Abstract
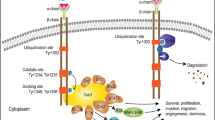
Malignant human gliomas are the most common formsof primary tumors in the central nerve system.Due to their location and invasive nature, treatmentso far has been mainly palliative. Thus, understandingthe molecular detail of tumor transformation and progressionis crucial for developing effective therapeutic strategy forthis fetal tumor. Among the genetic alternations foundin these tumors, p53 inactivation and PDGF/PDGFR activationrepresent the early events, and the loss ofchromosome 10 and gene amplification and rearrangement ofEGFR represent the late events. Studies with bothglioma cell lines and primary tumor tissues havestrongly suggested that TGF-α and EGFR function asan important autocrine loop in supporting proliferation ofhuman glioma, especially in high grade glioma, sinceelevated TGF-α expression is also found in thesehigh grade tumors. Furthermore, down regulation of theexpression of TGF-α by antisense constructs has beenshown to inhibit several types of human tumorcell growth including glioma. Other means of therapeuticapproaches using this autocrine loop as a targetalso include the use of monoclonal antibodies andtheir cytotoxic conjugated. Considerable understanding of the EGFR-mediatedsignal transduction pathways has become available recently, whichincluding GRB2/mSOS1 mediated MAP kinase activation; JAK/STATs pathway;PLC-γ pathway. However, much work still needs tobe done before a specific component of thesepathways can be applied for effective control oftumor growth in the clinic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Libermann TA, Nusbaum HR, Razon N, Kris R, Lax I, Soreq H, Whittle N, Waterfield MD, Ullrich A, Schlessinger J: Amplification, enhanced expression and possible rearrangement of EGF receptor gene in primary human brain tumors of glial origin. Nature 313: 144–147, 1985
Ullrich A, Schlessinger J: Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell 61: 203–212, 1990
Schechter AL, Stern DF, Vaidyanathan L, Decker SJ, Drebin JA, Greene MI, Weinberg RA: The neu oncogene: an erb-B-related gene encoding a 185,000-Mr tumour antigen. Nature 312: 513–516, 1984
Kraus MH, Issing W, Miki T, Popescu NC, Aaronson SA: Isolation and characterization of ERBB3, a third member of the ERBB/epidermal growth factor receptor family: evidence for overexpression in a subset of human mammary tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 9193–9197, 1988
Plowman GD, Culouscou JM, Whitney GS, Green JM, Carlton GW, Foy L, Neubauer MG, Shoyab M: Ligand-specific activation of HER4/p180erbB4, a fourth member of the epidermal growth factor receptor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 1746–1750, 1993
Louis DN, Gusella JF: A tiger behind many doors: multiple genetic pathways to malignant glioma. TIG 11: 412–415, 1995
Leon ST, Zhu J, Black PM: Genetic aberrations in human brain tumors. Neurosurg 34: 708–722, 1994
Steck PA, Bruner JM, Pershouse MA, Hadi A, Conrad CA, Yung WKA, Saya H: Molecular, genetic, and biologic aspects of primary brain tumors. Cancer Bull 45: 296–303, 1993
Rasheed BKA, Mclendon RE, Friedman HS, Friedman A, Fuchs HE, Bigner DD, Bigner SH: Chromosome 10 deletion mapping in human gliomas: a common deletion region in 10q25. Oncogene 10: 2243–2246, 1996
Collins VP: Amplied genes in human gliomas. Sem Cancer Biol 4: 27–32, 1993
Rasheed BKA, Mclendon RE, Herndon JE, Friedman HS, Friedman A, Fuchs HE, Bigner DD, Bigner SH: Alteration of the TP53 gene in human glioma. Cancer Res 54: 1324–1330, 1994
Von Demling A, Louis DN, Von Ammon K, Petersen I, Hoell T, Chung RY, Martuza RL, Schoenfeld DA, Yasargil MG, Eiestler OD, Seizinger BR: Association of epidermal growth factor receptor gene amplification with loss of chromosome 10 in human glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurosurg 77: 295–301, 1992
Wong AJ, Bigner SH, Bigner DD, Kinzler KW, Hamilton SR, Vogelstein B: Increased expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in malignant gliomas is invariably associated with gene amplification. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 6899–6903, 1987
