Abstract
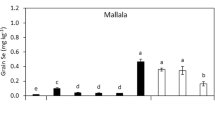
A field experiment was conducted for 2 years on an alkaline calcareous seleniferous soil to study the effect of different levels of gypsum (0.2 – 3.2 t ha−1) applied to wheat only in the first year on Se accumulation by wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) – rice (Oryza sativa L.) cropping sequence. With gypsum application, grain yield of both rice and wheat crops increased by 0.4 – 0.5 t ha−1; the increase in straw yield was 0.4 – 1.1 t ha−1. Significant reduction in Se accumulation by wheat was observed with gypsum application up to 0.8 t ha−1 and its residual effect was evident on the following crops for 2 years. Reduction in Se accumulation varied from 53 to 64% in wheat grain, 46 to 49% in wheat straw, 35 to 63% in rice grain and 36 to 51% in rice straw with an application of gypsum at 0.8 t ha−1. A corresponding increase in S concentration was observed. In the gypsum-treated plots, the ratio of S:Se increased by 6 – 8 times in wheat and 3 – 6 times in rice. Reduction in Se accumulation by crop plants through gypsum application may help in lowering the risk of Se over-exposure of animals and humans that depend on diet materials grown on high selenium soils.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arthur M A, Rubin G, Woodbury P B and Weinstein I H 1993 Gypsum amendment to soil can reduce selenium uptake by alfalfa grown in the presence of coal fly ash. Plant Soil 148, 83–90.
Brown T A and Shrift A 1982 Selenium: Toxicity and tolerance in higher plants. Biol. Rev. 57, 59–84.
Chao T T and Sanzolane R F 1985 Fractionation of soil Se by sequential partial dissolution. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 53, 749–753.
Chesnin L and Yien C H 1951 Turbidimetric determination of available sulphur. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 15, 149–151.
Cummins L M, Martin J L, Maag G Wand Maag D D 1964 A rapid method for the determination of selenium in biological materials. Anal. Chem. 36, 382–384.
Dhillon K S, Bawa S S and Dhillon S K 1992 Selenium toxicity in some plants and soils of Punjab. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 40, 132–136.
Dhillon K S and Dhillon S K 1991a Selenium toxicity in soils, plants and animals in some parts of Punjab, India. Inter. J. Environ. Studies 37, 15–24.
Dhillon K S and Dhillon S K 1991b Accumulation of selenium by sugarcane in seleniferous areas of Punjab, India. Environ. Geochem. Health 13, 165–170.
Dhillon K S and Dhillon S K 1997 Distribution of seleniferous soils in north-west India and associated toxicity problems in the soilplant-animal-human continuum. Land Contam. Reclam. 5, 313–322.
Dhillon K S, Randhawa N S and Sinha M K 1977 Selenium status of some common fodders and natural grasses of Punjab. Indian J. Dairy Sci. 30, 218–224.
Ferrari G and Renosto F 1972 Regulation of sulfate uptake by excised barley roots in the presence of selenate. Plant Physiol. 49, 114–116.
Gajri P R, Arora V K and Prihar S S 1995 Tillage management for efficient water and nitrogen use in wheat following rice. Soil Tillage Res. 24, 167–182.
Gissel-Nielsen G 1973 Uptake and distribution of added selenite and selenate by barley and red clover as influenced by sulphur. J. Sci. Fd. Agric. 29, 649–655.
Hira G S and Singh N T 1980 Irrigation water requirement for dissolution of gypsum in sodic soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 44, 930–933.
Hurd-Karrer A 1938 Relation of sulphate to selenium absorption by plants. Am. J. Bot. 25, 666–675.
Legget J F and Epstein E 1956 Kinetics of sulphate absorption by barley roots. Plant Physiol. 31, 222–226.
Marok A S and Dev G 1980 Movement of sulphate from different soils as influenced by applied water and phosphorus. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 28, 389–391.
Mikkelsen R L, Page A L and Bingham F T 1989 Factors affecting selenium accumulation by agricultural crops. In Selenium in Agriculture and the Environment. Ed. LW Jacobs. pp 65–94. SSSA Special Publication Number 23, Madison, WI, USA.
Mikkelsen R L, Page A L and Haghnia G H 1988 Effect of salinity and its composition on the accumulation of Se by alfalfa. Plant Soil 107, 63–67.
Mikkelsen R L and Wan H F 1990 The effect of selenium on sulphur uptake by barley and rice. Plant Soil 121, 151–153.
Peterson G and Butler G 1962 The uptake and assimilation of selenite by higher plants. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 15, 126–146.
Pratley J E and McFarlane J D 1974 The effect of sulphate on the selenium content of pasture plants. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. Anim. Husb. 14, 533–538.
Rosenfeld I and Beath O A 1964 Selenium: geobotany, biochemistry, toxicity and nutrition. Academic Press, NY, USA.
Singh R, Gajri P R, Gill K S and Khera R 1992 Puddling intensity and nitrogen use efficiency of rice on a sandy loam soil of Punjab. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 65, 749–751.
Snedecor G W and Cochran W G 1968 Statistical Methods. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co. 248
Sokkaro H M and Ohn A 1977 Determination of selenium in soils. Acta Agric. Scand. 27, 285–288.
Soltanpour P N and Workman S M 1980 Use of NH4HCO3-DTPA soil test to assess availability and toxicity of selenium to alfalfa plants. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 11, 1147–1156.
Wu L and Huang P M 1992 Selenium assimilation and nutrient element uptake in white clover and tall fescue under the influence of sulphate concentration and selenium tolerance of the plants. J. Exp Bot. 43, 549–555.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhillon, K., Dhillon, S. Selenium accumulation by sequentially grown wheat and rice as influenced by gypsum application in a seleniferous soil. Plant and Soil 227, 243–248 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026579116794
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026579116794