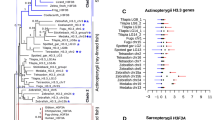
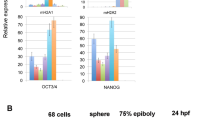
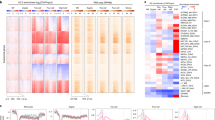
Abstract
The set of histone genes that are active late in embryogenesis of the sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus) are present in 5–12 copies per genome and, unlike the clustered, tandemly arrayed early histone genes, are dispersed and irregularly arranged. Late H2B gene expression is activated by events accompanying fertilization and its mRNAs are first detectable by as early as 6 h of development (16 cells) and increase only slightly in amount during the period of rapid cleavage between 6 and 14 h. However, during the short interval between 14 and 16 h, while the amount of early histone mRNA is declining, there is a >15-fold burst in the rate of late H2B mRNA accumulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruderman, J. V. & Gross, P. R. Devl Biol. 36, 286–298 (1974).
Cohen, L. H., Newrock, K. M. & Zweidler, A. Science 190, 994–997 (1975).
Grunstein, M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 4135–4139 (1978).
Newrock, K., Cohen, L., Hendricks, M., Donnelly, R. & Weinberg, E. Cell 14, 327–336 (1978).
Hieter, P., Hendricks, M., Hemminki, K. & Weinberg, E. Biochemistry 18, 2702–2716 (1979).
Childs, G., Maxson, R. & Kedes, L. H. Devl Biol. 73, 153–173 (1979).
Arceci, R. J. & Gross, P. R. Devl Biol. 80, 186–209 (1980).
Childs, G., Nocente, C., Lieber, T., Holt, C. & Knowles, J. Cell (in the press).
Sures, I., Lowry, J. & Kedes, L. H. Cell 15, 1033–1044 (1978).
Thomas, M., White, R. & Davis, R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 73, 2294–2298 (1976).
Maxson, R. E. & Wilt, F. H. Devl Biol. 83, 380–386 (1981).
Mauron, A., Kedes, L., Hough-Evans, B. & Davidson, E. H. Devl Biol. (in the press).
Childs, G., Maxson, R., Cohn, R. & Kedes, L. H. Cell 23, 651–663 (1981).
Hentschel, C. & Birnstiel, M. Cell 25, 301–313 (1981).
Strickland, M., Strickland, W., Brandt, W. & von Holt, C. Eur. J. Biochem. 77, 263–275 (1977).
Coen, E., Strachan, T. & Dover, G. J. molec. Biol. 158, 17–35 (1982).
Smith, H. O. & Birnstiel, M. L. Nucleic Acids Res. 3, 2387–2397 (1976).
Petes, T. D. Cell 19, 765–774 (1980).
Strohman, R. C. et al. Cell 10, 265–273 (1977).
Goldber, M., Lifton, R., Stark, G. & Williams, J. Meth. Enzym. 68, 206–220 (1979).
Donis-Keller, H., Maxam, A. & Gilbert, W. Nucleic Acids Res. 4, 2527–2538 (1977).
Gross, K., Probst, E., Schaffner, W. & Birnstiel, M. Cell 8, 455–470 (1976).
Maxam, A. M. & Gilbert, W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 560–564 (1977).
Anderson, D. et al. J. molec. Biol. 145, 5–28 (1981).
Benton, W. D. & Davis, R. W. Science 196, 180–182 (1977).
Davis, R., Botstein, P. & Roth, J. Advanced Bacterial Genetics (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1980).
Overton, C. & Weinberg, E. Cell 14, 247–257 (1978).
Laskey, R. A. & Mills, A. D. Eur. J. Biochem. 56, 335–341 (1975).
Rigby, P. W., Dieckmann, M., Rhodes, C. & Berg, P. J. molec. Biol. 113, 237–251 (1977).
Cohn, R. H., Lowry, J. C. & Kedes, L. H. Cell 9, 147–161 (1976).
Bolivar, F. et al. Gene 2, 95–113 (1977).
Von Holt, C., Strickland, W. N., Brandt, W. F. & Strickland, M. S. FEBS Lett. 100, 201–218 (1979).
McMaster, G. K. & Carmichael, G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 4835–4838 (1977).
Alwine, J. C., Kemp, D. J. & Stark, G. R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5350–5354 (1977).
Hinegardner, R. T. Crowell, New York (eds Wilt, F. & Wessels, N.) 139–155 (1967).
Giudice, G. Developmental Biology of the Sea Urchin Embryo (Academic, New York, 1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maxson, R., Mohun, T., Gormezano, G. et al. Distinct organizations and patterns of expression of early and late histone gene sets in the sea urchin. Nature 301, 120–125 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1038/301120a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/301120a0
This article is cited by
-
Common Evolutionary Origin and Birth-and-Death Process in the Replication-Independent Histone H1 Isoforms from Vertebrate and Invertebrate Genomes
Journal of Molecular Evolution (2005)
-
Organization and chromosomal location of the major histone cluster in brown trout, Atlantic salmon and rainbow trout
Chromosoma (1994)
-
Modifications in molecular mechanisms associated with control of cell cycle regulated human histone gene expression during differentiation
Cell Biophysics (1989)
-
Histone genes in three sea star species: Cluster arrangement, transcriptional polarity, and analyses of the flanking regions of H3 and H4 genes
Journal of Molecular Evolution (1988)
-
Synonymous nucleotide substitution rates of β-tubulin and histone genes conform to high overall genomic rates in rodents but not in sea urchins
Journal of Molecular Evolution (1988)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.