Abstract
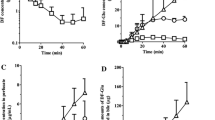
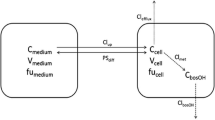
The kinetics of the individual enantiomers of verapamil (VER) and its metabolite, norverapamil (NOR), were studied in isolated perfused rat livers (IPRLs) after administration of racemic drug or the preformed metabolite. After constant infusion of 20 µg/min of racemic VER to single-pass IPRLs, the hepatic availabilities (F) of the enantiomers were low (S-VER, 0.069 ± 0.030; R-VER: 0.046 ± 0.025) and stereoselective (S:R ratio, 1.6 ± 0.2). After administration of similar doses, the F values of the preformed NOR enantiomers (S-NOR: 0.24 ± 0.04; R-NOR, 0.10 ± 0.02) were higher than those of the VER enantiomers. However, the stereoselectivity in F of NOR (S:R ratio, 2.2 ± 0.1), was in the same direction of that of VER. Further, the fractions of R enantiomers unbound to bovine serum albumin in the perfusate were higher than those of their antipodes for both VER (R:S ratio, 1.9 ± 0.1) and NOR (R:S ratio, 2.6 ± 0.2). Therefore, for unbound moieties, modest stereoselectivity in the metabolism of VER in favor of the S-isomer and no stereoselectivity in the metabolism of NOR were observed. Overall, our data suggest that the stereoselective protein binding is a primary determinant of stereoselectivity in the hepatic availability of VER and NOR in IPRLs.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
H. Echizen, M. Manz, and M. Eichelbaum. Electrophysiologic effects of dextro-and levo-verapamil on sinus node and AV node function in humans. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 12: 543–546 (1988).
S. R. Hamann, R. A. Blouin, and R. G. McAllister, Jr. Clinical pharmacokinetics of verapamil. Clin. Pharmacokin. 9: 26–41 (1984).
H. M. McIlhenny. Metabolism of [14C]Verapamil. J. Med. Chem. 14: 1178–1184 (1971).
R. G. McAllister, Jr., D. W. A. Bourne, and L. W. Dittert. The pharmacology of verapamil. I. Elimination kinetics in dogs and correlation of plasma levels with effect on the electrocardiogram. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 202: 38–44 (1977).
E. L. Todd and D. R. Abernethy. Physiological pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of (+/−)-verapamil in female rats. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 8: 285–297 (1987).
J. C. Giacomini, W. L. Nelson, L. Theodore, F. M. Wong, D. Rood, and K. M. Giacomini. The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of d-and dl-verapamil in rabbits. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 7: 469–475 (1985).
P. Manitpisitkul and W. L. Chiou. Intravenous verapamil kinetics in rats: Marked arteriovenous concentration difference and comparison with humans. Biopharm. Drug Dipos. 14: 555–566 (1993).
B. Vogelgesang, H. Echizen, E. Schmidt and M. Eichelbaum. Stereoselective first-pass metabolism of highly cleared drugs: studies of the bioavailability ofL-andD-verapamil examined with stable isotope technique. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 18: 733–740 (1984).
G. Mikus, M. Eichelbaum, C. Fischer, S. Gumulka, U. Klotz, and H. K. Kroemer. Interaction of verapamil and cimetidine: Stereochemical aspects of drug metabolism, drug disposition and drug action. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 253: 1042–1048 (1990).
H. K. Kroemer, H. Echizen, H. Heidemann, and M. Eichelbaum. Predictability of the in vivo metabolism of verapamil from in vitro data: Contribution of individual metabolic pathways and stereoselective aspects. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 260: 1052–1057 (1992).
D. R. Abernethy, I. W. Wainer, J. A. Longstreth, and N. S. Andrawis. Stereoselective verapamil disposition and dynamics in aging during racemic verapamil administration. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 266: 904–911 (1993).
S. A. Bai, S. M. Lankford, and L. M. Johnson. Pharmacokinetics of the enantiomers of verapamil in the dog. Chirality 5: 436–442 (1993).
K. S. Pang. Liver perfusion studies in drug metabolism and drug toxicity. In J. R. Mitchell and M. G. Horning (eds.), Drug Metabolism and Drug Toxicity, Raven Press, New York, 1984, pp. 331–352.
W. L. Nelson, E. D. Olsen, D. B. Beitner, and R. J. Pallow, Jr. Regiochemistry and substrate stereoselectivity of O-demethylation of verapamil in the presence of the microsomal fraction from rat and human liver. Drug Metab. Dispos. 16: 184–188 (1988).
W. L. Nelson and L. D. Olson. Regiochemistry and enantioselectivity in the oxidative N-dealkylation of verapamil. Drug Metab. Dispos. 16: 834–841 (1988).
J. R. Cashman. Enantioselective N-oxygenation of verapamil by the hepatic flavin-containing monooxygenase. Mol. Pharmacol. 36: 497–503 (1989).
R. Mehvar, J. M. Reynolds, and T. L. Shepard. Disposition of fluorescein-labelled dextran (150 kD) in isolated perfused livers from control and diabetic rats. Life Sci. 49: 1699–1706 (1991).
A. Shibukawa and I. W. Wainer. Simultaneous direct determination of the enantiomers of verapamil and norverapamil in plasma using a derivatized amylose high-performance liquid chromatographic chiral stationary phase. J. Chromatogr. 574: 85–92 (1992).
G. R. Wilkinson and D. G. Shand. A physiological approach to hepatic drug clearance. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 18: 377–390 (1975).
K. S. Pang and K. C. Kwan. A commentary: Methods and assumptions in the kinetics estimation of metabolite formation. Drug Metab. Dispos. 11: 79–84 (1983).
Y. K. Tam, M. Yau, R. Berzins, P. R. Montgomery, and M. Gray. Mechanisms of lidocaine kinetics in the isolated perfused rat liver. I. Effects of continuous infusion. Drug Metab. Dispos. 15: 12–16 (1987).
M. D. Hussain, Y. K. Tam, M. R. Gray, and R. T. Coutts. Mechanisms of time-dependent kinetics of diltiazem in the isolated perfused rat liver. Drug Metab. Dispos. 22: 36–42 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehvar, R., Reynolds, J.M., Robinson, M.A. et al. Enantioselective Kinetics of Verapamil and Norverapamil in Isolated Perfused Rat Livers. Pharm Res 11, 1815–1819 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018935921473
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018935921473