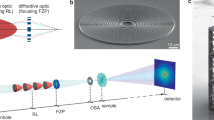
Abstract
The development of high brilliance X-ray sources coupled with advances in manufacturing technologies has led to significant improvements in submicrometre probes for spectroscopy, diffraction and imaging applications. The generation of a small beam spot size is commonly based on three principles1: total reflection (as used in optical elements involving mirrors or capillaries), refraction (such as in refractive lenses2) and diffraction. The latter effect is employed in Bragg–Fresnel or Soret lenses, commonly known as Fresnel zone plate lenses. These lenses currently give the best spatial resolution, but are traditionally limited to rather soft X-rays—at high energies, their use is still limited by their efficiency. Here we report the fabrication of high-efficiency, high-contrast gold and nickel multistep (quaternary) Fresnel zone plates using electron beam lithography. We achieve a maximum efficiency of 55% for the nickel plate at 7 keV. In addition to their high efficiency, the lenses offer the advantages of low background signal and effective reduction of unwanted diffraction orders. We anticipate that these lenses should have a significant impact on techniques such as microscopy3, micro-fluorescence4 and micro-diffraction5, which require medium resolution (500–100 nm) and high flux at fixed energies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dhez,P., Chevallier,P., Lucatorto, T. B. & Tarrio,C. Instrumental aspects of X-ray microbeams in the range above 1 keV. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 70, 1907– 1920 (1999).
Snigirev,A., Kohn,V., Snigireva,I. & Lengeler,B. A compound refractive lens for focusing high-energy X-rays. Nature 384, 49–51 (1996).
Kirz,J., Jacobsen,C. & Howells, M. Soft X-ray microscopes and their biological applications. Q. Rev. Biophys. 28, 33– 130 (1995).
Wang,J. et al. X-ray fluorescence correlation spectroscopy: a method for studying particle dynamics in condensed matter. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 1110–1113 (1998).
Rodrigues,W. et al. X-ray microdiffraction studies of an integrated laser-modulator system in Proc. 6th Conf. on Synchrotron Radiation Instrumentation (SRI97) (Himeji Citizen Hall, Hyogo, Japan, 1997).
Tatchyn,R. O. in X-ray Microscopy Vol. 43 (eds Smah, G. & Rudolph, D.) 40–50 (Springer Series in Optical Sciences, Springer, Berlin, 1990).
Lai,B. et al. Hard X-ray phase zone plate fabricated by Lithographic techniques. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1, 1877– 1880 (1992).
Di Fabrizio,E. et al. High-performance multilevel blazed X-ray microscopy Fresnel zone plates fabricating using X-ray lithography. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B. 12, 3979 (1994).
Yun, W. et al. Nanometer focusing of hard X-rays by phase zone plates. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 70, 2238–2241 ( 1999).
Michette,A. G. Optical Systems for Soft X-rays (Plenum, New York, 1986).
Schelokob,I. A. et al. Second generation of grazing-incidence-phase Fresnel zone plates. Opt. Commun. 159, 278– 284 (1999).
Kirz,J. Phase zone plates for X-rays and extreme UV. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 64, 301–309 (1974).
Barrett,R., Kaulich,B., Oestreich,S. & Susini,J. The scanning microscopy end-station at the ESRF X-ray microscopy beamline. Proc. SPIE 3499, 80–90 (1998).
Nieman,B. in X-ray Microscopy and Spectromicroscopy (eds Thieme, J., Schmahl, G., Rudolph, D. & Umbach, E.) 44–55 (Springer, Chernogolovka, Russia, 1998).
Spector,S. J., Jaconsen,C. J. & Tennant, D. M. Process optimization for production of sub-20 nm soft X-ray zone plate. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 15, 2872–2876 (1997).
David,C. et al. Low-distortion electron-beam lithography for fabrication of high-resolution germanium and tantalum phase zone plates. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 13, 2762–2766 ( 1995).
Schneider,G., Schliebe,T. & Aschoff, H. Cross linked polymers for nanofabrication of high resolution zone-plates in nickel and germanium. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 13, 2809–2812 (1995).
Weiss,D., Peuker,M. & Schneider, G. Radiation enhanced network formation in copolymer galvanoforms for diffractive nickel X-ray optics with high aspect ratios. Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 1805–1807 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Fabrizio, E., Romanato, F., Gentili, M. et al. High-efficiency multilevel zone plates for keV X-rays. Nature 401, 895–898 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/44791
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/44791
This article is cited by
-
Ultra-thin light-weight laser-induced-graphene (LIG) diffractive optics
Light: Science & Applications (2023)
-
Optical Fourier surfaces
Nature (2020)
-
Electrically focus-tuneable ultrathin lens for high-resolution square subpixels
Light: Science & Applications (2020)
-
A stacked prism lens concept for next-generation hard X-ray telescopes
Nature Astronomy (2019)
-
Remarkable optical coupling enhancement with laser selective focusing devices
Optical and Quantum Electronics (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.