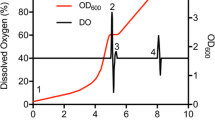
Abstract
The use of 2-L polyethylene terephthalate beverage bottles as a bacterial culture vessel has been recently introduced as an enabling technology for high-throughput structural biology [Sanville Millard, C. et al., 2003. Protein Express. Purif. 29, 311–320]. In the article following this one [Stols et al., this issue, pp. 95–102], this approach was elaborated for selenomethionine labeling used for multiwavelength anomalous dispersion phasing in the X-ray crystallographic determinations of protein structure. Herein, we report an effective and reproducible schedule for uniform 15N- and 13C-labeling of recombinant proteins in 2-L beverage bottles for structural determination by NMR spectroscopy. As an example, three target proteins selected from Arabidopsis thaliana were expressed in Escherichia coli Rosetta (DE3)/pLysS from a T7-based expression vector, purified, and characterized by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and NMR analysis by 1H-15N heteronuclear single quantum correlation spectroscopy. The results show that expressions in the unlabeled medium provide a suitable control for estimation of the level of production of the labeled protein. Mass spectral characterizations show that the purified proteins contained a level of isotopic incorporation equivalent to the isotopically labeled materials initially present in the growth medium, while NMR analysis of the [U-15N]-labeled proteins provided a convenient method to assess the solution state properties of the target protein prior to production of a more costly double-labeled sample.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heinemann, U., Frevert, J., Hofmann, K., Illing, G., Maurer, C., Oschkinat, H. and Saenger, W. (2000) Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 73, 347–362.
Ausubel, F.M. (2002) Plant Physiol. 129, 394–437.
Ding, H.T., Ren, H., Chen, Q., Fang, G., Li, L.F., Li, R., Wang, Z., Jia, X.Y., Liang, Y.H., Hu, M.H., Li, Y., Luo, J.C., Gu, X.C., Su, X.D., Luo, M. and Lu, S.Y. (2002) Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 58, 102–108.
Doyle, S.A., Murphy, M.B., Massi, J.M. and Richardson, P.M. (2002) J. Proteome Res. 1, 531–536.
Sanville Millard, C., Stols, L., Quartey, P., Kim, Y., Dementieva, I. and Donnelly, M.I. (2003) Protein Express. Purif. 29, 311–320.
Kennedy, M.A., Montelione, G.T., Arrowsmith, C.H. and Markley, J.L. (2002) J. Struct. Funct. Genom. 2, 155–169.
Kay, L., Keifer, P. and Saarinen, T. (1992) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 114, 10663–10665.
Rehm, T., Huber, R. and Holak, T.A. (2002) Structure (Camb.) 10, 1613–1681.
McIntosh, L.P. and Dahlquist, F.W. (1990) Q. Rev. Biophys. 23, 1–38.
Ikura, M., Krinks, M., Torchia, D.A. and Bax, A. (1990) FEBS Lett. 266, 155–158.
Wishart, D.S., Sykes, B.D. and Richards, F.M. (1993) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1164, 36–46.
Reilly, D. and Fairbrother, W.J. (1994) J. Biomol. NMR 4, 459–462.
Cai, M., Huang, Y., Sakaguchi, K., Clore, G.M., Gronenborn, A.M. and Craigie, R. (1998) J. Biomol. NMR 11, 97–102.
Studier, F.W. (1991) J. Mol. Biol. 219, 37–44.
Dubendorff, J.W. and Studier, F.W. (1991) J. Mol. Biol. 219, 45–59.
Pan, S.H. and Malcolm, B.A. (2000) BioTechniques 29, 1234–1238.
Dotsch, V. and Wagner, G.Y. (1998) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 8, 619–623.
Marley, J., Lu, M. and Bracken, C. (2001) J. Biomol. NMR 20, 71–75.
Studts, J.M. and Fox, B.G. (1999) Protein Express. Purif. 16, 109–119.
Weber, D.J., Gittis, A.G., Mullen, G.P., Abeygunawardana, C., Lattman, E.E. and Mildvan, A.S. (1992) Proteins 4, 275–287.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. and Maniatis, T. (2001) In Molecular Cloning, A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed., Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Marion, D. and Wüthrich, K. (1983) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 113, 967–974.
Stols, L., Sanville Millard, C., Dementieva, I. and Donnelly, M.I. (2004) J. Struct. Funct. Genom., 5, 95–102 (this issue).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Q., Frederick, R., Seder, K. et al. Production in two-liter beverage bottles of proteins for NMR structure determination labeled with either 15N- or 13C-15N. J Struct Func Genom 5, 87–93 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JSFG.0000029205.65813.42
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JSFG.0000029205.65813.42