30S PIC to which fMet-tRNAfMet is recruited. Binding of mRNA is independent of initiation factors and can take place at any time during 30S PIC assembly, depending on the cellular concentration of the mRNA and the structural determinants at the ribosome-binding site. The kinetic analysis shows both specific and cumulative effects of initiation factors as well as kinetic checkpoints of mRNA selection at the entry into translation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gualerzi, C.O. et al. Initiation factors in the early events of mRNA translation in bacteria. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 66, 363–376 (2001).
Laursen, B.S., Sorensen, H.P., Mortensen, K.K. & Sperling-Petersen, H.U. Initiation of protein synthesis in bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 69, 101–123 (2005).
Simonetti, A. et al. A structural view of translation initiation in bacteria. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 66, 423–436 (2009).
Milón, P. et al. The ribosome-bound initiation factor 2 recruits initiator tRNA to the 30S initiation complex. EMBO Rep. 11, 312–316 (2010).
Antoun, A., Pavlov, M.Y., Lovmar, M. & Ehrenberg, M. How initiation factors tune the rate of initiation of protein synthesis in bacteria. EMBO J. 25, 2539–2550 (2006).
Grigoriadou, C., Marzi, S., Kirillov, S., Gualerzi, C.O. & Cooperman, B.S. A quantitative kinetic scheme for 70 S translation initiation complex formation. J. Mol. Biol. 373, 562–572 (2007).
Milón, P., Konevega, A.L., Gualerzi, C.O. & Rodnina, M.V. Kinetic checkpoint at a late step in translation initiation. Mol. Cell 30, 712–720 (2008).
Marshall, R.A., Aitken, C.E. & Puglisi, J.D. GTP hydrolysis by IF2 guides progression of the ribosome into elongation. Mol. Cell 35, 37–47 (2009).
Tomsic, J. et al. Late events of translation initiation in bacteria: a kinetic analysis. EMBO J. 19, 2127–2136 (2000).
Studer, S.M. & Joseph, S. Unfolding of mRNA secondary structure by the bacterial translation initiation complex. Mol. Cell 22, 105–115 (2006).
Calogero, R.A., Pon, C.L., Canonaco, M.A. & Gualerzi, C.O. Selection of the mRNA translation initiation region by Escherichia coli ribosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 6427–6431 (1988).
Grigoriadou, C., Marzi, S., Pan, D., Gualerzi, C.O. & Cooperman, B.S. The translational fidelity function of IF3 during transition from the 30 S initiation complex to the 70 S initiation complex. J. Mol. Biol. 373, 551–561 (2007).
La Teana, A., Gualerzi, C.O. & Brimacombe, R. From stand-by to decoding site. Adjustment of the mRNA on the 30S ribosomal subunit under the influence of the initiation factors. RNA 1, 772–782 (1995).
Milón, P. et al. Transient kinetics, fluorescence, and FRET in studies of initiation of translation in bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 430, 1–30 (2007).
Julián, P. et al. The cryo-EM structure of a complete 30S translation initiation complex from Escherichia coli. PLoS Biol. 9, e1001095 (2011).
Celano, B., Pawlik, R.T. & Gualerzi, C.O. Interaction of Escherichia coli translation-initiation factor IF-1 with ribosomes. Eur. J. Biochem. 178, 351–355 (1988).
Zucker, F.H. & Hershey, J.W. Binding of Escherichia coli protein synthesis initiation factor IF1 to 30S ribosomal subunits measured by fluorescence polarization. Biochemistry 25, 3682–3690 (1986).
Misselwitz, R. et al. The fMet-tRNA binding domain of translational initiation factor IF2: role and environment of its two Cys residues. FEBS Lett. 459, 332–336 (1999).
Weiel, J. & Hershey, J.W. The binding of fluorescein-labeled protein synthesis initiation factor 2 to Escherichia coli 30 S ribosomal subunits determined by fluorescence polarization. J. Biol. Chem. 257, 1215–1220 (1982).
Petrelli, D. et al. Translation initiation factor IF3: two domains, five functions, one mechanism? EMBO J. 20, 4560–4569 (2001).
Karimi, R., Pavlov, M.Y., Buckingham, R.H. & Ehrenberg, M. Novel roles for classical factors at the interface between translation termination and initiation. Mol. Cell 3, 601–609 (1999).
Peske, F., Rodnina, M.V. & Wintermeyer, W. Sequence of steps in ribosome recycling as defined by kinetic analysis. Mol. Cell 18, 403–412 (2005).
