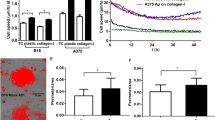
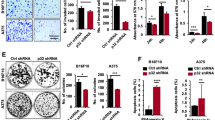
Abstract
We previously demonstrated that expression of the cell surface adhesion molecule MCAM/MUC18 correlates directly with the metastatic potential of human melanoma cells. In addition, the progression of human melanoma towards the metastatic phenotype is associated with loss of expression of the tyrosine-kinase receptor c-KIT. This review summarizes our recent data demonstrating that the expression of both genes is regulated by the AP-2 transcription factor. Moreover, we have observed a loss of AP-2 expression in metastatic melanoma cells. Re-expression of AP-2 in the highly metastatic A375SM cells decreased their tumorigenicity and inhibited their metastatic potential in nude mice. MCAM/MUC18 mRNA and protein expression was significantly downregulated while c-kit expression was upregulated in the AP-2 transfected cells. Since AP-2 also regulates other genes that are involved in the progression of human melanoma such as E-cadherin, MMP-2, p21WAF-1, HER-2, BCL-2, and insulin like growth factor receptor-1, we propose that loss of AP-2 is a crucial event in the development of malignant melanoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kopf AW, Slopek TG, Slade J, Marghoob AA, Bart RS: Techniques of cutaneous examination for the detection of skin cancer. Cancer 75: 684-690, 1995
Fidler IJ: Critical factors in the biology of human cancer metastasis. Cancer Res 50: 6130-6138, 1990
Lassam N, Bickford S: Loss of c-KIT expression in cultured melanoma cells. Oncogene 7: 51-56, 1992
Natali PG, Nicotra MR, Winkler AB, Cavaliere R, Bigotti A, Ullrich A: Progression of human cutaneous melanoma is associated with loss of expression of c-KIT protooncogene receptor. Int J Cancer 52: 197-201, 1992
Zakut R, Perlis R, Eliyahu S, Yarden Y, Givol D, Lyman SD, Halaban R: KIT ligand (mast cell growth factor) inhibits the growth of KIT-expressing melanoma cells. Oncogene 8: 2221-2229, 1993
Yarden Y, Kuang WJ, Yang-Feng T, Coussens L, Mumenitus S, Dull TJ, Chen E, Schlessinger J, Francke U, Ullrich A: A human proto-oncogene c-KIT: a new cell surface receptor tyro sine kinase for an unidentified ligand. EMBO J 6: 3342-3351, 1987
Chabot B, Stephenson DA, Chapman VM, Besmer P, Bernstein A: The protooncogene c-KIT encoding a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor maps to the mouse W locus. Nature 335: 88-89, 1988
Geisler EN, Ryan MA, Housman DE: The dominant white spotting (W) locus of the mouse encodes the c-KIT protooncogene. Cell 55, 185-192, 1988
Zsebo KM, Williams DA, Geissler EN, Broudy VC, Martin FH, Atkins HL, Hsu RY, Birkett NC, Okino KH, Murdock DC, Jacobson FW, Langley KE, Smith KA, Takeishi T, Cattanach BM, Galli SJ, Snuggs S: Stem cell factor is encoded at the SL locus of the mouse and is the ligand for the c-KIT tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell 63: 213-224, 1990
Nocka K, Majumder S, Chabot B, Ray P, Cervone M, Bernstein A, Besmer P: Expression of the c-KIT gene products in known cellular targets of W mutations in normal and W mutant mice: Evidence for impaired c-KIT kinase in mutant mice. Genes Dev 3: 816-826, 1989
Brannan CI, Lyman SD, Williams DE, Eisenman J, Anderson D, Cosman D, Bedell MA, Jenkins NA, Coopeland NG: Steel-Dickie mutation encodes a c-KIT ligand lacking transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 4671-4674, 1991
Nishikawa S, Kusakabe M, Yoshingaga K, Ogawa M, Hayashi SI, Kunisada T, Era T, Sakakura T, Nishikawa SI.: In vitro manipulation of coat color formation by a monoclonal anti-c-KIT antibody: two distinct waves of c-KIT dependency during melanocyte development. EMBO J 10: 2111-2118, 1991
Giebel LB, Spritz RA: Mutation of the KIT (mast/stem cell growth factor receptor) proto-oncogene in human piebaldism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA: 88: 8696-8699, 1991
