Abstract
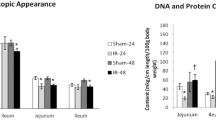
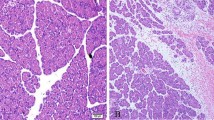
The effect of ischemia–reperfusion and 48-hr fasting on apoptosis was characterized in rat gastric mucosa and compared to small intestinal mucosa. Under halothane anesthesia, the celiac artery or superior mesenteric artery in the rat was occluded for 60 min followed by reperfusion. Occlusion of the celiac artery reduced blood flow in the stomach and occlusion of the mesenteric artery reduced blood flow in the small intestine. Additional rats were fasted for 48 hr to evaluate the effect of fasting on mucosal apoptosis. The ratios of fragmented DNA to total DNA, electrophoresis, and immunohistochemical staining were examined after ischemia–reperfusion or fasting. Apoptosis was not induced significantly in the gastric mucosa after ischemia–reperfusion, although it increased dramatically in the intestinal mucosa after ischemia–reperfusion. Further, after 48 fasting, apoptosis was induced in the small intestine, but not in the stomach. These results indicate that rat gastric mucosa is not as sensitive as small intestinal mucosa to ischemia–reperfusion or fasting-induced apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFRENCES
Kerr JFR, Wyllie AH, Currie AR: Apoptosis: A basic biological henomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 26:239–257, 1972
Aw TY, Nicotera P, Manzo L, Orrenius S: Tributyltin stimulates apoptosis in rat thymocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys 283:46–50, 1990
Potten CS: The significance of spontaneous and induced apoptosis in the gastrointestinal tract of mice. Cancer Metastasis Rev 11:179–195, 1992
Han H, Iwanaga T, Fujita T: Species differences in the process of apoptosis in epithelial cells of the small intestine: An ultrastructural and cytochemical study of luminal cell elements. Arch Histol Cytol 56:83–90, 1993
Hill IE, MacManus JP, Rasquinha I, Tuor UI: DNA fragmentation indicative of apoptosis following unilateral cerebral hypoxia- ischemia in the neonatal rat. Brain Res 676:398–403, 1995
Itoh G, Tamura J, Suzuki M, Suzuki Y, Ikeda H, Koike M, Nomura M, Jie T, Ito K: DNA fragmentation of human infarcted myocardial cells demonstrated by the nick end labeling method and DNA agarose gel electrophoresis. Am J Pathol 146:1325–1331, 1995
Fukuda K, Kojiro M, Chiu JF: Demonstration of extensive chromatin cleavage in transplanted Morris hepatoma 7777 tissue: Apoptosis or necrosis? Am J Pathol 142:935–946, 1993
Noda T, Iwakiri R, Fujimoto K, Matuo S, Aw TY: Programmed cell death induced by ischemia-reperfusion in rat intestinal mucosa. Am J Physiol 274:G270–G276, 1998
Ikeda H, Suzuki Y, Suzuki M, Koike M, Tamura J, Tong J, Nomura M, Itoh G: Apoptosis is a major mode of cell death caused by ischemia and ischemia/reperfusion injury to the rat intestinal epithelium. Gut 42:530–537, 1998
Sun Z, Wang X, Deng X, Lasson A, Wallen R, Hallberg E, Andersson R: The influence of intestinal ischemia and reperfusion on bidirectional intestinal barrier permeability, cellular membrane integrity, proteinase inhibitors, and cell death in rats. Shock10:203–212, 1998
Lightfoot E Jr, Horton JW, Maass DL, White DJ, McFarland RD, Lipsky PE: Major burn trauma in rats promotes cardiac and gastrointestinal apoptosis. Shock 11:29–34, 1999
Sun Z, Wang X, Wallen R, Deng X, Du X, Hallberg E, Andersson R: The influence of apoptosis on intestinal barrier integrity in rats. Scand J Gastroenterol 33:415–422, 1998
Cui L, Takagi Y, Wasa M, Sando K, Khan J, Okada A: Nitric oxide synthase inhibitor attenuates intestinal damage induced by zinc deficiency in rats. J Nutr 129:792–798, 1999
