Abstract
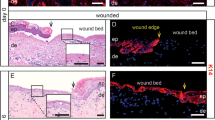
The survival of grafted donor skin for the treatment of burn injuries depends on several factors including wound bed vascularisation and the intensity of acute inflammation shortly after injury. However, acceptance rates approximate 50% at best and therefore a clinical need exists for improvement. The aim of the study was to develop a method for assessing the inflammatory response of cells in skin tissue based on activation of the NF-kappa B (NF-κB) transcription factor complex, thereby providing a basis for analysing the inflammatory component and anti-inflammatory strategies for tissue-engineered treatments. We have extended a standard method of measuring NF-κB in monolayer cultures that relies on determining translocation of the p65 subunit from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. Normal human skin and tissue engineered skin was analysed using an immunofluorescence microscopy technique, that revealed base line NF-κB activation in the epidermis and dermis were different. It was possible to determine the activation of NF-κB in skin tissue, enabling correlation that NF-κB measurement is a sensitive indicator of cellular responses in 3-D tissue. The approach will provide a basis for early responses of skin cells in determining the efficacy of anti-inflammatory delivery via tissue-engineered scaffolds for burn injuries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. T. BOYCE, Burns 27 (2001) 523.
S. J. GHOSH, K. KUMAR and P. M. GILBERT, Burns 23 (1997) 601.
K. H. CHAKRABARTY, R. A. DAWSON, P. HARRIS, C. LAYTON, M. BABU, L. GOULD, J. PHILLIPS, I. LEIGH, C. GREEN, E. FREEDLANDER and S. MACNEIL, Br. J. Dermatol. 141 (1999) 811.
J. A. KENCH, D. M. RUSSELL, V. A. FADOK, S. K. YOUNG, G. S. WORTHEN, J. JONES-CARSON, J. E. HENSON, P. M. HENSON and D. NEMAZEE, Clin. Immunol. 92 (1999) 300.
A. SCHWENTKER, Y. VODOVOTZ, R. WELLER and T. R. BILLIAR, Nitric Oxide 7 (2002) 1.
R. ODESSEY, J. Burn Care Rehabil. 13 (1992) 174.
M. MOUSTAFA, M. SZABO, G. E. GHANEM, R. MORANDINI, H. E. KEMP, S. MACNEIL and J. W. HAYCOCK, J. Invest. Dermatol. 119 (2002) 1244.
M. KARIN and Y. BEN-NERIAH, Ann. Rev. Immunol. 18 (2000) 621.
R. T. PETERS and T. MANIATIS, Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1471 (2001) M57.
Q. X. LAN, K. O. MERCURIUS and P. F. DAVIES, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 201 (1994) 950.
K. KUROKOUCHI, C. R. JACOBS and H. J. DONAHUE, J. Biol. Chem. 276 (2001) 13499.
G. ZüND, S. UEZONO, G. L. STAHL, A. L. DZUS, F. X. MCGOWAN, P. R. HICKEY and S. P. COLGAN, Am. J. Physiol. 273 (1997) C1571.
A. ANTONELLI, M. BIANCHI, R. CRINELLI, L. GENTILINI and M. MAGNANI, Blood Cells, Mole. Dis. 27 (2001) 978.
N. J. GOBERDAN, R. A. DAWSON, E. FREEDLANDER and S. MACNEIL, Br. J. Dermatol. 129 (1993) 678.
D. R. RALSTON, C. LAYTON and A. J. DALLEY, Br. J. Dermatol. 140 (1999) 605.
J. A. UKROPEC, M. K. HOLLINGER and M. J. WOOLKALIS, Exp. Cell. Res. 273 (2002) 240.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, T., Haycock, J.W., Szabo, M. et al. Measurement of NF-κB in normal and reconstructed human skin in vitro. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 15, 743–749 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSM.0000032812.18703.a9
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSM.0000032812.18703.a9