Abstract
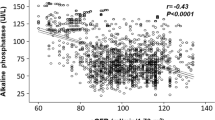
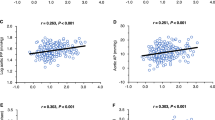
According to previous studies endogenous ouabain (EO) closely correlates with high blood pressure, congestive heart failure and kidney disease in humans. Our aims were to analyse associations between plasma, urinary EO level and various markers of cardiovascular damage in treated hypertensive patients. Forty-one adult patients with hypertension and/or diabetes mellitus (DM) and/or chronic kidney disease (CKD) were studied. We assessed plasma and urinary EO, pro-brain natriuretic peptide and catecholamines, profile of ambulatory blood pressure monitor and cardiovascular status by echocardiography and echo-tracking. The highest level of plasma EO (19.7±9.5 pmol l–1) was measured in hypertensive patients with DM and CKD. The nighttime mean arterial blood pressure independently correlated with the level of plasma EO (P=0.004), while independent predictor of the β-stiffness of carotid artery was the urinary EO (P=0.011). Elevated level of EO was associated with nighttime blood pressure and subclinical organ damage in treated hypertensive patients, suggesting possible role of EO in the pathogenesis of impaired diurnal blood pressure rhythm and arterial stiffness.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hamlyn JM, Blaustein MP, Bova S, DuCharme DW, Harris DW, Mandel F et al. Identification and characterization of an ouabain-like compound from human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991; 88: 6259–6263.
Bagrov AY, Shapiro JI . Endogenous digitalis: pathophysiologic roles and therapeutic applications. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 2008; 4: 378–392.
Manunta P, Ferrandi M, Bianchi G, Hamlyn JH . Endogenous ouabain in cardiovascular function and disease. J Hypertens 2009; 27: 9–18.
Stella P, Manunta P, Mallamaci F, Melandri M, Spotti D, Tripepi G et al. Endogenous ouabain and cardiomyopathy in dialysis patients. J Intern Med 2008; 263: 274–280.
Bauer N, Müller-Ehmsen J, Krämer U, Hambarchian N, Zobel C, Schwinger RH et al. Ouabain-like compound changes rapidly on physical exercise in humans and dogs: effects of ß-blockade and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition. Hypertension 2005; 45: 1024–1028.
Balzan S, Montali U, Biver P, Ghione S . Antidigoxin antibodies neutralize the effect of newborn endogenous digitalis-like factor on erythrocyte 86Rb uptake. J Nucl Biol Med 1991; 35: 38–40.
Bagrov AY, Shapiro JI, Fedorova OV . Endogenous cardiotonic steroids: physiology, pharmacology, and novel therapeutic targets. Pharmacol Rev 2009; 61: 9–38.
Blaustein MP, Zhang J, Chen L, Song H, Raina H, Kinsey SP et al. The pump, the exchanger, and endogenous ouabain: signaling mechanisms that link salt retention to hypertension. Hypertension 2009; 53: 291–298.
Dostanic-Larson I, Lorenz JN, Van Huysse JW, Neumann JC, Moseley AE, Lingrel JB . Physiological role of the alpha1- and alpha2-isoforms of the Na+-K+-ATPase and biological significance of their cardiac glycoside binding site. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2006; 290: R524–R528.
Huang BS, Huang X, Harmsen E, Leenen FHH . Chronic central versus peripheral ouabain, blood pressure, and sympathetic activity in rats. Hypertension 1994; 23: 1087–1090.
Skoumal R, Szokodi I, Aro J, Földes G, Göoz M, Seres L et al. Involvement of endogenous ouabain-like compound in cardiac hypertrophic process in vivo. Life Sci 2007; 80: 1303–1310.
Liu J, Tian J, Haas M, Shapiro JI, Askari A, Xie Z . Ouabain interaction with cardiac Na+/K+-ATPase initiates signal cascades independent of changes in intracellular Na+ and Ca2+ concentrations. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 27838–27844.
Aydemir-Koksoy A, Abramowitz J, Allen JC . Ouabain-induced signaling and vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 46605–46611.
Elkareh J, Kennedy DJ, Yashaswi B, Vetteth S, Shidyak A, Kim EG et al. Marinobufagenin stimulates fibroblast collagen production and causes fibrosis in experimental uremic cardiomyopathy. Hypertension 2007; 49: 215–224.
Manunta P, Stella P, Rivera R, Ciurlino D, Cusi D, Ferrandi M et al. Left ventricular mass, stroke volume, and ouabain-like factor in essential hypertension. Hypertension 1999; 34: 450–456.
Balzan S, Neglia D, Ghione S, D’Urso G, Baldacchino MC, Montali U et al. Increased circulating levels of ouabain-like factor in patient with asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction. Eur J Heart Fail 2001; 3: 165–171.
Willum-Hansen T, Staessen JA, Torp-Pedersen C, Rasmussen S, Thijs L, Ibsen H et al. Prognostic value of aortic pulse wave velocity as index of arterial stiffness in the general population. Circulation 2006; 113: 664–670.