Papaconstantinue HT, Hwang KO, Rajaraman S, Hellmich MR, Townsend CM Jr, Ko TC: Glutamine deprivation induces apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells. Surgery 124:152–160, 1998
Holt PR, Moss SF, Heydari AR, Richardson A: Diet restriction increases apoptosis in the gut of aging rats. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 53:B168–B172, 1998
Iwakiri R., Aw TY: Apoptosis in rat small intestine: Circadian rhythm and effect of feeding and fasting. Gastoenterology 108:A292, 1995
Piotrowski J, Piotrowski E, Skrodzka D, Slomiany A, Slomiany BL: Gastric mucosal apoptosis induced by ethanol: Effect of antiulcer agents. Biochem Mol Biol Int 42:247–254, 1997
Iwakiri R, Gotoh Y, Noda T, Sugihara H, Fujimoto K, Fuseler J, Aw TY: Programmed cell death in rat intestine: Effect of feeding and fasting. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2001 (in press)
Kusuhara H, Matsuyuki H, Matsuura M, Imayoshi T, Okumoto T, Matsui H: Induction of apoptotic DNA fragmentation by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in cultured rat gastric mucosal cells. Eur J Pharmacol 360:273–280, 1998
Slomiany BL, Piotrowski J, Slominany A: Role of basic fibroblast growth factor in the suppression of apoptotic caspase-3 during chronic gastric ulcer healing. J Physiol Pharmacol 49:489–450, 1998
Tatsuta M, Ischii H, Baba M, Hirasawa R, Yano H, Sakai N, Nakaizumi A: Attenuation by all-trans-retinoic acid of sodium chloride-enhanced gastric carcinogenesis induced by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine in Wistar rats. Br J Cancer 79:732–736, 1999
Piotrowski J, Slominany A, Slominany BL: Activation of apoptotic caspase-3 and nitric oxide synthase-2 in gastric mucosal injury by indomethacin. Scand J Gastroenterol 34:129–134, 1999
Piotrowski J, Piotrowski E, Skrodzka D, Slomiany A, Slomiany BL: Induction of acute gastritis and epithelial apoptosis by Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide. Scand J Gastroenterol 32:203–211, 1997
Li H, Andersson EM, Helander HF: Reactions from gastric mucosa during one year Helicobacter pylori infection. Dig Dis Sci 44:116–123, 1999
Wyllie AH: Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature 284:555–556, 1980
Burton K: A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J 62:315–323, 1956
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, Ben-Sasson SA: Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific Labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol 119:493–450, 1992
Wada K, Kamisaki Y, Ohkura T, Kanda G, Nkamoto K, Kishimoto Y, Ashida K, Itoh T: Direct measurement of nitric oxide release in gastric mucosa during ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Am J Physiol 274:G465–G471, 1998
Fujimoto K, Price VH, Granger DN, Specian R, Bergstedt, P Tso: Effect of ischemia-reperfusion on lipid digestion and absorption in rat intestine. Am J Physiol 261:G595–G602, 1991
Granger DN: Ischemia-reperfusion: Role of oxygen-derived free radicals. Acta Physiol Scand 548(suppl.):47–63, 1986
Kawai T, Joh T, Iwata F, Itoh M: Gastric epithelial damage induced by local ischemia-reperfusion with or without exogenous acid. Am J Physiol 266:G263–G270, 1994
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukuyama, K., Iwakiri, R., Noda, T. et al. Apoptosis Induced by Ischemia–Reperfusion and Fasting in Gastric Mucosa Compared to Small Intestinal Mucosa in Rats. Dig Dis Sci 46, 545–549 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005695031233
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005695031233