Fuller GN, Bigner SH: Amplified cellular oncogenes in neoplasms of the human central nervous system. Mutation Res 276: 299–306, 1992
Bigner SH, Mark J, Bigner DD: Cytogenetics of human brain tumors. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 47: 141–154, 1990
Ektrand AJ, James CD, Cavenee WK, Seliger B, Pettersson RF, Collins VP: Gene for epidermal growth factor receptor, transforming growth factor ?, and epidermal growth factor and their expression in human gliomas in vitro. Cancer Res 51: 2164–2172, 1991
Yamazaki H, Fukui Y, Ueyama Y, Tamaoki N, Kawamoto T, Tanguchi S, Shibuya M: Amplification of the structurally and functionally altered epidermal growth factor receptor gene (c-erbB) in human brain tumors. Mol Cell Biol 8: 1816–1820, 1988
Malden LT, Novak U, Kaya AH, Burgess AW: Selective amplification of the cytoplasmic domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Res 48: 277–2714, 1988
Humphrey PA, Wong AJ, Vogelstein B, Friedman HS, Werner MH, Bigner DD, Bigner SH: Amplification and expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in human glioma xenografts. Cancer Res 48: 2231–2238, 1988
Yamamato T, Nishida T, Miyajima N, Kawai S, Ooi T, Toyoshima K: The erbB gene of avian erythroblastosis virus is a member of the src gene family. Cell 35: 71–78, 1983
Gilmore T, DeClue JE, Martin GS: Protein phosphorylation at tyrosine is induced by the v-erbB gene product in vivoand in vitro. Cell 40: 609–618, 1985
Wong AJ, Ruppert JM, Bigner SH, Crzeschik CH, Humphrey PA, Bigner DS, Vogelstein B: Structural alterations of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in human gliomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 2965–2969, 1992
Sugawa N, Ekstrand AJ, James CD, Collins VP: Identical splicing of aberrant epidermal growth factor receptor transcripts from amplified rearranged genes in human glioblastomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 8602–8606, 1990
Ekstrand AJ, Longo N, Hamid ML, Olson JJ, Liu L, Collins VP, James CD: Functional characterization of an EGF receptor with a truncated extracellular domain expressed in glioblastomas with EGFR gene amplification. Oncogene 9: 2315–2320, 1994
Nishikawa R, Ji XD, Harmon RC, Lazar CS, Gill GN, Cavenee WK, Huang HJS: A mutant epidermal growth factor receptor common in human glioma confers enhanced tumorigenicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 7727–7731, 1994
Schwenheimer K, Huang S, Cavenee WK: EGFR gene amplification-rearrangement in human glioblastomas. Int J Cancer 62: 145–148, 1995
Ekstrand AJ, Liu L, Hamid ML, Longo N, Collins VP, James CD: Altered subcellular location of an activated and tumour-associated epidermal growth factor receptor. Oncogene 10: 2313–2320, 1995
Ness GO, Haugen DRF, Varhaug JE, Akslen LA, Lillehaug JR: Cytoplasmic location of EGF receptor in papillary thyroid carcinomas: association with the 150-kDa receptor form. Int J Cancer 65: 161–167, 1996
Ekstrand AJ, Sugawa N, James CD, Collins VP: Amplification and rearranged epidermal growth factor receptor genes in human glioblastomas reveal deletions of sequences encoding portions of N-and C-terminal tails. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 4309–4313, 1992
Chen WS, Lazar CS, Lund AK, Welsh JB, Chang CP, Walton GM, Der CJ, Wiley HS, Gill GN, Rosenfeld MG: Functional independence of the epidermal growth factor receptor from a domain required for ligand-induced internalization and calcium regulation. Cell 5: 33–43, 1989
Wells A, Welsh JB, Lazar CS, Whey HS, Gill GN, Rosenfeld MG: Ligand-induced transformation by a non internalizing epidermal growth factor receptor. Science 247: 962–964, 1990
Steck PA, Gallick GE, Maxwell SA, Kloetzer WS, Arlingaus RB, Moser RP, Gutterman JU, Yung WKA: Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor and associated glycoprotein on cultured human brain tumor cells. J Cell Biochem 32: 1–10, 1986
