Abstract
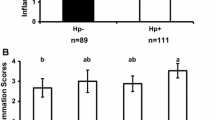
We investigated the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and COX-1 mRNAs during long-term Helicobacter pylori infection of the Mongolian gerbil (18 months) as well as the effect of eradication therapy and the cag pathogenicity island on COX mRNA expression. COX mRNA levels were determined by reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction. Pyloric channel ulcers were noted in one of 10 gerbils (10%) at 3 months, 33% at 6 months, 50% at 9 months, 17% at 10 months, 40% at 12 months and 25% at 18 months after inoculation of parental strains. Nineteen of 21 gerbils had successful H. pylori eradication and showed significant reduction of inflammation and no ulcerations. There were no significant differences in COX-1 mRNA expression between the groups. COX-2 mRNA expression was significantly increased 1 and 3 months after inoculation and then decreased to basal levels. In control animals, COX-2 mRNA expression was significantly higher at 12 and 18 months compared to younger animals. cagE knockout mutants did not induce gastric inflammation and induced significantly lower COX-2 mRNA expression compared to parental strains. COX-2 mRNA was induced early in H. pylori infection and then declined. COX-2 mRNA expression was also induced with aging.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamaoka Y, Kita M, Kodama T, Sawai N, Imanishi J: Helicobacter pylori cagA gene and expression ofcytokine messenger RNA in gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology 110:1744-1752, 1996
Yamaoka Y, Kita M, Kodama T, Sawai N, Kashima K, Imanishi J: Induction of various cytokines and development of severe mucosal inflammation by cagA gene-positive Helicobacter pylori strains. Gut 41:442-451, 1997
Yamaoka Y, Kita M, Kodama T, Sawai N, Tanahashi T, Kashima K, Imanishi J: Chemokines in the gastric mucosa in Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut 42:609-617, 1998
Yamaoka Y, Kodama T, M Kita, J Imanishi, Kashima K, Graham DY: Relation between clinical presentation, Helicobacter pylori density, interleukin-1 β and-8 production and cagA status. Gut 45:804-811, 1999
Ernst PB, Crowe SE, Reyes VE: How does Helicobacter pylori cause mucosal damage? The inflammatory response. Gastroenterology 113:S35-S42, 1997
Eberhart CE, DuBois RN: Eicosanoids and the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology 109:285-301, 1995
Robert A, Nezamis JE, Lancaster C, Hancher AJ: Cytoprotection by prostaglandins in rats. Prevention of gastric necrosis produced by alcohol, HCl, NaOH, hypertonic NaCl, and thermal injury. Gastroenterology 77:433-443, 1979
Tarnawski, Brzozowski T, Sarfeh IJ, Krause WJ, Ulich TR, Gergely H, Hollander D: Prostaglandin production of human isolated gastric glands against indomethacin and ethanol injury. Evidence for direct cellular action of prostaglandin. J Clin Invest 81:1081-1089, 1988
Vane JR: Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nature (London) New Biol 231:232-235, 1971
Fellows IW, Bhaskar NK, Hawkey CJ: The nature and time course of piroxicam-induced injury to human gastric mucosa. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 3:481-488, 1989
Vane J: Towards a better aspirin. Nature 367:215-216, 1994
Kargman S, Charleson S, Cartwright M, Frank J, Riendeau D, Mancini J, Evans J, O'Neill G: Characterization of prostaglandin G/H synthase 1 and 2 in rat, dog, monkey, and human gastrointestinal tracts. Gastroenterology 111:445, 1996
Coyne DW, Nickols M, Bertrand W, Morrison AR: Regulation of mesangial cell cyclooxygenase synthesis by cytokines and glucocorticoids. Am J Physiol 263:F97-F102, 1992
