Abstract
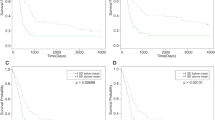
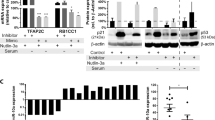
The median survival of patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) ranges from 3 to 5 years with current chemotherapeutic regimens. A common secondary genomic alteration detected in MCL is chromosome 13q31-q32 gain/amplification, which targets a microRNA (miRNA) cluster, miR-17∼92. On the basis of gene expression profiling, we found that high level expression of C13orf25, the primary transcript from which these miRNAs are processed, was associated with poorer survival in patients with MCL (P=0.021). We demonstrated that the protein phosphatase PHLPP2, an important negative regulator of the PI3K/AKT pathway, was a direct target of miR-17∼92 miRNAs, in addition to PTEN and BIM. These proteins were down-modulated in MCL cells with overexpression of the miR-17∼92 cluster. Overexpression of miR-17∼92 activated the PI3K/AKT pathway and inhibited chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in MCL cell lines. Conversely, inhibition of miR-17∼92 expression suppressed the PI3K/AKT pathway and inhibited tumor growth in a xenograft MCL mouse model. Targeting the miR-17∼92 cluster may therefore provide a novel therapeutic approach for patients with MCL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman J . Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 1st edn. IARC Press: Lyon, 2001.
Bosch F, Lopez-Guillermo A, Campo E, Ribera JM, Conde E, Piris MA et al. Mantle cell lymphoma: presenting features, response to therapy, and prognostic factors. Cancer 1998; 82: 567–575.
Tsujimoto Y, Jaffe E, Cossman J, Gorham J, Nowell PC, Croce CM . Clustering of breakpoints on chromosome 11 in human B-cell neoplasms with the t(11;14) chromosome translocation. Nature 1985; 315: 340–343.
Bodrug SE, Warner BJ, Bath ML, Lindeman GJ, Harris AW, Adams JM . Cyclin D1 transgene impedes lymphocyte maturation and collaborates in lymphomagenesis with the myc gene. EMBO J 1994; 13: 2124–2130.
Lovec H, Grzeschiczek A, Kowalski MB, Moroy T . Cyclin D1/bcl-1 cooperates with myc genes in the generation of B-cell lymphoma in transgenic mice. EMBO J 1994; 13: 3487–3495.
Wlodarska I, Pittaluga S, Hagemeijer A, De Wolf-Peeters C, Van Den Berghe H . Secondary chromosome changes in mantle cell lymphoma. Haematologica 1999; 84: 594–599.
Salaverria I, Zettl A, Bea S, Moreno V, Valls J, Hartmann E et al. Specific secondary genetic alterations in mantle cell lymphoma provide prognostic information independent of the gene expression-based proliferation signature. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 1216–1222.
Ota A, Tagawa H, Karnan S, Tsuzuki S, Karpas A, Kira S et al. Identification and characterization of a novel gene, C13orf25, as a target for 13q31-q32 amplification in malignant lymphoma. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 3087–3095.
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S et al. A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature 2005; 435: 828–833.
Hayashita Y, Osada H, Tatematsu Y, Yamada H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S et al. A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 9628–9632.
O’Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang CV, Mendell JT . c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature 2005; 435: 839–843.
Dews M, Homayouni A, Yu D, Murphy D, Sevignani C, Wentzel E et al. Augmentation of tumor angiogenesis by a Myc-activated microRNA cluster. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 1060–1065.
Lu Y, Thomson JM, Wong HY, Hammond SM, Hogan BL . Transgenic over-expression of the microRNA miR-17-92 cluster promotes proliferation and inhibits differentiation of lung epithelial progenitor cells. Dev Biol 2007; 310: 442–453.
Navarro A, Bea S, Fernandez V, Prieto M, Salaverria I, Jares P et al. MicroRNA expression, chromosomal alterations, and immunoglobulin variable heavy chain hypermutations in Mantle cell lymphomas. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 7071–7078.
Ventura A, Young AG, Winslow MM, Lintault L, Meissner A, Erkeland SJ et al. Targeted deletion reveals essential and overlapping functions of the miR-17 through 92 family of miRNA clusters. Cell 2008; 132: 875–886.
Koralov SB, Muljo SA, Galler GR, Krek A, Chakraborty T, Kanellopoulou C et al. Dicer ablation affects antibody diversity and cell survival in the B lymphocyte lineage. Cell 2008; 132: 860–874.