Steck PA, Lee P, Hung MC, Yung WKA: Expression of an altered epidermal growth factor receptor by human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 48: 5433–5439, 1988
King CR, Krus MH, DiFiore PP, Paik S, Kasprzyk PG: Implication of erbB-2 overexpression for basic science and clinical medicine. Sem Cancer Biol 1: 329–337, 1990
King CR, Borrello I, Bellot F, Comoglio P, Schlesinger J: EGF binding to its receptor triggers a rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of the erbB-2 protein in the mammary tumor cell line SK-BR-3. EMBO J 7: 1647–1651, 1988
Qian X, Dougall WC, Hellman ME, Greene MI: Kinase-deficient neu suppress epidermal growth factor receptor function and abolish cell transformation. Oncogene 9: 1507–1514, 1994
Weiner DB, Liu J, Cohen JA, Williams WV, Greene MI: A point mutation in the neu oncogene mimics ligand induction of receptor aggregation. Nature 339: 230–231, 1989
Pele E, Bacus SS, Koski RA, Lu HS, Wen D, Ogden SG, Levy RB, Yarden Y: Isolation of the neu/HER-2 stimulatory ligand: a 44 kd glycoprotein that induces differentiation of mammary tumor cells. Cell 69: 205–216, 1992
Falls DL, Rosen KM, Corfas G, Lane WS, Fischbach GD: ARIA, a protein that stimulates acetylcholine receptor synthesis, is a member of the neu ligand family. Cell 72: 801–815, 1993
Marchionni MA, Goodearl ADJ, Chen MS, Berminghan-McDonogh O, Kirk C, Hendricks M, Danehy F, Misumi D, Sudhalter J, Kobayashi K, Wroblewski D, Lynch C, Baldassare M, Hiles I, Davis JB, Hsuan JJ, Totty NF, Otsu M, McBurney RN, Waterfield MD, Stroobant P, Gwynne D: Glial growth factors are alternatively spliced erbB2 ligands expressed in the nervous system. Nature 362: 312–318, 1993
Carraway III KL, Sliwkowski MX, Akita R, Platko JV, Guy PM, Nuijens A, Diamonti J, Vandlen RL, Cantley LC, Cerione RA: The erbB3 gene product is a receptor for heregulin. J Biol Chem 269: 14303–14306, 1994
Sliwkowski MX, Schaefer G, Akita RW, Lofgren JA, Fitzpatrick VD, Nuijens A, Fendly BM, Cerione RA, Yandlen RL, Carraway III KL: Coexpression of erbB2 and erbB3 proteins reconstitutes a high affinity receptor for heregulin. J Biol Chem 269: 14661–14665, 1994
Plowman GD, Green JM, Culouscou JM, Carlton GW, Rothwell VM, Buckley S: Heregulin induces tyrosine phosphorylation of HER4/p180erb4. Nature 366: 473–475, 1993
Carraway III KL, Cantley LC: A neu acquaintance for erbB3 and erbB4: a role for receptor heterodimerization in growth signaling. Cell 78: 5–8, 1994
Birchmeier C, Sharma S, Wigler M: Expression and rearrangement of ROS1gene in human glioblastoma cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 9270–9274, 1987
Watkins D, Dion F, Poisson M, Delattre J-Y, Rouleau GA: Analysis of oncogene expression in primary human gliomas: evidence for increased expression of the ros oncogene. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 72: 130–136, 1994
Wu JK, Chikaraishi DM: Differential expression of ros oncogene in primary human astrocytomas and astrocytoma cell lines. Cancer Res 50: 3032–3035, 1990
Hermanson M, Funa K, Hartmen M, Claesson-Welsh L, Heldin CH, Westermark B, Nister M: Platelet-derived growth factor and its receptors in human glioma tissue: expression of messenger RNA and protein supports the presence of autocrine/paracrine loop. Cancer Res 52: 3213–3219, 1992
Nister M, Libermann TA, Betsholtz C, Pettersson M, Claesson-Welsh L, Heldin CH, Schlessinger J, Westermark B: Expression of messenger RNAs for platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor-??and their receptors in human malignant glioma cell lines. Cancer Res 48: 3910–3918, 1988
Yung WKA, Zhang X, Steck PA, Hung MC: Differential amplification of the TGF-??gene in human gliomas. Cancer Commun 2: 201–205, 1990
Schlegel U, Moots PL, Rosenblum MK, Thaler HT, Furneaux HM: Expression of transforming growth factor alpha in human gliomas. Oncogene 5: 1839–1842, 1990
Sporn MB, Todaro GJ: Autocrine secretion and malignant transformation of cells. N Engl J Med 303: 878–880
