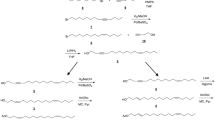
Abstract
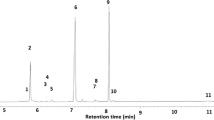
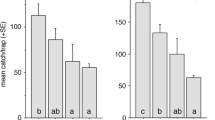
Behavioral activity of the recently identified sex pheromone components of the pea midge, Contarinia pisi, (2S,11S)-diacetoxytridecane, (2S,12S)-diacetoxytridecane, and 2-acetoxytridecane, was tested in wind tunnel and field-trapping experiments. In the wind tunnel, the attractancy of the three-component blend in a 7 : 10 : 0.1 ratio (following the above order, mimicking the ratios found in gland extract) did not differ significantly from female gland extract, whereas a mixture of the two major components (7 : 10) only attracted 2% of the males to the source. In the field, traps baited with the three-component blend caught by far the largest number of males. Traps baited with the two major components only caught slightly more than the blank traps, and catches in traps baited with 2-acetoxytridecane alone did not differ from catches in the blank traps. Traps baited with the racemate of all three components did not catch more than the blank traps, indicating that some of the enantiomers are inhibitory.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Anderbrant, O. 1993. Pheromone biology of sawflies, pp. 119–154, in M. R. Wagner and K. F. Raffa (eds.). Sawfly Life History Adapations to Woody Plants. Academic Press, San Diego.
Arn, H., StÄdler, E., and Rauscher, S. 1975. The electroantennographic detector—a selective tool in the gas chromatographic analysis of insectpheromones. Z. Naturforsch. 30c:722–725.
Arn, H., TÓth, M., and Priesner, E. 1999. The Pherolist, Internet edition. http://www.nysaes.cornell.edu/pheronet.
Birch, M. C. 1984. Aggregation in bark beetles, pp. 331–353, in W. J. Bell and R. T. Cardé, (eds.). Chemical Ecology of Insects. Chapman and Hall, London.
Dawson, G. W., Griffiths, D. C., Merrit, L. A., Mudd, A., Pickett, J. A., Wadhams, L. J., and Woodcock, C. M. 1988. The sex pheromone of the greenbug, Schizaphis graminum. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 48:91–93.
DOANE, J. F., OLFERT, O. O., and MUKERJI, M. I. 1987. Extraction precision of sieving and brineflotation for removal of wheat midge, Sitodiplosis mosellana (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae), cocoonsand larvae from soil. J. Econ. Entomol. 80:268–271.
El-Sayed, A., Unelius, R., Liblikas, I., LÖfqvist, J., Bengtsson, M., and Witzgall, P. 1998. Effect of codlemone isomers on codling moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) male attraction. Environ. Entomol. 27:1250–1254.
El-Sayed, A., GÖdde, J., Witzgall, P., and Arn, H. 1999. Characterization of pheromone blend for grapevine moth, Lobesia botrana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) by using flight track recording. J. Chem. Ecol. 25:389–400.
Foster, S. P., Harris, M. O., and Millar, J. G. 1991. Identification of the sex pheromone of the Hessian fly, Mayetiola destructor (Say). Naturwissenschaften 78:130–131.
Gagné, R. J. 1989. The plant-feeding gall midges of North America. Cornell University Press, Ithaca, New York.
Harris, M. O., and Foster, S. P. 1991. Wind tunnel studies of sex pheromone mediated behavior of the Hessian fly (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae). J. Chem. Ecol. 17:2421–2435.
Harris, M. O., and Foster, S. P. 1999. Gall midges, pp. 27–49, in J. Hardie and A. K. Minks (eds.). Pheromones of Non-Lepidopteran Insects Associated with Agricultural Plants. CAB International, Oxford, UK.
Hillbur, Y., Anderson, P., Arn, H., Bengtsson, M., LÖfqvist, J., Biddle, A. J., Smitt, O., HÖgberg, H-E., Plass, E., Franke, S., and Francke, W. 1999. Identification of sex pheromone components of the pea midge, Contarinia pisi (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae). Naturwissenschaften 86:292–294.
Leal, W. S. 1996. Chemical communication in scarab beetles: Reciprocal behavioral agonist-antagonist activities of chiral pheromones. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93:12112–12115.
LÖfstedt, C. 1991. Evolution of moth pheromones, pp. 57–73, in I. Hrdy (ed.). Insect Chemical Ecology. Academia Praha and SPB AcademicPublishing. The Hague.
LÖfstedt, C., Herrebout, W. M., and Menken, S. B. J. 1991. Sex pheromones and their potential role in the evolution of reproductive isolation in small ermine moths (Yponomeutidae). Chemoecology 2:20–28.
LÖfqvist, J. 1986. Species specificity in response to pheromone substances in diprionid sawflies, pp. 123–129, in T. L. Payne, M. C. Birch, and C. E. J. Kennedy (eds.). Mechanisms in Insect Olfaction. Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Ryan, J. A. 1960. Significance test for multiple comparison of proportions, variances and other statistics. Psychol. Bull. 57:318–328.
Systat. 1992, Systat Statistics, Version 5.2 edition. Systat, Inc., Evanston, Illinois.
SzÖcs, G., TÓth, M., Francke, W., Schmidt, F., Philipp, P., KÖnig, W. A., Mori, K., Hansson, B., and LÖfstedt, C. 1993. Species discrimination in five species of winter-flying geometrids (Lepidotera) based on chirality of semiochemicals and flight season. J. Chem. Ecol. 19:2721–2735.
Wall, C., Pickett, J. A., Garthwaite, D. G., and Morris, N. 1985. A female sex pheromone in the pea midge, Contarinia pisi. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 39:11–14.
Wall, C., Biddle, A. J., Blood Smyth, J., and Emmett, B. 1994. The potential contribution of local trap data for monitoring emergence of the pea midge (Contarinia pisi) and forecasting attacks. Aspects Appl. Biol. 37:269–274.
Witzgall, P., Chambon, J. P., Bengtsson, M., Unelius, C. R., Appelgren, M., Makranczy, G., Muraleedharan, N., Reed, D. W., Hellrigl, K., Buser, H-R., Hallberg, E., BergstrÖm, G., TÓth, M., LÖfstedt, C., and LÖfqvist, J. 1996. Sex pheromones and attractants in the Eucosmini and Grapholitini (Lepidoptera, Tortricidae). Chemoecology 7:13–23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hillbur, Y., El-Sayed, A., Bengtsson, M. et al. Laboratory and Field Study of the Attraction of Male Pea Midges, Contarinia pisi, to Synthetic Sex Pheromone Components. J Chem Ecol 26, 1941–1952 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005557026246
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005557026246