Abstract
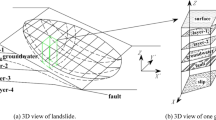
Based on a new Geographic Information Systems (GIS) grid-basedthree-dimensional (3-D) deterministic model and taking the slopeunit as the mapping unit, this study maps landslide hazard usingthe 3-D safety factor index and failure probability. Assuming theinitial slip to be the lower part of an ellipsoid, the 3-D critical slipsurface in the 3-D slope stability analysis is located by minimizingthe 3-D safety factor using the Monte Carlo random simulation.The failure probability of the landslide is calculated using anapproximate method in which the distributions of c, Φ andthe 3-D safety factor are assumed to be in normal distribution.The method has been applied to a case study on three-dimensionallyand probabilistically mapping landslide hazard.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleotti, P. and Chowdhury, R.: 1999, Landslide hazard assessment: Summary review and new perspectives, Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment 58, 21–44.
Anbalagan, D.: 1992, Landslide hazard evaluation and zonation mapping in mountainous terrain, Engineering Geology 32, 269–277.
Bishop, A. W.: 1955, The use of the slip circle in the stability analysis of slopes, Geotechnique 5(1), 7–17.
Brabb, E. E.: 1984, Innovative approaches to landslide hazard mapping, Proceedings of the IV International Symposium of Landslides, Toronto, Vol. 1, pp. 307–324.
Brabb, E. E.: 1995, The San Mateo County GIS project for predicting the consequences of hazardous geologic processes, In: A. Carrara and F. Guzzetti (eds), Geographical Information Systems in Assessing Natural Hazards, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht.
Carrara, A., Cardinali, M., Detti, R., Guzzetti, F., Pasqui, V., and Reichenbach, P.: 1991, GIS techniques and statistical models in evaluating landslide hazard, Earth Surface Process and Landforms 16, 427–445.
Carrara, A.: 1983, Multivariate models for landslide hazard evaluation, Mathematical Geology 403(27), 15–23.
Carrara, A.: 1995, GIS technology in mapping landside hazard, In: A. Carrara and F. Guzzetti (eds), Geographical Information Systems in Assessing Natural Hazards, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp. 135–176.
Carrara, A., Guzzetti, F., Cardinali, M., and Reichenbach, P.: 1999, Use of GIS technology in the prediction and monitoring of landslide hazard, Natural Hazard 20, 117–135.
Chen, R. and Chameau, J. L.: 1983, Three-dimensional limit equilibrium analysis of slopes, Geotechnique 33, 31–40.
Chowdhury, R. and Flentje, P.: 2002, Uncertainties in rainfall-induced landslide hazard, Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology 35, 61–69.
Dai, F. C. and Lee, C. F.: 2001, Terrain-based mapping of landslide susceptibility using a geographical information system: a case study, Canadian Geotechnical Journal 38, 911–923.
David, R. M.: 2002, Arc Hydro: GIS for Water Resources, ESRI Press, Redlands, CA.
De Roo, A. P. J.: 1993, Modeling surface runoff and soil erosion in catchments using geographical information systems, Nederlandse Geographische Studies, No. 157, Utrecht, pp. 295–304.
El-Ramly, H., Morgenstern, N. R., and Cruden, D. M.: 2002, Probabilistic slope stability analysis for practice, Canadian Geotechnical Journal 39, 665–683.
Gens, A., Hutchison, J. N., and Cavounidis, S.: 1988, Three-dimensional analysis of slices in cohesive soils, Geotechnique 38, 1–23.
Hovland, H. J.: 1977, Three-dimensional slope stability analysis method, Journal of the Geotechnical Engineering Division, Proceedings of the American Society of Civil Engineers 103(GT9), 971–986.
Hungr, O.: 1987, An extension of Bishop's simplified method of slope stability analysis to three dimensions, Geotechnique 37(1), 113–117.
Hungr, O.: 1994, A general limit equilibrium model for three-dimensional slope stability analysis: Discussion, Canadian Geotechnical Journal 31, 791–795.
Janbu, N., Bjerrum, L., and Kjaernsli, B.: 1956, Soil mechanics applied to some engineering problems, Norwegian Geotechnical Institute, Publication 16.
Janbu, N.: 1973, Slope stability computations, Embankment-Dam Engineering, Casagrande Volume, Wiley, New York, pp. 47–86.
Joseph, M. M. and Willian, M.: 1998, Using GIS in probabilistic assessment of earthquake triggered landslide hazard, Journal of Earthquake Engineering 2(4), 593–623.
Lam, L. and Fredland, D. G.: 1993, A general limit equilibrium model for three-dimensional slope stability analysis, Canadian Geotechnical Journal 30, 905–919.
Leshchinsky, D. and Huang Ching-Chang: 1992, Generalized three dimensional slope stability analysis, Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 118(11), 1748–1763.
National Academy of Sciences: 1978, In: L. S. Robert and J. K. Raymond (eds), Landslides Analysis and Control, Washington, D.C.
Sarma, S. K.: 1973, Stability analysis of embankments and slopes, Geotechnique 23(3), 423–433.
Varnes, D. J. and IAEG Commission on Landslides and Other Mass-Movements: 1984, Landslide Hazard Zonation: A Review of Principles and Practice, UNESCO Press, Paris.
Van Westen, C. J. and Terlien, M. T. J.: 1996, Deterministic landslide hazard analysis in GIS: A case study from Manizales (Colombia), Earth Surface Processes and Landforms 21, 853–868.
Van Westen, C. J., Rengers, N., Terlien, M. T. J., and Soeters, R.: 1997, Prediction of the occurrence of slope instability phenomena through GIS-based hazard zonation, Geologische Rundschau 86, 404–414.
Van Westen, C. J.: 1998, GIS in landslide hazard zonation: a view, with examples from the Andes of Colombia, In: M. P. Martin and D. I. Heywood (eds), Mountain Environment and Geographic Information Systems, Taylor and Francis, London, pp. 35–165.
Van Westen, C. J., Seijmonsbergen, A. C., and Mantovani, F.: 1999, Comparing landslide hazard maps, Natural Hazard 20, 137–158.
Xie, M., Zhou, G., and Esaki, T.: 2001, Landslide hazard assessment using Monte Carlo simulation based on GIS, In: The 10th International Conference of IACMAG, Arizona, pp. 169–173.
Zhou, G., Esaki, T., Mitani, Y., Xie, M., and Mori, J.: 2003, Spatial probabilistic modeling of slope failure using an integrated GIS Monte Carlo simulation approach, International Journal of Engineering Geology 68, 373–386.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, M., Esaki, T. & Zhou, G. GIS-Based Probabilistic Mapping of Landslide Hazard Using a Three-Dimensional Deterministic Model. Natural Hazards 33, 265–282 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NHAZ.0000037036.01850.0d
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NHAZ.0000037036.01850.0d