Xiao C, Srinivasan L, Calado DP, Patterson HC, Zhang B, Wang J et al. Lymphoproliferative disease and autoimmunity in mice with increased miR-17-92 expression in lymphocytes. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 405–414.
Rizzatti EG, Falcao RP, Panepucci RA, Proto-Siqueira R, Anselmo-Lima WT, Okamoto OK et al. Gene expression profiling of mantle cell lymphoma cells reveals aberrant expression of genes from the PI3K-AKT, WNT and TGFbeta signalling pathways. Br J Haematol 2005; 130: 516–526.
Ghobrial IM, McCormick DJ, Kaufmann SH, Leontovich AA, Loegering DA, Dai NT et al. Proteomic analysis of mantle-cell lymphoma by protein microarray. Blood 2005; 105: 3722–3730.
Rudelius M, Pittaluga S, Nishizuka S, Pham TH, Fend F, Jaffe ES et al. Constitutive activation of Akt contributes to the pathogenesis and survival of mantle cell lymphoma. Blood 2006; 108: 1668–1676.
Yamanaka Y, Tagawa H, Takahashi N, Watanabe A, Guo YM, Iwamoto K et al. Aberrant overexpression of microRNAs activate AKT signaling via down-regulation of tumor suppressors in natural killer-cell lymphoma/leukemia. Blood 2009; 114: 3265–3275.
Olive V, Bennett MJ, Walker JC, Ma C, Jiang I, Cordon-Cardo C et al. miR-19 is a key oncogenic component of mir-17-92. Genes Dev 2009; 23: 2839–2849.
Rosenwald A, Wright G, Wiestner A, Chan WC, Connors JM, Campo E et al. The proliferation gene expression signature is a quantitative integrator of oncogenic events that predicts survival in mantle cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2003; 3: 185–197.
Lenz G, Wright GW, Emre NC, Kohlhammer H, Dave SS, Davis RE et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma arise by distinct genetic pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 13520–13525.
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 15545–15550.
Legarza K, Yang LX . New molecular mechanisms of action of camptothecin-type drugs. Anticancer Res 2006; 26: 3301–3305.
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB . Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 2003; 115: 787–798.
Ebert MS, Neilson JR, Sharp PA . MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells. Nat Methods 2007; 4: 721–726.
Tagawa H, Seto M . A microRNA cluster as a target of genomic amplification in malignant lymphoma. Leukemia 2005; 19: 2013–2016.
Maehama T, Dixon JE . The tumor suppressor, PTEN/MMAC1, dephosphorylates the lipid second messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 13375–13378.
Andjelkovic M, Jakubowicz T, Cron P, Ming XF, Han JW, Hemmings BA . Activation and phosphorylation of a pleckstrin homology domain containing protein kinase (RAC-PK/PKB) promoted by serum and protein phosphatase inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 5699–5704.
Brognard J, Sierecki E, Gao T, Newton AC . PHLPP and a second isoform, PHLPP2, differentially attenuate the amplitude of Akt signaling by regulating distinct Akt isoforms. Mol Cell 2007; 25: 917–931.
Mendoza MC, Blenis J . PHLPPing it off: phosphatases get in the Akt. Mol Cell 2007; 25: 798–800.
O’Connor L, Strasser A, O’Reilly LA, Hausmann G, Adams JM, Cory S et al. Bim: a novel member of the Bcl-2 family that promotes apoptosis. Embo J 1998; 17: 384–395.
Chen L, Willis SN, Wei A, Smith BJ, Fletcher JI, Hinds MG et al. Differential targeting of prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins by their BH3-only ligands allows complementary apoptotic function. Mol Cell 2005; 17: 393–403.
Willis SN, Fletcher JI, Kaufmann T, van Delft MF, Chen L, Czabotar PE et al. Apoptosis initiated when BH3 ligands engage multiple Bcl-2 homologs, not Bax or Bak. Science 2007; 315: 856–859.
Tagawa H, Karnan S, Suzuki R, Matsuo K, Zhang X, Ota A et al. Genome-wide array-based CGH for mantle cell lymphoma: identification of homozygous deletions of the proapoptotic gene BIM. Oncogene 2005; 24: 1348–1358.
Egle A, Harris AW, Bouillet P, Cory S . Bim is a suppressor of Myc-induced mouse B cell leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 6164–6169.
