Abstract
Data on the annual production per area of mosses used as biomonitors is of major importance in the calculation of heavy metal deposition rates derived from concentration values. Therefore, annual biomass production per area was determined for Hylocomium splendens (127 ± 61 gm-2 yr-1), Pleurozium schreberi (161 ± 56 gm-2 yr-1), Hypnum cupressiforme (188 ± 62 gm-2 yr-1) and Abientinella abietina (144 ± 45 gm-2 yr-1) at 54 sites in Austria. Annual increments were detected by morphological criteria. Central European populations of mosses produce on average 10% (H. splendens) and 39% (P. schreberi) more biomass per area than populations from Northern Europe or Canada.
Due to great differences in biomass production at various sites it is suggested calculating heavy metal deposition rates by using mean values only for larger areas and to take only data from accurate measurements of annual growth rates for the calculations of the depositions at single sites.
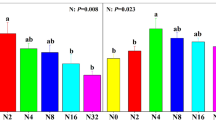
A comparison between heavy metal concentrations (As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Hg, Mo, Ni, Pb, V, Zn) in H. cupressiforme and A. abietina showed comparable uptake efficiences for both mosses with somewhat higher values (quotient > 1) in H. cupressiforme. These results correspond with those obtained from other monitoring species (e.g. H. splendens).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atanasiu, L.: 1971, 'Photosynthesis and Respiration of Three Mosses at Winter Low Temperatures', Brylogist 74, 23–27.
Bakken, S.: 1994, 'Growth and Nitrogen Dynamics of Dicranum majus Under Two Contrasting Nitrogen Deposition Regimes', Lindbergia 19, 63–72.
Barret, K., Seland, Ø., Foss, A., Mylona, S., Styeve, H. and Tarrason, L.: 1995, European Transboundary Acidifying Air Pollution, EMEP/MSC-WE Report.
Bates, J. W.: 1993, 'Comparative Growth Patterns of the Thalloid Liverworts Pallavicinia lyellii and Pellia epiphylla at Silwood Park, Southern England', Journal of Bryology 17, 439–445.
Bengtson, C., Folkeson, L. and Göransson, A.: 1982, 'Growth Reduction and Branching Frequency in Hylocomium splendens Near a Foundry Emitting Copper and Zinc', Lindbergia 8, 19–138.
Berg, T., Røset, O. and Steinnes, E.: 1995, 'Moss (Hylocomium splendens) Used as Biomonitor of Atmospheric Trace Element Deposition: Estimation of Uptake Efficiencies', Atmospheric Environment 29, 353–360.
Brown, D. H. and Bates, J. W.: 1990, 'Bryophytes and Nutrient Cycling', Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 104, 129–147.
Busby, J. R., Bliss, L. C. and Hamilton, C. D.: 1978, 'Microclimate Control of Growth Rates and Habitats of the Boreal Forest Mosses, Tomenthypnum nitens and Hylocomium splendens', Ecological Monographs 48, 95–110.
Callaghan, T.V., Collins, N. J. and Callaghan, C. H.: 1978, 'Photosynthesis, Growth and Reproduction of Hylocomium splendens and Polytrichum commune in Swedish Lapland', Oikos 31, 73–88.
Dirkse, G. M. and Martakis, G. F. P.: 1992, 'Effects of Fertilizer on Bryophytes in Swedish Experiments of Forest Fertilization', Biol. Concerv. 59, 155–161.
During, H.: 1979, 'Life Strategies of Bryophytes: A Preliminary Review', Lindbergia 5, 2–18.
During, H.: 1992, 'Ecological classification of bryophytes and lichens', In: Bates, J. and Farmer, A. (eds.): Bryophytes and lichens in a changing environment, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 2–32.
Farmer, A. M., Bates, J. W. and Bell, J. N.: 1992, 'Ecophysiological Effects of Acid Rain on Bryophytes and Lichens', in: Bates, J. W and Farmer, A. (eds.): Bryophytes and Lichens in a Changing Environment, Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp. 284–313.
Furness, S. B. and Grime, J. P.: 1982, 'Growth Rate and Temperature Responses in Bryophytes', Journal of Ecology 70, 525–536.