Grossmann M, Jamieson MJ, Kirch W . Effects of digoxin and digitoxin on circadian blood pressure profile in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Invest 1998; 28: 701–706.
Kirch C, Grossmann M, Fischer S, Neumeister V, Kirch W . Effect of digoxin on circadian blood pressure values in patients with congestive heart failure. Eur J Clin Invest 2000; 30: 285–289.
Grossmann M . Effects of cardiac glycosides on 24-h ambulatory blood pressure in healthy volunteers and patients with heart failure. Eur J Clin Invest 2001; 31 (Suppl 2): S26–S30.
Clerico A, Giampietro O, Gregori G, Del Chicca MG, Bertoli S, Miccoli R et al. Excretion of digoxin-like immunoreactivity in urine of normal subjects: Correlations with excretion of creatinine and electrolytes. Clin Chem 1988; 34: 554–556.
Vakkuri O, Arnason SS, Joensuu P, Jalonen J, Vuolteenaho O, Leppäluoto J . Radioionated tyroly-ouabain and measurement of a circulating ouabain-like compound. Clin Chem 2001; 47: 95–101.
Collinson PO, Barnes SC, Gaze DC, Galasko G, Lahiri A, Senior R . Analytical performance of the N terminal pro B type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) assay on the Elecsys 1010 and 2010 analysers. Eur J Heart Fail 2004; 6: 365–368.
Gottdiener JS, Bednarz J, Devereux R, Gardin J, Klein A, Manning WJ et al. American Society of Echocardiography. American Society of Echocardiography recommendations for use of echocardiography in clinical trials; a report from the American Society of Echocardiography's Guidelines and Standards Committee and The Task Force on Echocardiography in Clinical Trials. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2004; 17: 1086–1119.
Niki K, Sugawara M, Chang D, Harada A, Okada T, Sakai R et al. A new noninvasive measurement system for wave intensity: evaluation of carotid arterial wave intensity and reproducibility. Heart Vessels 2002; 17: 12–21.
Schillaci G, Verdecchia P, Borgioni C, Ciucci A, Gattobigio R, Sacchi N et al. Predictors of diurnal blood pressure changes in 2042 subjects with essential hypertension. J Hypertens 1996; 14: 1167–1173.
Giles TD . Circadian rhythm of blood pressure and the relation to cardiovascular events. J Hypertens Suppl 2006; 24: 11–16.
Tripodi G, Citterio L, Kouznetsova T, Lanzani C, Florio M, Modica R et al. Steroid biosythesis and renal excretion in human essential hypertension: association with blood pressure and endogenous ouabain. Am J Hypertens 2009; 22: 357–363.
Vakkuri O, Arnason SS, Pouta A, Vuolteenaho O, Leppäluoto J . Radioimmunoassay of plasma oaubain in healthy and pregnant individuals. J Endocrinol 2000; 165: 669–677.
Manunta P, Iacoviello M, Forleo C, Messaggio E, Hamlyn JM, Lucarelli K et al. High circulating levels of endogenous ouabain in the offspring of hypertensive and normotensive individuals. J Hypertens 2005; 23: 1677–1681.
Crabos M, Ausiello DA, Haupert Jr GT, Cantiello HF . Atrial natriuretic peptide regulates release of Na+, K+-ATPase inhibitor from rat brain. Am J Physiol 1988; 254: F912–F917.
Salomaa V, Riley W, Kark JD, Nardo C, Folsom AR . Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and fasting glucose and insulin concentrations are associated with arterial stiffness indexes. The ARIC Study. Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Circulation 1995; 91: 1432–1443.
Blacher J, Guerin AP, Pannier B, Marchais SJ, Safar ME, London GM . Impact of aortic stiffness on survival in end-stage renal disease. Circulation 1999; 99: 2434–2439.
Safar ME, Levy BI, Struijker-Boudier H . Current perspectives on arterial siffness and pulse pressure in hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2003; 107: 2864–2869.
Briones AM, Xavier FE, Arribas SM, González MC, Rossoli LV, Alonso MJ et al. Alterations in structure and mechanics of resistance arteries from ouabain-induced hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2006; 291: H193–H201.
Kawamoto R, Kohara K, Tabara Y, Miki T, Ohtsuka N, Kusunoki T et al. An association between decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate and arterial stiffness. Intern Med 2008; 47: 593–598.
Nakagawa N, Takahashi F, Chinda J, Kobayashi M, Hayashi Y, Abe M et al. A newly estimated glomerular filtration rate is independently associated with arterial stiffness in Japanase patients. Hypertens Res 2008; 31: 193–201.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This paper has been seen and approved by all authors and is not under consideration for publication elsewhere in a similar form, in any language.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagy, G., Gaszner, B., Lányi, É. et al. Selective association of endogenous ouabain with subclinical organ damage in treated hypertensive patients. J Hum Hypertens 25, 122–129 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2010.24
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2010.24
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Predicting acute kidney injury: current status and future challenges
Journal of Nephrology (2018)