Abstract
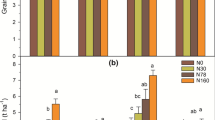
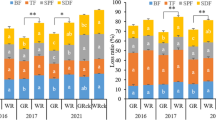
A long-term field and lysimeter experiment under different amount of fertilizer-N application was conducted to explore the optimal N application rates for a high productive rice–wheat system and less N leaching loss in the Yangtse Delta region. In this region excessive applications of N fertilizer for the rice–wheat production has resulted in reduced N recovery rates and environment pollution. Initial results of the field experiments showed that the optimal N application rate increased with the yield. On the two major paddy soils (Hydromorphic paddy soil and Gleyed paddy soil) of the region, the optimal N application rate was 225–270 kg N hm−2 for rice and 180–225 kg N hm−2 for wheat, separately. This has resulted in the highest number of effective ears and Spikelets per unit area, and hence high yield. Nitrogen leaching in the form of NO −3 -N occurs mainly in the wheat-growing season and in the ponding and seedling periods of the paddy field. Its concentration in the leachate increased with the N application rate in the lysimeter experiment. When the application rate reached 225 kg N hm−2, the concentration rose to 5.4–21.3 mgN l−1 in the leachate during the wheat-growing season. About 60% of the leachate samples determined contained NO −3 -N beyond the criterion (NO −3 -N 10 mg l−1) for N pollution. In the field experiment, when the N application rate was in the range of 270–315 kg hm−2, the NO −3 -N concentration in the leachate during the wheat-growing season ranged from 1.9 to 11.0 mg l−1. About 20% of the leachate samples reached close to, and 10% exceeded, the criterion for N pollution. Long-term accumulation of NO −3 -N from leaching will no doubt constitute a potential risk of N contamination of the groundwater in the Yangtse Delta Region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Cepuder P, Shukla MK, Liebhard P, Tuller M. 1998 Optimizing soil fertility and plant nutrition to prevent groundwater pollution. In Transaction of 16th World Soil Congress, 16th World Congress of Soil Science, August 11-18, 1998, Montpellier, France, Symposium 14.
Cui YT, Cheng X, Han CR, Li RG. 1998 Nitrogen recovery rate of rice and nitrogen leaching in Taihu Lake watershed in south Jiangsu Province. J China Agricult Univ 3(5), 51–54 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li WB, Wu LS, Liao HQ. 1997 Application and crop recovery of N-fertilizer in high-yielding paddy fields of Taihu Region. Acta Pedol Sin 34(1), 61–73, (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lin B, Lin JX, Li JK. 1996 Change in crop yields and soil fertility in long term fertilization experiments. In Lin B. et al., eds. Compilation of Papers on Fertilizer Experimental Network of China Beijing. China Agricultural Press, pp. 1–12 (in Chinese).
Lowrance R. 1992 Nitrogen outputs from a field-size agricultural watershed. J Environ Qual 21, 602–607.
Ma LS, Qian MR. 1987 Pollution of nitrates and nitrites in the Taihu Lake Valley and its assessment. Chinese J Environ Sci 8(2), 60–65 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Owens LB, Edwards WM, Van Keuren RW. 1992 Nitrate levels in shallow groundwater under pastures receiving ammonium nitrate or slow-release nitrogen fertilizer. J Environ Qual 21, 607–613.
Pan ZP, Xu WY, Wan CB. 1984 Technique for rational application of nitrogen fertilizer in Taihu Lake Region. VII. Effectiveness and optimum rate of N-fertilizer for single late rice. Jiangsu Agric Sci (12), 1–4 (in Chinese).
Wan CB, You DM, Pan ZP. 1982 Technique for rational application of nitrogen fertilizer in Suzhou District. III. Application rate and methods for winter wheat. Jiangsu Agric Sci (7), 1–6 (in Chinese).
Wang DJ, Lin JH, Xia LZ. 2001 Characteristics of nitrogen leaching of farmland under rice-wheat rotation in Taihu Lake Region. Chinese J Eco-Agricult 9(1), 16–18 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yi XL, Li YK, Han LF. 1983 Determination of soil nitrate nitrogen by ultraviolet spectrophotometry. Chinese J Soil Sci (6), 35–40 (in Chinese).
Zhang GL, Zhang S. 1998 Nitrogen leaching from farmlands — A review. Soils (6), 291–296 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang SL, Zhu ZL, Xu YH. 1988 Optimal nitrogen fertilizer application rate for rice and wheat in Taihu Lake Region. Soils 20(1), 5–9 (in Chinese).
Zhao QG. 1998 General situation and trend of international study on soil and environmental problems — a review of the 16th International Congress of Soil Science. Soils (6), 281–310 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Liu, Q., Lin, J. et al. Optimum Nitrogen Use and Reduced Nitrogen Loss for Production of Rice and Wheat in the Yangtse Delta Region. Environmental Geochemistry and Health 26, 221–227 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EGAH.0000039584.35434.e0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EGAH.0000039584.35434.e0