Abstract
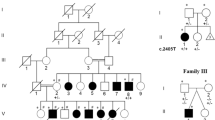
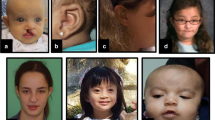
We found mutations in the gene PQBP1 in 5 of 29 families with nonsyndromic (MRX) and syndromic (MRXS) forms of X-linked mental retardation (XLMR). Clinical features in affected males include mental retardation, microcephaly, short stature, spastic paraplegia and midline defects. PQBP1 has previously been implicated in the pathogenesis of polyglutamine expansion diseases. Our findings link this gene to XLMR and shed more light on the pathogenesis of this common disorder.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others

References
Ropers, H.H. et al. Trends Genet. 19, 316–320 (2003).
Sutherland, G.R., Gedeon, A.K., Haan, E.A., Woodroffe, P. & Mulley, J.C. Am. J. Med. Genet. 30, 493–508 (1988).
Deqaqi, S.C. et al. Ann. Genet. 41, 11–16 (1998).
Hamel, B.C., Mariman, E.C., van Beersum, S.E., Schoonbrood-Lenssen, A.M. & Ropers, H.H. Am. J. Med. Genet. 51, 591–597 (1994).
Iwamoto, K., Huang, Y. & Ueda, S. Gene 259, 69–73 (2000).
Okazawa, H., Sudol, M. & Rich, T. Brain Res. Bull. 56, 273–280 (2001).
Waragai, M. et al. Hum. Mol. Genet. 8, 977–987 (1999).
Komuro, A., Saeki, M. & Kato, S. Nucleic Acids Res. 27, 1957–1965 (1999).
Waragai, M. et al. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 273, 592–595 (2000).
Reuter, K., Nottrott, S., Fabrizio, P., Luhrmann, R. & Ficner, R. J. Mol. Biol. 294, 515–525 (1999).
Okazawa, H. et al. Neuron 34, 701–713 (2002).
Komuro, A., Saeki, M. & Kato, S. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 36513–36519 (1999).
Craggs, G. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 30552–305560 (2001).
Chelly, J. & Mandel, J.L. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2, 669–680 (2001).
Shoichet, S. et al. Am. J. Hum. Genet. (in the press).
Acknowledgements
We thank I. van der Burgt, C. de Die-Smulders, R. Robledo and M. Siniscalco for providing blood from affected individuals; M. Vingron for discussion; R. Reinhardt for support with mutation search; R. McEvilly for the rat Brn-2 cDNA clone; H. Madle and S. Freier for establishing lymphoblastoid cell lines; P. Nierle for help in the initial stage of the mutation screening; and M. Klein, V. Suckow, Z. Kijas, B. Lipkowitz, K. Lower, O. Mckenzie, S. Kübart and M. Mangelsdorf for technical assistance. This work was supported by a grant from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council to J.G., by the Deutsches Humangenom-Programm, by the Nationales Genomforschungsnetzwerk and by the 5th EU Framework.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalscheuer, V., Freude, K., Musante, L. et al. Mutations in the polyglutamine binding protein 1 gene cause X-linked mental retardation. Nat Genet 35, 313–315 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1264
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1264
This article is cited by
-
Molecular consequences of PQBP1 deficiency, involved in the X-linked Renpenning syndrome
Molecular Psychiatry (2023)
-
The Hippo signaling component LATS2 enhances innate immunity to inhibit HIV-1 infection through PQBP1-cGAS pathway
Cell Death & Differentiation (2022)
-
Emerging roles of spliceosome in cancer and immunity
Protein & Cell (2022)
-
Tau activates microglia via the PQBP1-cGAS-STING pathway to promote brain inflammation
Nature Communications (2021)
-
PQBP1: A New Player in Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Signaling and Synaptic Plasticity
Neuroscience Bulletin (2021)