Gjengedahl, E. and Steinnes, E.: 1990, 'Uptake of Metal Ions in Moss From Artificial Precipitation', Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 14, 77–87.
Hayward, P. M. and Clymo, R. S.: 1983, 'The Growth of Sphagnum: Experiments on and Simulation of Some Effects of Light Flux and Water Table Depth', Journal of Ecology 71, 845–863.
Herpin, U., Markert, B., Siewers, Y. and Lieth, H.: 1994, Monitoring der Schwermetallbelastung in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland mit Hilfe von Moosanalysen, Bundesministerium für Umwelt, Naturschutz und Reaktorsicherheit; Ökologie, Forschungsbericht 108 02 087.
Kallio, P. and Heinonen, S.: 1973, 'Ecology of Racomitrium lanuginosum (Hedw.) Brid', Report from the Kevo Subarctic Research Station 10, 43–54.
Kovar, A. and Puxbaum, H.: 1992, Nasse Depositionen im Ostalpenraum, Bericht 14/92 TU. Wien.
Longton, R. E. and Greene, S. W.: 1979, 'Experimental Studies of Growth and Reproduction in the Moss Pleurozium schreberi (Bird.) Mitt', Journal of Bryology 10, 321–338.
Mägdefrau, K.: 1982, 'Life-forms of Bryophytes', in: Smith, A. J. E. (ed.), Bryophyte Ecology, Chapman and Hall, London, pp. 45–58.
Pakarinen, P. and Rinne, R. J. K.: 1979, 'Growth Rates and Heavy Metal Concentrations of Five Moss Species in Paludified Spruce Forests', Lindbergia 5, 77–83.
Pitkin, H. P.: 1975, 'Variability and Seasonality of the Growth of Some Corticolous Pleurocarpous Mosses', Journal of Bryology 8, 337–356.
Proctor, M. C. F.: 1982, 'Physiological Ecology: Water Relations, Light and Temperature Responses, Carbon balance', in: Smith, A. J. E. (ed.), Bryophyte Ecology, Chapman and Hall, London, pp. 333–381.
Raeymaekers, G.: 1987, 'Effects of Simulated Acidic Rain and Lead on the Biomass, Nutrient Status, and Heavy Metal Content of Pleurozium schreberi (Brid.) Mitt.', Journal Hattori Botanical Labratory 63, 219–230.
Rincon, E. and Grime, J. P.: 1989, 'An Analysis of Seasonal Patterns of Bryophyte Growth in a Natural Habitat', Journal of Ecology 77, 447–455.
Ross, H. B.: 1990, 'On the use of Mosses (Hylocomium splendens and tiPleurozium schreben) for Estimating Atmospheric Trace Metal Deposition', Water, Air, Soil Pollution 50, 63–76.
Rühling, Å.: 1985, 'Mätning av metalldeposition genom mossanalys', Rapport. IVL B-publikation Stockholm 782, 1–10.
Rühling, Å. (ed.): 1994a, 'Atmospheric Heavy Metal Deposition in Europe – Estimation Based on Moss Analysis', NORD 1994 9, 1–53.
Rühling, Å.: 1994b. Monitoring of atmospheric heavy-metal deposition in Europe using bryophytes and humus samples as indicators'. Proposal for an international programme 1995, Lund.
Rühling, Å. (ed.): 1997, 'Survey of Atmospheric Heavy Metal Deposition in the Nordic Countries in 1995 – Monitored by Moss Analysis', Nordisk Ministerrad, NORD 1996, 6, 37.
Rühling, Å., Rasmussen, L., Pilegaard, K., Mäkinen, A. and Steinnes, E.: 1987, 'Survey of Atmospheric Heavy Metal Deposition in the Nordic Countries in dy1985–Monitored by Moss Analysis', Nordisk Ministerrad, NORD 1987 21, 1–44.
Schmid-Grob, I., Thöni, L. and Hertz, J.: 1992, 'Applicability of the Moss Hypnum cupressiforme Hedw. s.l. for Biomonitoring of Heavy Metals: 2. A Comparison With the Moss Hylocomium splendens (Hedw.) Schimp. and the Freights in Bulk Precipitation in Switzerland', Metal Compounds in Environmental and Life 4, 153–162.
