Abstract
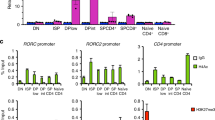
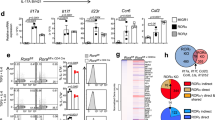
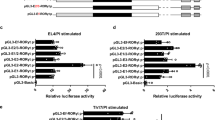
T helper (Th)17 cells constitute a distinct subset of CD4+ helper T cells that is mainly characterized by abundant interleukin (IL)-17 production and is involved in the host defence against bacteria and fungi as well as in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. The retinoic orphan receptor (ROR)γt directs the transcriptional activation of the IL17 gene. Here, we report the presence of a novel RORγt isoform, RORγt-Δ(5–8), which lacks the hinge-encoding exons 5–8 and represses potently IL17 and IL21 gene transcription. It thereby reduces the expression of multiple Th17-assigned cytokines. We propose that RORγt-Δ(5–8) acts as a dominant-negative regulator of RORγt-mediated gene regulation and the balance between the full-length RORγt and the novel repressor isoform may arbitrate IL-17 production in human T cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Harrington LE, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Turner H, Murphy TL, Murphy KM et al. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol 2005; 6: 1123–1132.
Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein WM, Mattson J, Basham B, Sedgwick JD et al. IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med 2005; 201: 233–240.
Nistala K, Wedderburn LR . Th17 and regulatory T cells: rebalancing pro- and anti-inflammatory forces in autoimmune arthritis. Rheumatology 2009; 48: 602–606.
Hundorfean G, Neurath MF, Mudter J . Functional relevance of T helper 17 (Th17) cells and the IL-17 cytokine family in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2011; 18: 180–186.
Zepp J, Wu L, Li X . IL-17 receptor signaling and T helper 17-mediated autoimmune demyelinating disease. Trends Immunol 2011; 32: 232–239.
Chen Z, Laurence A, O’Shea JJ . Signal transduction pathways and transcriptional regulation in the control of Th17 differentiation. Semin Immunol 2007; 19: 400–408.
Mangelsdorf DJ, Thummel C, Beato M, Herrlich P, Schutz G, Umesono K et al. The nuclear receptor superfamily: the second decade. Cell 1995; 83: 835–839.
Eberl G, Littman DR . The role of the nuclear hormone receptor RORgamma t in the development of lymph nodes and Peyer's patches. Immunol Rev 2003; 195: 81–90.
He YW, Deftos ML, Ojala EW, Bevan MJ . RORgamma t, a novel isoform of an orphan receptor, negatively regulates Fas ligand expression and IL-2 production in T cells. Immunity 1998; 9: 797–806.
Ivanov II, McKenzie BS, Zhou L, Tadokoro CE, Lepelley A, Lafaille JJ et al. The orphan nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell 2006; 126: 1121–1133.
Zhou L, Ivanov II, Spolski R, Min R, Shenderov K, Egawa T et al. IL-6 programs T(H)-17 cell differentiation by promoting sequential engagement of the IL-21 and IL-23 pathways. Nat Immunol 2007; 8: 967–974.
Brustle A, Heink S, Huber M, Rosenplanter C, Stadelmann C, Yu P et al. The development of inflammatory T(H)-17 cells requires interferon-regulatory factor 4. Nat Immunol 2007; 8: 958–966.
Zhang F, Meng G, Strober W . Interactions among the transcription factors Runx1, RORgammat and Foxp3 regulate the differentiation of interleukin 17-producing T cells. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 1297–1306.
Schraml BU, Hildner K, Ise W, Lee WL, Smith WA, Solomon B et al. The AP-1 transcription factor Batf controls T(H)17 differentiation. Nature 2009; 460: 405–409.
Wagner RL, Huber BR, Shiau AK, Kelly A, Cunha Lima ST, Scanlan TS et al. Hormone selectivity in thyroid hormone receptors. Mol Endocrinol 2001; 15: 398–410.
Yoshikawa N, Shimizu N, Sano M, Ohnuma K, Iwata S, Hosono O et al. Role of the hinge region of glucocorticoid receptor for HEXIM1-mediated transcriptional repression. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 2008; 371: 44–49.
Crispin JC, Oukka M, Bayliss G, Cohen RA, Van Beek CA, Stillman IE et al. Expanded double negative T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus produce IL-17 and infiltrate the kidneys. J Immunol 2008; 181: 8761–8766.
Ichiyama K, Yoshida H, Wakabayashi Y, Chinen T, Saeki K, Nakaya M et al. Foxp3 inhibits RORgammat-mediated IL-17A mRNA transcription through direct interaction with RORgammat. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 17003–17008.
Juang YT, Rauen T, Wang Y, Ichinose K, Benedyk K, Tenbrock K et al. Transcriptional activation of the CREM promoter in human T cells is regulated by PP2A-mediated dephosphorylation of SP-1 and reflects disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 1795–1801.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Institute of Health Grants R01 AI85567 and R01 AI49954 (to GCT) and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (grant RA1927/1-1 to TR). We thank Melissa Zajdel for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Genes and Immunity website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rauen, T., Juang, YT., Hedrich, C. et al. A novel isoform of the orphan receptor RORγt suppresses IL-17 production in human T cells. Genes Immun 13, 346–350 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2011.85
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2011.85
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Increased circulating Th17 cell populations in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Immunogenetics (2023)
-
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Children and Young People
Current Rheumatology Reports (2021)
-
Variations in T cell transcription factor gene structure and expression associated with the two disease forms of sheep paratuberculosis
Veterinary Research (2016)
-
A ticking clock links metabolic pathways and organ systems function in health and disease
Clinical and Experimental Medicine (2014)