Antoun, A., Pavlov, M.Y., Lovmar, M. & Ehrenberg, M. How initiation factors maximize the accuracy of tRNA selection in initiation of bacterial protein synthesis. Mol. Cell 23, 183–193 (2006).
Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 3406–3415 (2003).
Bremer, H. & Dennis, P.P. Modulation of chemical composition and other parameters of the cell by growth rate. in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Cellular and Molecular Biology (ed. Neidherdt, F.C.) 1527–1542 (American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, 1987).
Passalacqua, K.D. et al. Structure and complexity of a bacterial transcriptome. J. Bacteriol. 191, 3203–3211 (2009).
Yusupova, G., Jenner, L., Rees, B., Moras, D. & Yusupov, M. Structural basis for messenger RNA movement on the ribosome. Nature 444, 391–394 (2006).
Kudla, G., Murray, A.W., Tollervey, D. & Plotkin, J.B. Coding-sequence determinants of gene expression in Escherichia coli. Science 324, 255–258 (2009).
Carter, A.P. et al. Crystal structure of an initiation factor bound to the 30S ribosomal subunit. Science 291, 498–501 (2001).
Qin, D. & Fredrick, K. Control of translation initiation involves a factor-induced rearrangement of helix 44 of 16S ribosomal RNA. Mol. Microbiol. 71, 1239–1249 (2009).
Kapralou, S. et al. Translation initiation factor IF1 of Bacillus stearothermophilus and Thermus thermophilus substitute for Escherichia coli IF1 in vivo and in vitro without a direct IF1–IF2 interaction. Mol. Microbiol. 70, 1368–1377 (2008).
Caserta, E. et al. Translation initiation factor IF2 interacts with the 30 S ribosomal subunit via two separate binding sites. J. Mol. Biol. 362, 787–799 (2006).
Belotserkovsky, J.M., Dabbs, E.R. & Isaksson, L.A. Mutations in 16S rRNA that suppress cold-sensitive initiation factor 1 affect ribosomal subunit association. FEBS J. 278, 3508–3517 (2011).
Qin, D., Abdi, N.M. & Fredrick, K. Characterization of 16S rRNA mutations that decrease the fidelity of translation initiation. RNA 13, 2348–2355 (2007).
Surkov, S., Nilsson, H., Rasmussen, L.C., Sperling-Petersen, H.U. & Isaksson, L.A. Translation initiation region dependency of translation initiation in Escherichia coli by IF1 and kasugamycin. FEBS J. 277, 2428–2439 (2010).
McCarthy, J.E. & Gualerzi, C. Translational control of prokaryotic gene expression. Trends Genet. 6, 78–85 (1990).
Marzi, S. et al. Structured mRNAs regulate translation initiation by binding to the platform of the ribosome. Cell 130, 1019–1031 (2007).
Rodnina, M.V. & Wintermeyer, W. GTP consumption of elongation factor Tu during translation of heteropolymeric mRNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 1945–1949 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank W. Wintermeyer for critically reading and shortening the manuscript, C. Kothe for doing some stopped-flow experiments and O. Geintzer, S. Kappler, C. Kothe and T. Wiles for expert technical assistance. We also thank the participants of the methods course on transient kinetics of the Göttingen Graduate School for Neurosciences, Biophysics and Molecular Biosciences for doing some stopped-flow experiments. This work was supported by grants of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (M.V.R.) and Italian Ministero dell′Instruzione, dell′Universitá e della Ricerca (C.O.G.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.M., C.O.G. and M.V.R. conceived the research. P.M. and M.V.R. designed the experiments and analyzed the data. P.M., C.M. and L.F. prepared materials and conducted experiments. P.M., C.O.G. and M.V.R. wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–5 and Supplementary Tables 1–3 (PDF 428 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milón, P., Maracci, C., Filonava, L. et al. Real-time assembly landscape of bacterial 30S translation initiation complex. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19, 609–615 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2285
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2285
This article is cited by
-
Direct measurements of mRNA translation kinetics in living cells
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Multiplexed genomic encoding of non-canonical amino acids for labeling large complexes
Nature Chemical Biology (2020)
-
Taxonomic and functional characterization of a microbial community from a volcanic englacial ecosystem in Deception Island, Antarctica
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
A conformational switch in initiation factor 2 controls the fidelity of translation initiation in bacteria
Nature Communications (2017)
-
Deep sequencing reveals global patterns of mRNA recruitment during translation initiation
Scientific Reports (2016)