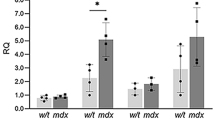
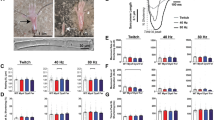
Abstract
THERE are dihydropyridine (DHP)-sensitive calcium currents in both skeletal and cardiac muscle cells, although the properties of these currents are very different in the two cell types1 (for simplicity, we refer to currents in both tissues as L-type12). The mechan-isms of depolarization-contraction coupling also differ. As the predominant voltage-dependent calcium current of cardiac cells1, the L-type current represents a major pathway for entry of extra-cellular calcium. This entry triggers the subsequent large release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) 3–5. In contrast, depolarization of skeletal muscle releases calcium from the SR6,7 without the requirement for entry of extracellular calcium through L-type calcium channels8,9. To investigate the molecular basis for these differences in calcium currents and in excitation-contraction (?–C) coupling, we expressed complementary DNAs for the DHP receptors from skeletal10 and cardiac muscle11 in dysgenic skeletal muscle. We compared the properties of the L-type channels pro-duced and showed that expression of a cardiac calcium channel in skeletal muscle cells results in ?–C coupling resembling that of cardiac muscle.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bean, B. P. A. Rev. Physiol. 51, 367–384 (1989).
Nowycky, M. C., Fox, A. P. & Tsien, R. W. Nature 316, 440–443 (1985).
Fabiato, A. J. gen. Physiol. 85, 291–320 (1985).
Beuckelmann, D. J. & Wier, W. G. J. Physiol., Lond. 405, 233–255 (1988).
Näbauer, M., Callewaert, G., Cleemann, L. & Morad, M. Science 244, 800–803 (1989).
Costantin, L. L. Prog. Biophys. molec. Biol. 29, 197–224 (1975).
Endo, M. Physiol. Rev. 57, 71–108 (1977).
Armstrong, C. M., Bezanilla, F. M. & Horowicz, P. Biochim. biophys. Acta 267, 605–608 (1972).
Knudson, C. M., Jay, S. D. & Beam, K. G. Biophys. J. 49, 13a (1986).
Tanabe, T. et al. Nature 328, 313–318 (1987).
Mikami, A. et al. Nature 340, 230–233 (1989).
Klaus, M. M., Scordilis, S. P., Rapalus, J. M., Briggs, R. T. & Powell, J. A. Devl Biol. 99, 152–165 (1983).
Beam, K. G., Knudson, C. M. & Powell, J. A. Nature 320, 168–170 (1986).
Tanabe, T., Beam, K. G., Powell, J. A. & Numa, S. Nature 336, 134–139 (1988).
Sanchez, J. A. & Stefani, E. J. Physiol., Lond. 283, 197–209 (1978).
Donaldson, P. L. & Beam, K. G. J. gen. Physiol. 82, 449–468 (1983).
Isenberg, G. & Klöckner, U. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 395, 30–41 (1982).
Lee, K. S. & Tsien, R. W. Nature 297, 498–501 (1982).
Kass, R. S. & Sanguinetti, M. C. J. gen. Physiol. 84, 705–726 (1984).
Beam, K. G. & Knudson, C. M. J. gen. Physiol. 91, 781–798 (1988).
Perez-Reyes, E. et al. Nature 340, 233–236 (1989).
Adams, B. A. & Beam, K. G. J. gen. Physiol. 94, 429–444 (1989).
Schneider, M. F. & Chandler, W. K. Nature 242, 244–246 (1973).
Rios, E. & Brum, G. Nature 325, 717–720 (1987).
Hamill, O. P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B. & Sigworth, F. J. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 391, 85–100 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanabe, T., Mikami, A., Numa, S. et al. Cardiac-type excitation-contraction coupling in dysgenic skeletal muscle injected with cardiac dihydropyridine receptor cDNA. Nature 344, 451–453 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/344451a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/344451a0
This article is cited by
-
Blockade of microglial Cav1.2 Ca2+ channel exacerbates the symptoms in a Parkinson’s disease model
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Voltage sensing mechanism in skeletal muscle excitation-contraction coupling: coming of age or midlife crisis?
Skeletal Muscle (2018)
-
Regions of ryanodine receptors that influence activation by the dihydropyridine receptor β1a subunit
Skeletal Muscle (2015)
-
Reciprocal dihydropyridine and ryanodine receptor interactions in skeletal muscle activation
Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility (2011)
-
Ca2+/CaM-dependent inactivation of the skeletal muscle L-type Ca2+ channel (Cav1.1)
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2008)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.