Rosenthal A, Lindquist PB, Bringman TS, Goeddel DV, Derynck R: Expression in rat fibroblasts of a human transforming growth factor-??cDNA results in transformation. Cell 46: 301–309, 1986
Di Marco E, Pierce JH, Fleming TP, Kraus MH, Molloy CJ, Aaronson SA, Di Fiore PP: Autocrine interaction between TGF ??and EGF-receptor: quantitative requirements for induction of the malignant phenotype. Oncogene 4: 831–838, 1989
Gullick WJ: Prevalence of aberrant expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor in human cancers. Br Med Bull 47: 87–98, 1991
Clarke R, Brunner N, Katz D, Glanz P, Dickson RB, Lippman ME, Kern FG: The effects of a constitutive expression of transforming growth factor-?on the growth of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells in vitroand in vivo. Mol Endocrinol 3: 372–380, 1989
Reiss M, Stash EB, Vellucci VF, Zhou ZL: Activation of the autocrine transforming growth factor ??pathway in human squamous carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 51: 6254–6262, 1991
Ciardiello F, Valverius EM, Colucci-D'Amato GL, Kim N, Bassin RH, Salomon DS: Differential growth factor expression in transformed mouse NIH-3T3 cells. J Cell Biochem 42: 45–57, 1990
Filmus J, Shi W, Spencer T: Role of transforming growth factor alpha (TGF-?) in the transformation of ras-transfected rat intestinal epithelial cells. Oncogene 8: 1017–1022, 1993
Dugosz AA, Cheng C, Williams EK, Darwiche N, Dempsey PJ, Mann B, Dunn AR, Coffey RJ, Yuspa SH: Autocrine transforming growth factor ??is dispensible for v-rasHa-induced epidermal neoplasia: potential involvement of alternate epidermal growth factor receptor ligands. Cancer Res 55: 1883–1893, 1995
Derynck R: The physiology of transforming growth factor-?. Adv Cancer Res 58: 27–52, 1992
Cardiello F, Bianco C, Normanno N, Baldassarre G, Pepe S, Tortora G, Bianco AR, Salomon DS: Infection with a transforming growth factor an anti-sense retroviral expression vector reduces the in vitrogrowth and transformation of a human colon cancer cell line. Int J Cancer 54: 952–958, 1993
Kenney NJ, Saeki T, Gottardis M, Kim N, Garcia-Morales P, Martin MB, Normanno N, Ciardiello F, Day A, Cutler ML, Salomon DS: Expression of transforming growth factor a antisense mRNA inhibits the estrogen-induced production of TGFa and estrogen-induced proliferation of estrogen-responsive human breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol 156: 497–514, 1993
Laired AD, Brown PI, Fausto N: Inhibition of tumor growth in liver epithelial cells transfected with a transforming growth factor a antisense gene. Cancer Res 54: 4224–4232, 1994
Sizeland AM, Burgess AW: Anti-sense transforming growth factor ??oligonucleotides inhibit autocrine stimulated proliferation of a colon carcinoma cell line. Mol Biol Cell 3: 1235–1243, 1992
Normanno N, Bianco C, Damiano V, De Angelis E, Selvam MP, Grassi M, Magliulo G, Tortora G, Bianco AR, Mendelsohn J, Salomon DS, Ciardiello F: Growth inhibition of human colon carcinoma cells by combinations of anti-epidermal growth factor-related growth factor antisense oligonucleotides. Clin Cancer Res 2: 601–609, 1996
Sandgren EP, Luetteke NC, Palmiter RD, Brinster RL, Lee DC: Overexpression of TGF??in transgenic mice: induction of epithelial hyperplasia, pamcreatic metaplasia, and carcinoma of the breast. Cell 61: 1121–1135, 1990
Jhappan Stahle C, Harkins RN, Fausto N, Smith GH, Merlino GT: TGF??overexpression in transgenic mice induces liver neoplasia and abnormal development of the mammary gland and pancreas. Cell 61: 1137–1146, 1990
Matsui Y, Halter SA, Holt JT, Hogan BLM, Coffey RJ: Development of mammary hyperplasia and neoplasia in MMTV-TGF??transgenic mice. Cell 61: 1147–1155, 1990
Mann GB, Fowler KJ, Gabriel A, Nice EC, Williams RL, Dunn AR: Mice with a null mutation of the TGF??gene have abnormal skin architecture, wavy hair, and curly whiskers and often develop corneal inflammation. Cell 73: 249–261, 1993