DuBois RN, Awad J, Morrow J, Roberts LJ 2nd, Bishop PR: Regulation of eicosanoid production and mitogenesis in rat intestinal epithelial cells by transforming growth factor-β and phorbol ester. J Clin Invest 93:493-498, 1994
Fu JY, Masferrer JL, Seibert K, Raz A, Needleman P: The induction and suppression of prostaglandin H2 synthase (cyclooxygenase) in human monocytes. J Biol Chem 265:16737-16740, 1990
Kargman SL, O'Neill GP, Vickers PJ, Evans JF, Mancini JA, Jothy S: Expression of prostaglandin G/H synthase-1 and-2 protein in human colon cancer. Cancer Res 55:2556-2559, 1995
O'Sullivan MG, Huggins EMJ, Meade EA, De Witt DL, McCall CE: Lipopolysaccharide induces prostaglandin H synthase-2 in alveolar macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 187:1123-1127, 1992
Herschman HR: Prostaglandin synthase 2. Biochim Biophys Acta 1299:124-140, 1996
Mizuno H, Sakamoto C, Matsuda K, Wada K, Uchida T, Noguchi H, Akamatsu T, Kasuga M: Induction of cyclooxygenase 2 in gastric mucosal lesions and its inhibition by the specific antagonist delays healing in mice. Gastroenterology 112:387-397, 1997
Gretzer B, Ehrlich K, Maricic N, Lambrecht N, Respondek M, Peskar BM: Selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors and their influence on the protective effect of a mild irritant in the rat stomach. Br J Pharmacol 123:927-935, 1998
Schmassmann A, Peskar BM, Stettler C, Netzer P, Stroff T, Flogerzi B, Halter F: Effects of inhibition of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase-2 in chronic gastro-intestinal ulcer models in rats. Br J Pharmacol 123:795-804, 1998
Hirayama F, Takagi S, Yokoyama Y, Iwao E, Ikeda Y: Establishment of gastric Helicobacter pylori infection in Mongolian gerbils. J Gastroenterol 31(suppl 9):24-28, 1996
Hirayama F, Takagi S, Kusuhara H, Iwao E, Yokoyama Y, Ikeda Y: Induction of gastric ulcer and intestinal metaplasia in Mongolian gerbils infected with Helicobacter pylori. J Gastroenterol 31:755-757, 1996
Watanabe T, Tada M, Nagai H, Sasaki S, Nakao M: Helicobacter pylori infection induces gastric cancer in Mongolian gerbils. Gastroenterology 115:642-648, 1998.
Takahashi S, Fujita T, Yamamoto A: Role of cyclooxygenase-2 in Helicobacter pylori induced gastritis in Mongolian gerbils. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 279:G791-G798, 2000
Odenbreit S, Puls J, Sedlmaier B, Gerland E, Fischer W, Haas R: Translocation of Helicobacter pylori CagA into gastric epithelial cells by type IV secretion. Science 287:1497-1500, 2000
Censini S, Lange C, Xiang Z, Crabtree JE, Ghiara P, Borodovsky M, Rappuoli R, Covacci A: cag, a pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori, encodes type I-specific and disease-associated virulence factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:14648-14653, 1996
Ogura K, Maeda S, Nakao M, Watanabe T, Tada M, Kyutoku T, Yoshida H, Shiratori Y, Omata M: Virulence factors of Helicobacter pylori responsible for gastric disease in Mongolian gerbil. J Exp Med 192:1601-1609, 2000
Yamaoka Y, Kwon DH, Graham DY: A M(r) 34,000 proinflammatory outer membrane protein (oipA) of Helicobacter pylori. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:7533-7538, 2000
Shimizu N, Ikehara Y, Inada K, Nakanishi H, Tsukamoto T, Nozaki K, Kaminishi M, Kuramoto S, Sugiyama A, Katsuyama T, Tatematsu M: Eradication diminishes enhancing effects of Helicobacter pylori infection on glandular stomach carcinogenesis in Mongolian gerbils. Cancer Res 60:1512-1514, 2000
O'Banion MK, Winn VD, Young DA: cDNA cloning and functional activity of a glucocorticoid-regulated inflammatory cyclooxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:4888-4892, 1992
