Abstract
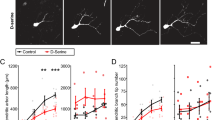
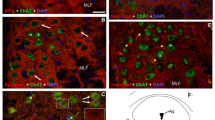
Enkephalin and substance P are two peptides found in vertebrate nervous systems that have been intensively studied with regard to cellular distribution and receptor mechanisms1–3. Invertebrate nervous systems, which are extremely useful in elucidating general principles of neural functions4–6, can also be used as models for the analysis of peptidergic mechanisms7,8. The accessibility, regularity, small number and relatively large size of the neural components of one such system, the crustacean compound eye, have facilitated the accumulation of detailed information about their anatomy9–11 and physiology12–14, and provided insight into basic principles of intercellular communication12–14. We report here that immunoreactivity of enkephalin and substance P can be localized to specific neural elements in the visual system of the spiny lobster, Panulirus interruptus. Our observations suggest that this highly organized, simple in vivo system may be a convenient model to evaluate the cellular mechanisms of these peptides. Although several neuropeptides have been localized in vertebrate retinal inter-neurones15, our results are the first to detect a known peptide in primary photoreceptors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Snyder, S. H. Science 209, 976–983 (1980).
Iversen, L. L., Nicoll, R. A. & Vale, W. W. Neurosci. Res. Prog. Bull. 16, 214–360 (1978).
Zieglgansberger, W. in Peptides: Integrators of Cell and Tissue Function (ed. Bloom, F. E.) 219–233 (Raven, New York, 1980).
Kuffler, S. W. & Nicolls, J. G. From Neuron to Brain, 355 (Sinauer, Massachusetts, 1976).
Schmitt, F. O. & Worden, F. G. The Neurosciences, III Study Program, 341–431 (MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 1974).
Kandel, E. R. The Cellular Basis of Behavior, 29–66 (Freeman, San Francisco, 1976).
Barker, J. L. Neurosci. Res. Prog. Bull. 16, 535–555 (1978).
Frontali, N. & Gainer, H. in Peptides in Neurobiology (ed. Gainer, H.) 259–294 (Plenum, New York, 1977).
Bullock, T. H. & Horridge, G. A. Structure and Function in the Nervous System of Invertebrates Vol. 2, 1063–1115 (Freeman, San Francisco, 1965).
Hanstrom, B. Ark. Zool. 16, 1 (1924).
Meyer-Rochow, V. B. Cell Tissue Res. 162, 439–457 (1975).
Ratliff, F. & Hartline, H. K. Studies on Excitation and Inhibition in the Retina (Rockefeller University Press, New York, 1974).
York, B. & Wiersma, C. A. G. Prog. Neurobiol. 5, 127–166 (1975).
Wiersma, C. A. G. Invertebrate Nervous Systems, 269–284 (University of Chicago Press, 1967).
Brecha, N., Karten, H. & Laverack, C. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 3010–3014 (1979).
Hamori, J. & Horridge, G. A. J. Cell Sci. 1, 249–256 (1966).
Scharrer, B. A. Rev. Physiol. 15, 466–467 (1953).
Passano, L. M. Anat. Rec. 111, 502 (1951).
Zieglgansberger, W. & Tulloch, I. F. in Endorphins in Mental Health Research (eds Usdin, E., Bunney, W. E. & Kline, N. S.) 293–301 (Oxford University Press, New York, 1979).
Duggan, A. W., Hall J. G. & Headley, P. M. Nature 264, 456–458 (1976).
Jessell, T. M. & Iversen, L. L. Nature 268, 549–561 (1977).
Hamori, J. & Horridge, G. A. J. Cell Sci. 1, 257–270 (1966).
Zipser, B. Nature 283, 857–858 (1980).
Alumets, J., Hakanson, R., Sundler, F. & Thorell, J. Nature 279, 805–806 (1979).
Gros, C., Lafon-Cazal, M. & Dray, F. C.r. hebd. Séanc. Acad. Sci., Paris 287, 647–650 (1978).
Andrew, R. D., Orchard, I. & Saleuddin, A. S. M. Cell Tissue Res. 190, 235–246 (1978).
Bunt, A. H. & Ashby, E. A. Gen. comp. Endocr. 9, 334–342 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mancillas, J., McGinty, J., Selverston, A. et al. Immunocytochemical localization of enkephalin and substance P in retina and eyestalk neurones of lobster. Nature 293, 576–578 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1038/293576a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/293576a0
This article is cited by
-
Roles of Neurotransmitters in Decapod Reproduction
Thalassas: An International Journal of Marine Sciences (2020)
-
Crustacean neuropeptides
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2010)
-
Immunolocalisation of crustacean-SIFamide in the median brain and eyestalk neuropils of the marbled crayfish
Cell and Tissue Research (2007)
-
Immunocytochemical localization of neuropeptide Y, serotonin, substance P and β-endorphin in optic ganglia and brain ofMetapenaeus ensis
Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology (2006)
-
Autoradiographic localization of opioid binding sites combined with immunogold detection of Leu-enkephalin, crustacean hyperglycaemic hormone and moult inhibiting hormone at the electron microscopic level in the sinus gland of the shore crab,Carcinus maenas
Histochemistry (1993)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.