Fleischman RA, Saltman KL, Stastny V, Zneimer S: Deletion of the c-KIT protooncogene in the human development defect piebald trait. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 10885-10889, 1991
Huang S, Luca M, Gutman M, McConkey DJ, Langley KE, Lyman SD, Bar-Eli M: Enforced c-KIT expression renders highly metastatic human melanoma cells susceptible to stem cell factor induced apoptosis and inhibits their tumorigenic and metastatic potential. Oncogene 13: 2339-2347, 1996
Lehmann JM, Holzmann B, Breitbart EW, Schmiegelow P, Riethmuller G, Johnson JP: Discrimination between benign and malignant cells of melanocytic lineage by two novel antigens, a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 76,000. Cancer Res 47: 841-845, 1987
Holzmann B, Brocker EB, Lehmann JM, Rutter DJ, Sorg C, Riethmuller G, Johnson JP: Tumor progression in human melanoma: five stages defined by their antigenic phenotypes. Int J Cancer 39: 466-471, 1987
Breslow A: Thickness, cross-sectional areas and depth of invasion in the prognosis of cutaneous melanoma. Ann Surg 172: 902-908, 1970
Luca M, Hunt B, Bucana CD, Johnson JP, Fidler IJ, Bar-Eli M: Direct correlation between MUC18 expression and metastatic potential of human melanoma cells. Melanoma Res 3: 35-41, 1993
Bani MR, Rak J, Adachi D, Wiltshire R, Trent JM, Kerbel RS, Ben-David Y: Multiple features of advanced melanoma recapitulated in tumorigenic variants of early state (radial growth phase) human melonoma cell lines: evidence for a dominant phenotype. Cancer Res 56: 3075-3086, 1996
Xie S, Huang S, Luca M, Gutman M, Reich R, Johnson JP, Bar-Eli M: Expression of MCAM/MUC18 by human melanoma cells leads to increased tumor growth and metastasis. Cancer Res 57: 2295-2303, 1997
Lehmann JM, Riethmuller G, Johnson JP: MUC18, a marker of tumor progression in human melanoma, shows sequence similarity to the neural cell adhesion molecules of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Proc Natl Sci USA 89: 9891-9895, 1989
Sers C, Kirsch K, Rothbacher U, Riethmuller G, Johnson JP: Genomic organization of the melanoma-associated glycoprotein MUC18: implications for the evolution of the immunoglobulin domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 8514-8518, 1993
Shih IM, Elder DE, Speicher D, Johnson JP, Herlyn M: Isolation and functional characterization of the A32 melanoma-associated antigen. Cancer Res 54: 2514-2520, 1995
Johnson JP, Bar-Eli M, Jansen B, Markhuf E: Melanoma progression-associated glycoprotein MUC18/MCAM mediates homotypic cell adhesion through interaction with a heterophilic ligand. Int J Cancer 73: 769-774, 1997
Bar-Eli M: Molecular mechanisms of melanoma metastasis. J Cell Physiol 173: 275-278, 1997
Williams T, Admon A, Luscher B, Tjian R: Cloning and expression of AP-2, a cell-type-specific transcription factor that activates inducible enhancer elements. Genes Dev 2: 1557-1569, 1988
Gaynor RB, Muchardt C, Xia YR, Klisak I, Mohandas T, Sparkes RS, Lusis AJ: Localization of the gene for the DNA-binding protein AP-2 to human chromosome 6p 22.3 pter. Genomics 10: 1100-1102, 1991
Mitchell PJ, Timmons PM, Hebert JM, Rigby PW, Tjian R: Transcription factor AP-2 is expressed in neural crest cell lineages during mouse embryogenesis. Genes Dev 5: 105-119, 1991
Mitchell PJ, Wang C, Tjian R: Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: Enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 antigen. Cell 50: 847-861, 1987
Williams T, Tjian R: Characterization of a dimerization motif in AP-2 and its function in heterologous DNA-binding proteins. Science 251: 1067-1071, 1991
Buettner R, Kannan P, Imhof A, Bauer R, Yim SO, Glackshuber R, van Dyke MW, Tainsky MA: An alternatively spliced mRNA from the AP-2 gene encodes a negative regulator of transcriptional activation of AP-2. Mol Cell Biol 13: 4174-4185, 1993
Luscher B, Mitchell PJ, Williams T, Tjian R: Regulation of transcriptional factor AP-2 by the morphogen retinoic acid and by second messengers. Genes Dev 3: 1507-1517, 1989
