Abstract
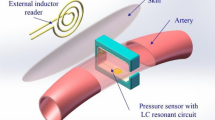
This paper presents an implantable microsystem for tonometric blood pressure measurement in small animals. The microsystem consists of four major components: (1) a titanium base for supporting a pressure sensor and an interface chip, (2) a micromachined capacitive pressure sensor array, (3) a switched-capacitor interface chip, and (4) a titanium cap. A new micromachining fabrication process has been developed to create capacitive pressure transducers with a flat surface necessary for tonometric pressure measurement. An array of three capacitive sensors is used to increase signal output and improve stability. A custom-designed switched-capacitor CMOS interface circuit is used to measure changes in capacitance. In vitro calibration tests have been performed on the complete cuff using a silastic tube to mimic a pliable blood vessel. A sensitivity of 2 mV/mmHg @ 100 mmHg and a resolution of 0.5 mmHg (based on 1 mV RMS interface chip noise floor) has been obtained. The dimensions of the cuff system 10(L)×6.5(W)×3(H) mm3.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.P. Broten, S.D. Kivlighn, C.M. Harvey, A.L. Scott, T.W. Schorn, and P.K.S. Siegl, in Measurement of Cardiovascular Function, J.H. McNeil, (ed.), (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1997).
R.A. Peura, in Medical Instrumentation Application and Design, John G. Webster, (ed.), (John Wiley, New York, 1998).
B. Brockway, P.A. Mills, and S.M. Azar, Clinical and Experimental Hypertension-Theory and Practice 13, 885 (1991).
Konigsberg Instrument, Inc., Biomedical Product Cathalog, April 1994.
H. Goldmann, in Glaucoma: Transactions of the Second Conference, F.W. Newell, (ed.) (Princeton, NJ, Dec. 1956), 167.
R.S. MacKay and E. Marg, IRE Trans. Med. Electronics 7, 61 (1960).
J.S. Eckerle, J. Fredrick, and P. Jeuck, Proceedings IEEE EMBS 635 (1984).
G.M. Drzeweicki, J. Melbin, and A. Noordergraaf, J. Biomechanics 16, 141 (1983).
S. Terry, J.S. Eckerle, R.D. Kurnbluh, T. Low, and C.M. Ablow, Sensors and Actuators A21-A23, 1070 (1990).
H.L. Chau and K.D. Wise, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 235, 2355 (1988).
M. Di Giovanni, Flat and Corrugated Diaphragm Design Handbook (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1982).
Y. Zhang and K.D. Wise, Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems 3, 59 (1994).
Y.E. Park and K.D. Wise, Digest IEEE Custom IC Conference 380 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ziaie, B., Najafi, K. An Implantable Microsystem for Tonometric Blood Pressure Measurement. Biomedical Microdevices 3, 285–292 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012452613720
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012452613720