Abstract
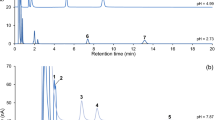
A redox-based chemical delivery system for estradiol (E2-CDS) has been shown capable of sustained and brain-selective delivery of estradiol (E2). A re versed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) method is presented for the analysis of E2-CDS and its oxidized quaternary metabolite (E2-Quat) in biological fluids or tissues. The assay utilizes a precolumn enrichment technique and detects plasma levels down to 10 ng/ml E2-Quat and 20 ng/ml E2-CDS. Sample preparation is rapid and simple. Samples are homogenized with acetonitrile, then centrifuged, and the supernatant is directly injected into the HPLC system. A water delivering pump injects the sample on a precolumn where the drug is concentrated. The mobile phase backflushes the retained compound onto the analytical column. At the same time, another sample can be injected onto a second precolumn. This alternating precolumn sample enrichment technique allows the injection of large volumes, up to 1800 µl. Plasma and tissue samples of rats collected after i.v. administration of a single 15-mg/kg E2-CDS dose were analyzed for E2-CDS and E2-Quat by this procedure. The results show sustained brain levels of E2-Quat and prolonged half-life in brain compared to six peripheral tissues measured. These data support the concept of brain-targeted delivery using redox carrier systems of this type.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
N. Bodor, H. H. Farag, and M. E. Brewster. Science 214:1370–1373 (1981).
N. Bodor and M. E. Brewster. Pharmacol. Ther. 19:337–386 (1983).
N. Bodor and H. H. Farag. J. Med. Chem. 26:313–318 (1983).
N. Bodor and J. W. Simpkins. Science 221:65–67 (1983).
N. Bodor and H. H. Farag. J. Pharm. Sci. 73:385–389 (1984).
J. W. Simpkins, N. Bodor, and A. Enz. J. Pharm. Sci. 74:1033–1036 (1985).
N. Bodor. In H. Bundgaard (ed.), Design of Prodrugs, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1985, pp. 333–354.
N. Bodor. In K. Widder (ed.), Methods in Enzymology, Drug and Enzyme Targeting, Academic Press, New York, 1985, pp. 381–396.
N. Bodor, J. McCornack, and M. E. Brewster. Int. J. Pharm. 35:47–59 (1987).
J. W. Simpkins, J. McCornack, K. S. Estes, M. E. Brewster, E. Shek, and N. Bodor. J. Med. Chem. 29:1809–1812 (1986).
K. Estes, M. E. Brewster, J. Simpkins, and N. Bodor. Life Sci. 40:1327–1334 (1987).
R. L. Goodman, and E. Knobil. Neuroendocrinology 32:57–63 (1981).
F. Labrie, A. Dupont, A. Belanger, F. A. Lefebyre, L. Cusan, G. Monfette, J. G. Leberge, J. P. Emond, J. P. Raymond, J. M. Husson, and A. T. A. Fazekas. Steroid Biochem. 19:999–1007 (1983).
S. S. C. Yen. J. Reprod. Med. 18:287–289 (1977).
W. Roth, K. Beschke, R. Jauch, A. Zimmer, and F. W. Koss. J. Chromatogr. 222:13–22 (1981).
J. Blanchard. J. Chromatogr. 226:455–460 (1981).
J. M. Larner and R. B. Hochberg. Endocrinology 117:1209–1214 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mullersman, G., Derendorf, H., Brewster, M.E. et al. High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Assay of a Central Nervous System (CNS)-Directed Estradiol Chemical Delivery System and Its Application After Intravenous Administration to Rats. Pharm Res 5, 172–177 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015964907110
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015964907110