Stahl M, Dijkers PF, Kops GJ, Lens SM, Coffer PJ, Burgering BM et al. The forkhead transcription factor FoxO regulates transcription of p27Kip1 and Bim in response to IL-2. J Immunol 2002; 168: 5024–5031.
You H, Pellegrini M, Tsuchihara K, Yamamoto K, Hacker G, Erlacher M et al. FOXO3a-dependent regulation of Puma in response to cytokine/growth factor withdrawal. J Exp Med 2006; 203: 1657–1663.
Yusuf I, Zhu X, Kharas MG, Chen J, Fruman DA . Optimal B-cell proliferation requires phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent inactivation of FOXO transcription factors. Blood 2004; 104: 784–787.
Inomata M, Tagawa H, Guo YM, Kameoka Y, Takahashi N, Sawada K . MicroRNA-17-92 down-regulates expression of distinct targets in different B-cell lymphoma subtypes. Blood 2009; 113: 396–402.
Sengupta S, Nie J, Wagner RJ, Yang C, Stewart R, Thomson JA . MicroRNA 92b controls the G1/S checkpoint gene p57 in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 2009; 27: 1524–1528.
Dews M, Fox JL, Hultine S, Sundaram P, Wang W, Liu YY et al. The myc-miR-17∼92 axis blunts TGF{beta} signaling and production of multiple TGF{beta}-dependent antiangiogenic factors. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 8233–8246.
Ghosh AK, Shanafelt TD, Cimmino A, Taccioli C, Volinia S, Liu CG et al. Aberrant regulation of pVHL levels by microRNA promotes the HIF/VEGF axis in CLL B cells. Blood 2009; 113: 5568–5574.
Sylvestre Y, De Guire V, Querido E, Mukhopadhyay UK, Bourdeau V, Major F et al. An E2F/miR-20a autoregulatory feedback loop. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 2135–2143.
Ji M, Rao E, Ramachandrareddy H, Shen Y, Jiang C, Chen J et al. The miR-17-92 MicroRNA Cluster Is Regulated by Multiple Mechanisms in B-Cell Malignancies. Am J Pathol 2011; 179: 1645–1656.
Bechard M, Dalton S . Subcellular localization of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta controls embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Mol Cell Biol 2009; 29: 2092–2104.
Brennan P, Babbage JW, Burgering BM, Groner B, Reif K, Cantrell DA . Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase couples the interleukin-2 receptor to the cell cycle regulator E2F. Immunity 1997; 7: 679–689.
Manni I, Artuso S, Careccia S, Rizzo MG, Baserga R, Piaggio G et al. The microRNA miR-92 increases proliferation of myeloid cells and by targeting p63 modulates the abundance of its isoforms. FASEB J 2009; 23: 3957–3966.
Fontana L, Fiori ME, Albini S, Cifaldi L, Giovinazzi S, Forloni M et al. Antagomir-17-5p abolishes the growth of therapy-resistant neuroblastoma through p21 and BIM. PLoS One 2008; 3: e2236.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health grant U01 CA114778 to WCC; the Lymphoma Research Foundation/Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Clinical Investigator Career Development Award to KF; and UNMC Eppley Cancer Center Pilot Grant to KF; MJ and XH are supported by a scholarship from the China Scholarship Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Author Contributions
TWM, WCC and KF designed the study and provided administrative support; WCC and KF provided the study materials and patient information; ER, CJ, MJ, JI, XH, GL, GW and KF collected and assembled the data; ER, CJ, JI, GL, GW, LS, YZ, TWM, WCC and KF performed data analysis and interpretation; ER, CJ, TWM and KF wrote the manuscript; all authors have checked and approved the final version of the paper.
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, E., Jiang, C., Ji, M. et al. The miRNA-17∼92 cluster mediates chemoresistance and enhances tumor growth in mantle cell lymphoma via PI3K/AKT pathway activation. Leukemia 26, 1064–1072 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.305
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.305
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MYC drives platinum resistant SCLC that is overcome by the dual PI3K-HDAC inhibitor fimepinostat
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2023)
-
Underexplored reciprocity between genome-wide methylation status and long non-coding RNA expression reflected in breast cancer research: potential impacts for the disease management in the framework of 3P medicine
EPMA Journal (2023)
-
Adipocyte PHLPP2 inhibition prevents obesity-induced fatty liver
Nature Communications (2021)
-
miR-100 inhibits cell proliferation in mantle cell lymphoma by targeting mTOR
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2020)
-
The role and mechanisms of action of microRNAs in cancer drug resistance
Clinical Epigenetics (2019)