Luetteke NC, Qiu TH, Peiffer RL, Oliver P, Smithies O, Lee AC: TGF??deficiency results in hair follicle and eye abnormalities in targeted and waved-1mice. Cell 73: 263–278, 1993
Murillas R, Larcher F, Conti CJ, Santos M, Ullrich A, Jorcano JL: Expression of a dominant negative mutant of epidermal growth factor in the epidermis of transgenic mice elicits striking alterations in hair follicle development and skin structure. EMBO J 14: 5216–5223, 1995
Hall A: A biochemical function for ras–at last. Science 264: 1413–1414, 1994
Marshall CJ: Specificity of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: transient versus sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Cell 80: 179–185, 1995
Kumar V, Bustin SA, McKay IA: Transforming growth factor alpha. Cell Biol International 19: 373–388, 1995
Campos-Gonzalez R, Glenney JR Jr: Tyrosine phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in cells with tyrosine kinase negative epidermal growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem 267: 14535–14538, 1992
Zhong Z, Wen Z, Darnell JE Jr: Stat3: a stat family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science 264: 95–98, 1994
Ihle JN: STATs: signal transducers and activators of transcription. Cell 84: 331–334, 1996
Harrison DA, Binar R, Nahreini TS, Gilman M, Perrimon N: Activation of a Drosophila Janus kinase (JAK) causes hemotopoietic neoplasia and developmental defects. EMBO J 14: 2857–2865, 1995
Rotin D, Margolis B, Mohammadi M, Daly RJ, Daum G, Li N, Fischer EH, Burgess WH, Ullrich A, Schlessinger J: SH2 domains prevent tyrosine dephosphorylation of the EGF receptor: identification of tyr 992 as the high-affinity binding site for SH2 domains of PLC?. EMBO J 11: 559–567, 1992
Obermerier A, Tinhofer I, Grunicke HH, Ullrich A: Transforming potentials of epidermal growth factor and nerve growth factor receptors inversely correlate with their phospholipase C??affinity and signal activation. EMBO J 15: 73–82, 1996
Reeves ST, Chavez-Kappel C, Davis R, Rosenblum M, Isreal MA: Developmental regulation of Annexin II (Lipocortin 2) in human brain and expression in high grade glioma. Cancer Res 52: 6871–6876, 1992
Karunogaran D, Tzahar E, Beerli RR, Chen X, Graus-Porta D, Ratzkin BJ, Seger R, Hynes NE, Yarden Y: ErbB-2 is a common auxiliary subunit of NDF and EGF receptors: implications for breast cancer. EMBO J 15: 254–264, 1996
Shum L, Reeves SA, Kuo AC, Fromer ES, Derynck R: Association of the transmembrane TGF-??precursor with a protein kinase complex. J Cell Biol 125: 903–916, 1994
Goldman CK, Kim J, Wong WL, King V, Brock T, Gillespie GY: Epidermal growth factor stimulates vascular endothelial growth factor production by human malignant glioma cells: a model of glioblastoma multiforme pathophysiology. Mol Biol Cell 4: 121–133, 1993
Mendelsohn J: The epidermal growth factor receptor as a target for therapy with antireceptor monoclonal antibodies. Sem Cancer Biol 1: 339–344, 1990
Goldenlsohn A, Masui H, Divgi C, Kamrath H, Pentlow K, Mendelsohn J: Imaging of human tumor xenografts with an indium-111-labeled anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody. J Natl Cancer Inst 81: 1616–1625, 1989
Siegall CB, FitzGerald DJ, Pastan I: Selective killing of tumor cells using EGF or TGF ?-Pseudomonas exotoxin chimeric molecules. Sem Cancer Biol 1: 345–350, 1990
Lovqvist A, Lindstrom A, Carlsson J: Binding, internalization and excretion of TGF ?-dextran associated radioactivity in cultured human glioma cells. Cancer Biother 8: 345–356, 1993
Phillips PC, Levow C, Catterall M, Colvin OM, Pastan I, Brem H: Transforming growth factor-?-Pseudomonas exotoxin fusion protein (TGF-?-PE38) treatment of subcutaneous and intracranial human glioma and medulloblastoma xenografts in athmic mice. Cancer Res 54: 1008–1015, 1994
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, P., Steck, P.A. & Yung, W.A. The autocrine loop of TGF-α/EGFR and brain tumors. J Neurooncol 35, 303–314 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005824802617
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005824802617