Steinhauser, F.: 1972, Niederschlagskarte von Österreich für das Normaljahr 1901–1950. Maßstab 1:500.000, Hydrographisches Zentralbüro im BM für Land-und Forstwirtschaft, Wien.
Steinnes, E.: 1985, 'Use of Mosses in Heavy Metal Deposition Studies', EMEO/CCC Report 3/85, 161–170.
Sveinbjörnson, B. and Oechel, W. C.: 1992, 'Controls on Growth and Productivity of Bryophytes: Environmental Limitations Under Current and Anticipated Conditions', in: Bates, J. W. and Farmer, A. (eds.): Bryophytes and Lichens in a Changing Environment, Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp. 77–102.
Tamm, C. O.: 'Growth, Yield and Nutrition in Carpets of a Forest Moss (Hylocomium splendens)', Meddelanden Fran Statens Skogsforskningsinstitute 43, 1–140.
Thöni. L: 1996, Vergleich von Elementkonzentrationen in drei Biomonitoringmoosen untereinander und mit Depositionsfrachten im Bulksammler nach Bergerhoff, Bericht, BUWAL, Zürich.
Thöni, L., Schnyder, N. and Krieg, F.: 1996, 'Comparison of Metal Concentrations in Three Species of Mosses and Metal Freight in Bulk Precipitations', Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 354, 703–708.
Umweltkontrollbericht: 1996, Umweltsituation in Österreich, 4. Umweltkontrollbericht des BM für Umwelt an den Nationalrat. Umweltbundesamt, Wien.
Vitt, D. H.: 1990, 'Growth and Production Dynamics of BorealMosses Over Climatic, Chemical and Topographic Gradients', Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 140, 35–59.
Vitt, D. H. and Pakarinen, P.: 1977, 'The Bryophyte Vegetation, Production and Organic Components of Truelove Lowland', in: Bliss, L. C. (ed.): </del>Truelove Lowland, Devon Island, Canada: A high Arctic ecosystem, University Press, Edmonton, pp. 225–244.
Walther, H. and Lieth, H.: 1960, Klimadiagramm Weltatlas, G. Fischer, Jena.
Wehr, J. D. and Whitton, B. A.: 1986, 'Ecological Factors Relating to Morphological Variations in the Aquatic Moss Rhynchostegium riparoides (Hedw.) C. Jens', Journal of Bryology 14, 269–280.
Wieder, R. K. and Lang, G. E.: 1983, 'Net Primary Production of the Dominant Bryophytes in a Sphagnum-dominated Wetland in West Virginia', Bryologist 86, 280–286.
Wiegolaski, F. E., Bliss, L. C., Svoboda, J. and Doyle, G.: 1981, 'Primary Production of Tundra', in: Bliss, L. C., Heal, O. W. and Moore, J. J. (eds.) Tundra Ecosystems: A Comparative Analysis, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp. 187–226.
Wolterbeek, H., Kuik, P., Verburg, T. G., Herpin, U., Markert, B. and Thöni, L.: 1995, 'Moss Interspecies Comparisons in Trace Element Concentrations', Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 35, 263–286.
Zechmeister, H. G.: 1994, 'Biomonitoring der Schwermetalldeposition mittels Moosen in Österreich', Monographien des Umweltbundesamtes Wien 42, 1–168.
Zechmeister, H. G.: 1995a, 'Growth Rates of Five Pleurocarpous Moss Species Under Various Climatic Conditions', Journal of bryology 18, 455–468.
Zechmeister, H. G.: 1995b, 'Correlation Between Altitude and Heavy Metal Deposition in the Alps', Environmental pollution 89, 73–80.
Zechmeister, H. G.: 1997, 'Biomonitoring der atmosphärischen Schwermetalldeposition in Österreich – Studie 95', Monographien des Umweltbundesamtes, 94, 1–142.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zechmeister, H.G. Annual Growth of Four Pleurocarpous Moss Species and Their Applicability for Biomonitoring Heavy Metals. Environ Monit Assess 52, 441–451 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005843032625
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005843032625