Yamagata K, Andreasson KI, Kaufmann WE, Barnes CA, Worley PF: Expression of a mitogen-inducible cyclooxygenase in brain neurons: regulation by synaptic activity and glucocorticoids. Neuron 11:371-386, 1993
Hla T, Neilson K: Human cyclooxygenase-2 cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:7384-7388, 1992
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR: DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463-5467, 1977
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ. Clustal W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673-4680, 1994
Saitou N, Nei M: The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406-425, 1987
Yamaoka Y, Kodama T, Kita M, Imanishi J, Kashima K, Graham DY: Relation between cytokines and Helicobacter pylori in gastric cancer. Helicobacter 6:116-124, 2001
Genta RM, Robason GO, Graham DY: Simultaneous visualization of Helicobacter pylori and gastric morphology: a new stain. Hum Pathol 25:221-226, 1994
Dixon MF, Genta RM, Yardley JH, Correa P: Classification and grading of gastritis: the updated Sydney system. Am J Surg Pathol 20:1161-1181, 1996
Takashima M, Furuta T, Hanai H, Sugimura H, Kaneko E: Effects of Helicobacter pylori infection on gastric acid secretion and serum gastrin levels in Mongolian gerbils. Gut 48:765-773, 2001
Israel DA, Salama N, Arnold CN, Moss SF, Ando T, Wirth HP, Tham KT, Camorlinga M, Blaser MJ, Falkow S, Peek RM Jr: Helicobacter pylori strain-specific differences in genetic content, identified by microarray, influence host inflammatory responses. J Clin Invest 107:611-620, 2001
Nakamura M, Takahashi S, Matui H, Nishikawa K, Akiba Y, Ishii H: Persistent increase in myofibroblasts in Helicobacter Helimannii-infected mice but not in Helicobacter pylori-infected Mongolian gerbils: colocalization of COX-2 and bFGF immunoreactivity. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 16:174-179, 2002
Vogiagis D, Glare EM, Misajon A, Brown W, O'Brien PE: Cyclooxygenase-1 and an alternatively spliced mRNA in the rat stomach: effects of aging and ulcers. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 278:G820-G827, 2000
Lee M, Feldman M: Age-related reductions in gastric mucosal prostaglandin levels increase susceptibility to aspirin-induced injury in rats. Gastroenterology 107:1746-1750, 1994
Uchida M, Kawano O, Misaki N, Saitoh K, Irino O: Healing of aetic asidinduced gastric ulcer and regulation of its mRNA expression in gastric ulcers and gastric mucosal PGI2 level in rats. Dig Dis Sci 35:80-85, 1990
Soll A, Weinstein W, Kurata J, McCarthy D: Nonsteroi-dal antiinflammatory drugs and peptic ulcer disease. Ann Intern Med 114:307-319, 1991
McCarthy CJ, Crofford LJ, Greenson J, Scheiman JM: Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in gastric antral mucosa before and after eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection. Am J Gastroenterol 94:1218-1223, 1999
Jackson LM, Wu KC, Mahida YR, Jenkins D, Hawkey CJ: Cyclooxygenase (COX) 1 and 2 in normal, inflamed, and ulcerated human gastric mucosa. Gut 47:762-770, 2000
Fu S, Ramanujam KS, Wong A, Fantry GT, Drachenberg CB, James SP, Meltzer SJ, Wilson KT: Increased expression and cellular localization of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase 2 in Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Gastroenterology 116:1319-1329, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakai, T., Fukui, H., Franceschi, F. et al. Cyclooxygenase Expression During Helicobacter pylori Infection in Mongolian Gerbils. Dig Dis Sci 48, 2139–2146 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:DDAS.0000004517.83166.26
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:DDAS.0000004517.83166.26