Schorle H, Meier P, Buchert M, Jaenisch R, Mitchell PJ: Transcription factor AP-2 essential for cranial closure and craniofacial development. Nature 381: 235-238, 1996
Zhang J, Hagopian-Donaldson S, Serbedzija G, Elsemore J, Plehn-Dujowich D, McMahon AP, Flavell RA, Williams T: Neural tube, skeletal and body wall defects in mice lacking transcription factor AP-2. Nature 381: 238-241
Karjalainen JM, Kellokoski JK, Eskelinen MJ, Alhava EM, Kosma V-M: Downregulation of transcription factor AP-2 predicts poor survival in stage I cutaneous malignant melanoma. J Clin Oncol 16: 3584-3591,1998
Yamamoto K, Tojo A, Aoki N, Shibuya A: Characterization of the promoter region of the human c-KIT protooncogene. Jpn J Cancer Res 84: 1136-1144, 1993
Orr-Urtreger A, Avivi A, Zimmer Y, Givol D, Yarden Y, Lonai P: Developmental expression of c-KIT, a proto-oncogene encoded by the W locus. Development 109: 911-923, 1990
Huang S, Jean D, Luca M, Tainsky M, Bar-Eli M: Loss of AP-2 results in downregulation of c-KIT and enhancement of melanoma tumorigenicity and metastasis. EMBO J 17: 4358-4369, 1998
Luca M, Xie S, Gutman M, Huang S, Bar-Eli M: Abnormalities in the CDKN2 (p16INK4/mts-l) gene in human melanoma cells: relevance to tumor growth and metastasis. Oncogene 11: 1399-1402, 1995
Jean D, Gershenwald JE, Huang S, Luca M, Hudson MJ, Tainsky AM, Bar-Eli M: Loss of AP-2 results in upregulation of MCAM/MUC18 and an increase in tumor growth and metastasis of human melanoma cells. J Biol Chem 273: 16501-16508, 1988
Luca M, Huang S, Gershenwald JE, Singh RK, Reich R, Bar-Eli M: Expression of IL-8 by human melanoma cells upregulates MMP-2 activity and increases tumor growth and metastasis. Am J Pathol 151: 1105-1113, 1997
Singh RK, Gutman M, Reich R, Bar-Eli: Ultraviolet B irradiation promotes tumorigenic and metastatic properties in primary cutaneous melanoma via induction of interleukin 8. Cancer Res 55: 3669-3674, 1995
Cowley GP, Smith ME: Cadherin expression in melanocytic naevi and malignant melanomas. Am J Pathol 179: 183-187, 1996
Jiang H, Lin J, Su ZZ, Herlyn M, Kerbel RS, Weissman BE, Welch DR, Fisher PB: The melanoma differentiation-associated gene mda-6, which encodes the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21, is differentially expressed during growth, differentiation and progression in human melanoma cells. Oncogene 10: 1855-1864, 1995
Vidal MJ, Loganzo F Jr, de Oliveira AR, Hayward NK, Albino AP: Mutations and defective expression of the WAF-1 p21 tumor-suppressor gene in malignant melanomas. Melanoma Res 5: 243-250, 1995
Natali PG, Nicotra MR, Digiesi G, Cavaliere R, Bigotti A, Trizio D, Segatto O: Expression of gp 185 HER-2 in human cutaneous melanoma: implications for experimental immunotherapeutics. Int J Cancer 56: 341-346, 1994
Descheemaeker KA, Syns S, Nelles L, Auwerx J, Ny T, Collen D: Interaction of AP-1-like, AP-2-like and SP-1-like proteins with two distinct sites in the upstream regulatory region of the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene mediates the phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate response. J Biol Chem 267: 15086-15091, 1992
van den Oord JJ, Vandeghinste N, De Ley M, De Wolf-Peeters C: Bcl-2 expression in human melanocytes and melanocytic tumors. Am J Pathol 145: 294-300, 1994
Bosher JM, Williams T, Hurst HC: The developmentally regulated transcription factor AP-2 is involved in c-erbB-2 overexpression in human mammary carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 744-747, 1995
Zeng YX, Somasundaran K, El-Deiry WS: AP-2 inhibits cancer cell growth and activates p21WAF/CIP1 expression. Nature Genet 15: 78-82, 1997
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bar-Eli, M. Role of AP-2 in Tumor Growth and Metastasis of Human Melanoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev 18, 377–385 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006377309524
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006377309524